List of Panavia Tornado operators
This is a list of operators of the Panavia Tornado multi-role combat aircraft.
| Panavia Tornado operators | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A Royal Air Force Tornado in flight during Operation Iraqi Freedom |
Operators
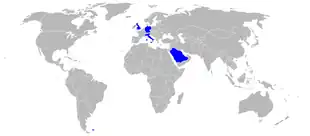
Operators of the Panavia Tornado
As of 2018, 320 operational Tornados are in use.[1] Active units are in bold.

Italian Tornado IDS takes on fuel over Afghanistan

Italian Tornado ADV at Gioia del Colle airbase

Formation of German Tornadoes, together with a MiG-29
.jpg.webp)
UK Tornado IDS in formation with an Avro Lancaster

A pair of UK Tornado ADVs operating over the Falkland Islands
.jpg.webp)
Saudi Tornado IDS operating over Doha

Saudi Tornado ADV takes off during Operation Desert Shield
- Aeronautica Militare - Italy procured a total of 100 IDS aircraft, of which 99 were production models and one was a pre-series aircraft converted to production standard. Twelve of these were dual-control versions. Sixteen were subsequently converted to ECR aircraft.[2][3] In 1993, an agreement was reached with the United Kingdom to lease a total of 24 ADV aircraft, which were operated until 2004.[4][5] As of 2018, Italy operates 70 Tornado IDS and 5 Tornado ECR.[1]
- 102° Gruppo, 6° Stormo at Ghedi, flying IDS. Active from 1993.
- 154° Gruppo, 6° Stormo at Ghedi, flying IDS. Active from 1982.
- 155° Gruppo E.T.S., 6° Stormo at Ghedi, flying IDS/ECR. Active from 1985, equipped with ECR from 1998. Previously assigned to 50° Stormo at Piacenza.
- 156° Gruppo, 6° Stormo at Ghedi, flying IDS. First operational with Tornados from 1984. Now inactive. Previously assigned to 36° Stormo specialised in antishipping and TASMO roles.
- 12° Gruppo, 36° Stormo at Gioia del Colle, flying ADV, now inactive, operational between 1984/1995-2004, replaced by Eurofighter Typhoon.
- 21° Gruppo, 36° Stormo at Gioia del Colle, flying ADV. Now with 9° Stormo flying helicopters in special operations. Previously assigned to 53° Stormo at Cameri airbase.
- Luftwaffe - Germany's air force obtained a total of 245 Tornado aircraft, with 210 of them as the IDS version, and 35 ECR.[8]
- Jagdbombergeschwader 31 "Boelcke" at Nörvenich flying IDS. Converted to Eurofighter Typhoon in 2009.[9]
- Jagdbombergeschwader 32 at Lagerlechfeld flying ECR (34 aircraft). Disbanded in March 2013, operated between August 1985 – March 2013.
- Taktisches Luftwaffengeschwader 33 at Büchel flying IDS. Active, 46 aircraft.[10]
- Jagdbombergeschwader 34 "Allgäu" at Memmingen. Disbanded in 2003.
- Jagdbombergeschwader 38 "Friesland" at Jever. Disbanded, German Tactical Conversion unit, August 1983 – September 2005.[11][12]
- Taktisches Luftwaffengeschwader 51 "Immelmann" at Jagel/Schleswig, flying ECR. Active, 25 aircraft.[13]
- Fliegerisches Ausbildungszentrum der Luftwaffe at Holloman Air Force Base, NM, USA, flying IDS. Operational Conversion Unit. Disbanded December 2019.[14]
- Marineflieger - The German Naval Air Arm obtained 112 IDS aircraft for the anti-shipping mission.[8]
- Royal Air Force - The United Kingdom obtained a total of 228 IDS aircraft; of these, 16 were subsequently converted to undertake the reconnaissance mission, alongside a further 14 new build airframes. Another 28 were converted for the anti-shipping mission.[16] In addition, a total of 165 ADV aircraft were obtained, comprising 18 F.2s and 147 F.3s.[17] The United Kingdom was the first country to completely phase out the Tornado when its last two units were disbanded in March 2019.[18]
- No. II (Army Co-operation) Squadron at Laarbruch then Marham, flying GR4/4A (12 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between September 1988 – January 2015.[19][20]
- No. V (Army Co-operation) Squadron at Coningsby, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between 1987 – January 2003[21]
- No. IX (Bomber) Squadron at Honington, then Brüggen and Marham, flying GR4/4A (~12 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between 6 January 1982 – 14 March 2019.[22]
- No. XI (Fighter) Squadron at Leeming, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between August 1988 – October 2005.[23]
- No. 12 Squadron at Lossiemouth, flying GR4/4A (~12 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between September 1993 – 31 March 2014; 9 January 2015 – 14 February 2018.[24]
- No. XIII Squadron at Honington then Marham, flying GR4/4A (12 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between 1 January 1990 – 13 May 2011.[25]
- No. 14 Squadron at Brüggen then Lossiemouth, flying GR4/4A (12 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between 1 November 1985 – 1 June 2011.[26]
- No. XV (Reserve) Squadron at Laarburch, then Honington (became GR4 Operational Conversion Unit) and Lossiemouth, flying GR4 (26 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between 1 September 1983 – 31 March 2017.[27]
- No. 16 Squadron at Laarbruch, flying GR1. Disbanded, operated between 13 December 1983 – 11 September 1991.[28]
- No. XVII Squadron at Brüggen, flying GR1. Disbanded, operated between 1 March 1985 – 31 March 1999.[28][29]
- No. 20 Squadron at Laarbruch, flying GR1. Disbanded, operated between 29 June 1984 – 31 July 1992.[28]
- No. 23 (Fighter) Squadron at Leeming, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between 1 November 1988 – 28 February 1994.[28]
- No. XXV (Fighter) Squadron at Leeming, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between July 1989 – 4 April 2008.[30]
- No. 27 Squadron at Marham, flying GR1. Disbanded and reformed as 12 Squadron, operated between 12 August 1983 – 1 October 1993.[29]
- No. 29 (Fighter) Squadron at Coningsby, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between April 1987– 31 October 1998.[31]
- No. 31 Squadron at Brüggen then Marham, flying GR4/4A (~10 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between September 1984 – 14 March 2019.[32]
- No. 41 (Reserve) Squadron at Coningsby. The Typhoon & Tornado Test and Evaluation Squadron (TES) (2 Aircraft). Disbanded, operated between 1 April 2006 – 16 November 2017
- No. 43 (Fighter) Squadron at Leuchars, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between September 1989 – 13 July 2009.[33]
- No. 45 (Reserve) Squadron at Honington, flying GR1. Renumbered XV(R) Sqn, operated between January 1984 – 31 March 1992.[34]
- No. 56 (Reserve) Squadron at Leuchars, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between 1 August 1992– 22 April 2008.[35]
- No. 111 (Fighter) Squadron at Leuchars, flying F3. Disbanded, operated between June 1990 – 22 March 2011.[36]
- No. 617 Squadron at Marham then Lossiemouth, flying GR4/4A (12 aircraft). Disbanded, operated between 1 January 1983 – 28 March 2014.[37]
- No. 229 Operational Conversion Unit (No 65 (Reserve) Squadron) at Coningsby, flying F2/3. Renumbered 56(R) Sqn, operated between 1984 – 31 July 1992.[38]
- No. 1435 Flight at Mount Pleasant, flying F3 (4 aircraft). Replaced by Typhoon FGR4, operated between July 1992 – September 2009.[39]
- F3 Operational Evaluation Unit at Coningsby, flying F3.[40] Merged with SAOEU becoming FJWOEU, operated between 1987 – 2004.[41]
- Fast Jet and Weapons Operational Evaluation Unit (FJWOEU) at Coningsby, flying F3/GR4. Redesignated as 41(R) Sqn, operated between 2004 – April 2006.[42]
- Strike Attack Operational Evaluation Unit (SAOEU) at Boscombe Down, flying GR1/4. Merged with F3 OEU becoming FJWOEU, operated between 5 October 1987 – 2004.[42]
- Tri-National Tornado Training Establishment (TTTE) at Cottesmore, flying IDS, GR1. Disbanded, operated between 1 July 1980 – 31 March 1999.[29][43]
- Tornado Weapons Conversion Unit (TWCU) at Honington, flying GR1. Redesignated 45(R) Sqn, operated between 1 August 1980 – January 1984.[29][43]
- Tornado Operational Evaluation Unit at Boscombe Down, flying GR1. Redesignated as SAOEU, operated between 1 September 1983 – 5 October 1987.[41]
- Royal Saudi Air Force - Saudi Arabia initially obtained 72 Tornados, comprising 48 IDS and 24 ADV. A further 48 IDS aircraft were subsequently obtained.[44]
References
- "World Air Forces 2018". Flightglobal.com. Retrieved 12 February 2019.
- "Italy". Panavia. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- "Italy awaits Luftwaffe ECR tests" (PDF). Flight International. 137 (4203): 25. 14 February 1990.
- Sacchetti, Renzo (October 2003). "Italy's British Tornados". AirForces Monthly. Key Publishing. p. 50.
- The Royal Air Force Handbook. London: Anova Books. 2006. p. 30. ISBN 9780851779522.
- Lake World Air Power Journal Volume 32, pp. 134–135.
- Niccoli Air International April 2008, pp. 46–47.
- "Germany". Panavia. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- "The German Air Force receives its first fighter-bomber Eurofighter Typhoons." Eurofighter press release, 16 December 2009 via ''Flight Global Training. Retrieved: 29 November 2011.
- "Jagdbombergeschwader 33 der Luftwaffe in Büchel | FLUG REVUE". www.flugrevue.de. Archived from the original on 31 October 2014.
- Lake World Air Power Journal Volume 32, p. 131.
- List Air International May 2006, p. 51.
- "Die fliegenden Verbände der Luftwaffe - Taktisches Luftwaffengeschwader 51 "Immelmann" (ehemals AG 51) | FLUG REVUE". www.flugrevue.de. Archived from the original on 31 October 2014.
- "Fliegerisches Ausbildungszentrum der Luftwaffe". Standortdatenbank der Bundeswehr. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- Lake World Air Power Journal Volume 32, p. 132.
- "Panavia Tornado IDS". Aeroflight. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- Aeroguide 21 1988, p. 9.
- "Tornado Squadrons Disbandment Parade". RAF. 14 March 2019. Retrieved 14 March 2019.
- "RAF - 2 Squadron". Archived from the original on 14 July 2008.
- "2 Squadron." Royal Air Force. Retrieved: 9 April 2011.
- "5 Squadron." Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "9 Squadron." Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "11 Squadron." Archived 6 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "12 Squadron." Archived 6 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "No XIII Squadron Disbandment – RAF Marham". Royal Air Force. 13 May 2011. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2011.
- "14 Squadron." Archived 2 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "15 Squadron" Archived 14 July 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Royal Air Force. Retrieved 29 December 2010.
- Lake World Air Power Journal Volume 32, p. 122.
- Lake Air International April 2008, p. 26.
- "25 Squadron." Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "29 Squadron." Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "31 Squadron." Archived 26 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- Urquhart, Frank (15 April 2009). "Historic squadron is disbanded – but Fighting Cocks may fly again". The Scotsman.
- Royal Air Force Salute - Tornado. Stamford: Key Publishing Ltd. 2019. p. 27.
- "56 Squadron." Archived 10 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "111 Squadron." Archived 30 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine Royal Air Force, Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- "617 Squadron." Archived 14 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine Royal Air Force. Retrieved: 5 December 2011.
- Lake World Air Power Journal Volume 32, p. 125.
- "Typhoons arrive in Falklands." Archived 23 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine Falklands.gov, September 2009.
- "41 Squadron". Royal Air Force. Archived from the original on 14 January 2011. Retrieved 22 March 2019.
- Royal Air Force Salute - Tornado. Stamford: Key Publishing Ltd. 2019. p. 29.
- Royal Air Force Salute - Tornado. Stamford: Key Publishing Ltd. 2019. p. 28.
- Lake World Air Power Journal Volume 32, p. 126.
- "Kingdom of Saudi Arabia". Panavia. Retrieved 14 February 2018.
- Lake World Air Power Journal Volume 32, p. 137.
- Lake, Jon. "Aircraft of the RAF: Part 1 – Panavia Tornado". Air International, Vol. 74, No. 4, April 2008, pp. 24–29. ISSN 0306-5634.
- Lake, Jon. "Tornado Variant Briefing: Part III: Tornado Operators". World Air Power Journal, Volume 32, Spring 1998, pp. 118–137. London: Aerospace Publishing. ISBN 1-86184-006-3. ISSN 0959-7050.
- List, Friedrich. "German Air Arms Review". Air International, Vol. 70, No. 5, May 2006, pp. 50–57. ISSN 0306-5634.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Panavia Tornado.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.