Lucifer sheartail
The lucifer sheartail or lucifer hummingbird (Calothorax lucifer) is a medium-sized, 10 cm long, green hummingbird with a slightly curved bill and distinctive outward flare of its gorget feathers. Its habitat is in high-altitude areas of northern Mexico and southwestern United States. It winters in central Mexico.
| Lucifer sheartail | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| Male lucifer sheartail | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Strisores |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Genus: | Calothorax |
| Species: | C. lucifer |
| Binomial name | |
| Calothorax lucifer (Swainson, 1827) | |
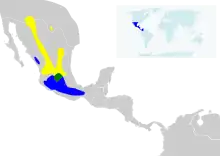 | |
breeding range Non-breeding range | |
Description
The lucifer sheartail is a medium-sized, 10-centimetre (3.9 in) long, green hummingbird with a long curved bill, small wings, and white streak behind its eye.[3] The male has an iridescent plumage, forked dark tail, green crown, long magenta gorget, and white underparts.[3][4] The female is larger with duller plumage, pale throat and white or buff feathers underside, usually with crimson trim.[3][4]
Distribution
The lucifer sheartail is distributed to deserts and arid areas with agave plants in the southwestern United States, from southwest Texas, extreme southwestern New Mexico to southeastern Arizona, and in central and northern Mexico.[3] It is also found in the Madrean sky islands of the northern end of the Sierra Madre Occidental, Mexico. Its preferred habitat tends to be at altitudes of 3,500–5,500 feet (1,100–1,700 m) in canyons, mountain slopes, and dry washes having desert shrubs and cacti.[3] In winter, the birds migrate to central Mexico.[3]
Diet
The diet consists mainly of nectar from agave and colorful desert flowers, spiders and small insects.[3] Lucifer sheartails have a typical hummingbird flight style while feeding from flowers, catching insects in flight, and flying in straight lines to specific destinations for other food, the nest or for roosting.[3] Males defend feeding areas from males, other females, and black-chinned hummingbirds.[3]
Breeding and behavior
During courtship, males attract females by hovering high above the female, then dive with the wings or tail making a snap sound, then flying away with the tail feathers forked and making a different series of snapping sounds.[3] The display lasts 30 to 45 seconds and may repeat several times an hour.[3]
Females build nests on desert shrubs or cacti on steep, dry, rocky slopes, typically 2–10 feet (0.61–3.05 m) above ground, sometimes on top of a previous nest.[3]
The female lays two white eggs in the small cup-like nest, having one or two broods per season.[3] The egg incubation duration is about 15 days, and the chicks nest for about 23 days.[3]
Status
A locally common species in its range, the lucifer sheartail is evaluated as stable and Least Concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.[1][5]
Gallery
 Painting of a male with flared gorget feathers by William Swainson (1789–1855)
Painting of a male with flared gorget feathers by William Swainson (1789–1855).jpg.webp) Female
Female_-_Rusty's_-_Rodeo_-_NM_-_2015-09-15at13-18-3314_(21596362732).jpg.webp) Female at feeder; curved beak
Female at feeder; curved beak_Kartchner_Caverns_Sierra_Vista_AZ_2018-05-29_09-18-39_(32914785057).jpg.webp) Male in flight showing iridescent gorget
Male in flight showing iridescent gorget
References
- BirdLife International (2016). "Calothorax lucifer". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22688185A93185872. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22688185A93185872.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- "Lucifer hummingbird overview". www.allaboutbirds.org. All About Birds, Cornell University Laboratory of Ornithology. 2019. Retrieved 2020-04-13.
- "Lucifer hummingbird". Visual resources for ornithology, The Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University. 2015. Retrieved 2020-04-13.
- "Lucifer hummingbird, Calothorax lucifer". Data Zone, Bird Life International. 2020.
