Lexical diffusion
Lexical diffusion is the hypothesis that a sound change is an abrupt change that spreads gradually across the words in a language to which it is applicable.[1] It contrasts with the Neogrammarian view that a sound change results from phonetically-conditioned articulatory drift acting uniformly on all applicable words, which implies that sound changes are regular, with exceptions attributed to analogy and dialect borrowing.
Similar views were expressed by Romance dialectologists in the late 19th century but were reformulated and renamed by William Wang and coworkers studying varieties of Chinese in the 1960s and the 1970s. William Labov found evidence for both processes but argued that they operate at different levels.
Neogrammarians

A key assumption of historical linguistics is that sound change is regular. The principle was summarized by the Neogrammarians in the late 19th century in the slogan "sound laws suffer no exceptions" and forms the basis of the comparative method of reconstruction and the tree model of linguistic evolution.[3] Inspired by the Uniformitarian Principle of geology, Neogrammarians such as Hermann Paul described regularity as a consequence of the operation of sound change as an imperceptible articulatory drift conditioned by the phonetic environment.[4][5] Leonard Bloomfield later summarized this view:[6][7]
sound change is merely a change in the speaker's manner of producing phonemes and accordingly affects a phoneme at every occurrence, regardless of the nature of any particular linguistic form in which the phoneme happens to occur.
He summarized the mechanism as "phonemes change".[8] Despite the unequivocal form in which these slogans are often quoted, the Neogrammarians admitted two exceptions to regular sound change: analogy and dialect borrowing.[9]
Dialectologists
Uniform sound change was first challenged by Hugo Schuchardt, a dialectologist of Romance languages, who wrote in his criticism of the Neogrammarians:[10][11]
Rarely-used words lag behind; very frequently used ones rush ahead. Exceptions to the sound laws are thus formed on both sides.
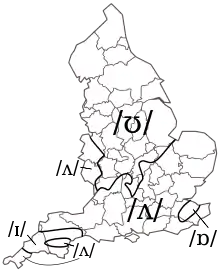
Dialectologists studying the Romance languages found many apparent exceptions to uniformity, as reflected in their slogan, chaque mot a son histoire ('every word has its own history'). This is commonly ascribed to Jules Gilliéron but also originated with Schuchardt.[12] An example is the shortening of English 'u' (the foot-strut split), resulting in different vowels in the words cut and put. When the isogloss defining this feature in England is examined closely, it emerges that individual words are moving from /ʊ/ to /ʌ/ over time, and individual speakers fluctuate in their pronunciation of the same words.[13]
Some sound changes, such as metathesis or haplology, are inherently discontinuous and hence incompatible with gradual, imperceptible change.[14]
Wang's reformulation

In 1962, Peking University published the Hanyu Fangyin Zihui, containing transcriptions of 2444 morphemes in 17 modern varieties of Chinese.[16] The DOC project at the University of California, Berkeley, headed by William Wang, attempted to apply the comparative method to a computerized form of this data.[17] However, the Chinese data revealed pervasive irregularities.[16]
For example, Middle Chinese words in the third tone class (the "departing" tone) with voiced initials have two reflexes in the modern Teochew dialect, but no phonetic factor has been found to condition the split.[18][19] Cheng and Wang list 12 pairs of words that were homophonous in Middle Chinese but have different modern pronunciations.[20] Similar examples were found on other Chinese varieties and other language families.[21] Wang accounted for such irregularities by positing a form of lexical diffusion:[22]
we hold that words change their pronunciations by discrete, perceptible increments (i.e. phonetically abrupt), but severally at a time (i.e. lexically gradual) rather than always in a homogeneous block.
In his view, a sound change would be regular if the change had completed its progress through the lexicon, but irregularity would be seen if the change were still incomplete or if it were interrupted by another change.[23][24]
Other linguists responded that the explanation of the irregularities should be sought in dialect mixture.[25][26][27] Indeed, Wang and Lien discovered that the Teochew phenomenon was the result of borrowing from the local literary reading tradition.[28] They present a revised model that distinguishes between the initial "actuation" of a sound change by language contact or internal factors, and its "implementation" by lexical diffusion.[29]
Evaluation
Labov found evidence for both processes, but argued that they operate at different levels:[30]
- Regular sound change occurs when the phonetic realization of a phoneme varies gradually and continuously. The process affects all words containing the phoneme uniformly. Examples include vowel shifts and diphthongization, weakening of glides and unstressed vowels, vocalization of liquids, and changes in the manner of articulation of consonants.
- Lexical diffusion represents a change in the phonemes in a word (substitution, metathesis, elision, epenthesis). It is abrupt and applies to words selected by lexical, grammatical or social criteria.
Paul Kiparsky argues that under a proper definition of analogy as optimization, lexical diffusion is a non-proportional type of analogy similar to leveling, rather than a type of sound change.[31]
References
- Crystal (2008), p. 145.
- Wang & Cheng (1977), p. 149, Fig. 1.
- Campbell (2013), pp. 15, 188.
- Labov (1994), pp. 21–23.
- Kiparsky (1982), p. 1.
- Bloomfield (1933), p. 353.
- Labov (1994), p. 441.
- Bloomfield (1933), p. 354.
- Labov (1994), p. 440.
- Schuchardt (1885), p. 25.
- Phillips (2015), p. 361.
- Campbell (2013), p. 188.
- Chambers & Trudgill (1998), pp. 106–113.
- Labov (1994), p. 539.
- Wang & Cheng (1977), p. 154, Fig. 4.
- Labov (1994), p. 424.
- Streeter (1972).
- Cheng & Wang (1977).
- Labov (1994), pp. 425–426.
- Cheng & Wang (1977), p. 97.
- Labov (1994), pp. 426–428.
- Wang & Cheng (1977), p. 150.
- Wang (1969), p. 9.
- Wang & Cheng (1977), p. 151.
- Egerod (1982).
- Pulleyblank (1982).
- Mazaudon & Lowe (1993).
- Labov (1994), p. 451.
- Wang & Lien (1993), p. 382.
- Labov (1994), pp. 542–543.
- Kiparsky (1996).
Works cited
- Bloomfield, Leonard (1933), Language, New York: Henry Holt, ISBN 0-226-06067-5.
- Campbell, Lyle (2013), Historical Linguistics: An Introduction (3rd ed.), Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press, ISBN 978-0-7486-4601-2.
- Chambers, J. K.; Trudgill, Peter (1998), Dialectology (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-59646-6.
- Cheng, Chin-Chuan; Wang, William S-Y. (1977), "Tone change in Chao-zhou Chinese: a study in lexical diffusion", in Wang, William S-Y. (ed.), The Lexicon in Phonological Change, Monographs on Linguistic Analysis, vol. 5, Mouton De Gruyter, pp. 86–100, ISBN 978-3-11-177423-7.
- Crystal, David (2008), A Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics (6th ed.), Blackwell, ISBN 978-1-4051-5296-9.
- Egerod, Søren (1982), "How not to split tones – the Chaozhou case", Fangyan, 3: 169–173.
- Kiparsky, Paul (1982), Explanation in phonology, Foris, ISBN 978-90-70176-37-2.
- ——— (1996), "The phonological basis of sound change", in Goldsmith, John A. (ed.), The Handbook of Phonological Theory, Blackwell, pp. 640–670, ISBN 978-0-631-18062-3.
- Labov, William (1994), Principles of Linguistic Change, Volume 1: Internal Factors, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Blackwell, ISBN 978-0-631-17913-9.
- Mazaudon, Martine; Lowe, John B. (1993), "Regularity and Exceptions in Sound Change", in Domenici, Marc; Demolin, Didier (eds.), Annual Conference of the Linguistic Society of Belgium, Brussels, pp. 1–25.
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Phillips, Betty S. (2015), "Lexical Diffusion in Historical Phonology", in Honeybone, Patrick; Salmons, Joseph (eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Historical Phonology, Oxford University Press, pp. 359–373, ISBN 978-0-19-923281-9.
- Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1982), "The Lexicon in Phonological Change. Monographs on Linguistic Analysis, no. 5 by William S-Y Wang", Journal of Chinese Linguistics, 10 (2): 392–416, JSTOR 23767018.
- Schuchardt, Hugo (1885), Ueber die Lautgesetze – Gegen die Junggrammatiker, Berlin: Oppenheim.
- Streeter, Mary L. (1972), "DOC, 1971: A Chinese Dialect Dictionary on Computer", Computers and the Humanities, 6 (5): 259–270, doi:10.1007/BF02404242, JSTOR 30199498, S2CID 62249218.
- Wang, William S-Y. (1969), "Competing Changes as a Cause of Residue", Language, 45 (1): 9–25, doi:10.2307/411748, JSTOR 411748.
- Wang, William S-Y.; Cheng, Chin-Chuan (1977), "Implementation of phonological change: the Shuāng-Fēng Chinese case", in Wang, William S-Y. (ed.), The Lexicon in Phonological Change, Monographs on Linguistic Analysis, vol. 5, Mouton De Gruyter, pp. 148–158, ISBN 978-3-11-177423-7.
- Wang, William S-Y.; Lien, Chinfa (1993), "Bidirectional diffusion in sound change", in Jones, Charles (ed.), Historical Linguistics: Problems and Perspectives, London: Longman, pp. 345–400, ISBN 978-0-582-06085-2.
Further reading
- Phillips, Betty (2006), Word Frequency and Lexical Diffusion, New York: Palgrave MacMillan, ISBN 978-1-4039-3232-7.
- Wang, William S-Y., ed. (1977), The Lexicon in Phonological Change, Monographs on Linguistic Analysis, vol. 5, Mouton De Gruyter, ISBN 978-3-11-177423-7.
- Hashimoto, Mantaro J. (1981), "The lexicon in phonological change Edited by William S-Y. Wang (review)", Language, 57 (1): 183–191, doi:10.1353/lan.1981.0053, JSTOR 414291, S2CID 142237599.
- Walker, Douglas C. (1979), "The lexicon in phonological change: W.S.Y. Wang, Mouton, The Hague, 1977 Monographs on Linguistic Analysis 5. 278 pp. 112 DM", Lingua, 49 (4): 361–363, doi:10.1016/0024-3841(79)90050-0.