Direction of movement
In ballroom dancing (and in some other types of partner dance), directions of progressive movement, in particular directions of steps, can be indicated either in relation to the room or in relation to the body position. Directions of turns, although there are only two of them, may also be indicated in several ways.

Directions of progressive movement
Basic directions of movement with respect to the room
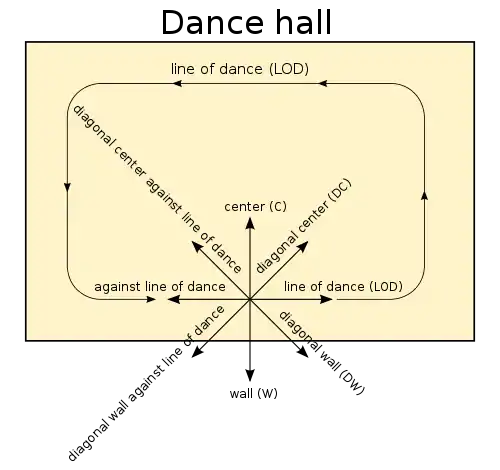
Dancers can align their bodies and move in any of these directions:
- line of dance (LOD)
- against LOD
- center (C)
- wall (W)
- diagonal center (DC)
- diagonal wall (DW)
- diagonal center against LOD (DC against LOD)
- diagonal wall against LOD (DW against LOD)
These directions may be taken either facing if the dancer's feet are pointing in the direction of the movement, or backing if the dancer's feet are oriented in the opposite direction and the dancer is moving backwards with respect to their body. For example, "backing DC against LOD" means that a dancer is moving diagonally to the center against the line of dance, but as they are dancing backwards, the feet (and, roughly, the body) are pointing diagonally to the wall.[1][2]
The term pointing refers explicitly to the direction the feet are pointing, which is useful if they are not, or not yet, aligned with the orientation of the body. For example, a dancer can be pointing DW while facing the wall.[1][2]
Basic directions of step with respect to body position
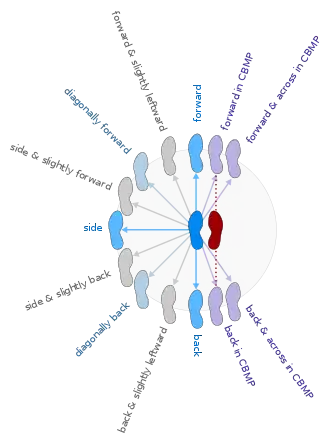
These are described in one of the following ways.
- With respect to the line of the supporting foot, the next step may be placed[3]
- in one of the primary directions:
- forward,
- back,
- side(ways),
- in a diagonal line:
- diagonally forward,
- diagonally back,
- in a hybrid diagonal:
- forward and slightly leftward (for the left foot) or rightward (for the right foot)
- side(ways) and slightly forward
- side(ways) and slightly back
- back and slightly leftward (for the left foot) or rightward (for the right foot)
- in contra body movement position (CBMP):
- forward in CBMP (i.e., the moving foot is placed directly in front of the supporting foot),
- forward and across in CBMP (i.e., the moving foot crosses in front of the supporting foot),
- back in CBMP,
- back and across in CBMP.
- in one of the primary directions:
- By clock: The leader (man) is said to face 12 o'clock immediately before a figure starts. Then directions can be described by saying, for example, that the direction of the second step is 3 o'clock, and the direction of the third step is between 4 and 5 o'clock.[4]
- By compass points: Assuming that the dancer faces North at any moment, one may say, e.g., "take a step North-West".
Directions of turns
Ballroom dancing distinguishes
- natural (that is, right or clockwise) and reverse (left or counter-clockwise) turns,[5][6]
- inside and outside turns (not to be confused with a dancer being on the inside or on the outside of a turn).
Natural vs. reverse turns
The term "natural turn" describes a right or clockwise turn of the dance couple.[7] This usage originated from the names of waltz moves and was transferred to other, similar dances.
A commonly stated theory of the origin of the term is that considering the right-shifted position in a couple (even more pronounced in older times) and the counter-clockwise direction of travel along the line of dance, the right turns are easier to perform, they are more "natural".[8][9] This is especially true at the corners of the dance floor: the amount of the right turn is effectively only 3⁄4 of a full turn, and the amount of the left turn is effectively as much as 5⁄4, because the LOD changes its direction by 90 degrees to the left (CCW).
The partner dancing forward is said to be on the outside of the turn, having the longer way to move, and the partner dancing backward is on the inside of the turn.[10]
Inside vs. outside turns
The terms "inside turn" and "outside turn" apply only to an individual turn of a partner, not to a turn of a couple. They occur in Latin dances and in American style. An "inside turn" is a turn that begins with the held hands (often the leader's left and the follower's right) moving toward the "inside" of the couple (along the imaginary line between the centers of the partners); an "outside turn" is the opposite. The turns may be performed in numerous ways and using different handholds. In dances such as swing and salsa, inside and outside turns typically refer to underarm turns performed by the follower. In these dances the follower's right arm is normally used to lead a turn (most commonly by the leader's left arm, but sometimes by the leader's right arm when a cross-hand or "handshake" position is used), an inside turn is normally a left (counter-clockwise) turn, while an outside turn is a right (clockwise) turn. However, if the follower's left arm is used to initiate the turn, the intended direction of turning may be opposite.
"Inside turn" is most intuitively clear if initially the couple is in an open single-handhold position facing each other, and the name corresponds to the direction of the lead. To lead the inside turn, the leader moves the follower's arm inside, and conversely for the outside turn. In other positions the term is not so clear, therefore in some dances, some prefer to use this term according to its usage in ballet, based on footwork rather than arm style. In ballet, when describing pirouettes, an outward (en dehors) turn is the turn in the direction towards the working leg. Accordingly, an inward (en dedans) turn is the turn in the direction towards the support leg. See also rond de jambe.
The latter definition is unambiguous, but in other contexts it is only applicable to a single footstep. For example, according to this definition, chaînés turns are alternating inside and outside turns, although the direction of the rotation is the same. Therefore, it is common to name the turning figure according to the direction of the first turning step.
References
- "Alignment diagram". DanceCentral.info. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "Alignments". BallroomDancers.com. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "Directional movements". BallroomDancers.com. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- How to Dance Waltz Natural Turn from WDSF PD Champions on YouTube. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "Natural turn". DanceCentral.info. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "Reverse turn". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "Natural turn". BallroomDancers.com. Retrieved 2021-05-19.
- "What Is Natural About A Natural Turn?". Round Dancing. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "How to do a Dance Turn: Reverse and Natural Turns". SocialBallroom.dance. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- "Inside and Outside of Turns". Ballroom Guide. Retrieved 2020-04-30.