Limonoid
Limonoids are phytochemicals of the triterpenoid class which are abundant in sweet or sour-scented citrus fruit and other plants of the families Cucurbitaceae, Rutaceae, and Meliaceae.[1] Certain limonoids are antifeedants such as azadirachtin from the neem tree.[2]
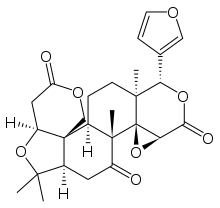
Chemical structure of the prototypical limonoid limonin
Chemically, the limonoids consist of variations of the furanolactone core structure. The prototypical structure consists of four six-membered rings and a furan ring. Limonoids are classed as tetranortriterpenes.
Citrus fruits contain the limonoids limonin, nomilin and nomilinic acid, while both neem seeds and leaves contain the limonoid azadirachtin, although higher concentrations are present in the former.
See also
References
- Amit Roy and Shailendra Saraf (2006). "Limonoids: Overview of Significant Bioactive Triterpenes Distributed in Plants Kingdom". Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29 (2): 191–201. doi:10.1248/bpb.29.191. PMID 16462017.
- Donald E.Champagne; Opender Koul; Murray B. Isman; Geoffrey G. E.Scudder; G. H. Neil Towers (1992). "Biological activity of limonoids from the rutales". Phytochemistry. 31 (2): 377–394. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(92)90003-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.