Lunar standstill
A lunar standstill or lunistice is when the Moon reaches its furthest north or furthest south point during the course of a month (specifically a draconic month of about 27.2 days). The declination (a celestial coordinate measured as the angle from the celestial equator, analogous to latitude) at lunar standstill varies in a cycle 18.6 years long between 18.134° (north or south) and 28.725° (north or south), due to lunar precession. These extremes are called the minor and major lunar standstills.
The last minor lunar standstill was in October 2015, and the next one will be in May 2034. The last major lunar standstill was in June 2006, and the next one will be in January 2025.
Presently the northern lunistice occurs when the Moon is seen in the direction of Taurus, northern Orion, Gemini, or sometimes the southernmost part of Auriga (as at the time of a major lunistice). The southern lunistice occurs when the Moon is in Sagittarius or Ophiuchus. Due to precession of the Earth's axis, the northernmost and southernmost locations of the Moon in the sky move westward, and in about 13,000 years the northern lunistice will occur in Sagittarius and Ophiuchus and the southern lunistice in the area of Gemini.
During a minor lunar standstill, tidal forces are slightly increased in some places, leading to increased amplitude of tides and tidal flooding.[1]
At a major lunar standstill, the Moon's range of declination, and consequently its range of azimuth at moonrise and moonset, reaches a maximum. As a result, viewed from the middle latitudes, the Moon's altitude at upper culmination (the daily moment when the object appears to contact the observer's meridian) changes in two weeks from its maximum possible value to its minimum possible value above the horizon, due north or due south (depending on the observer's hemisphere). Similarly, its azimuth at moonrise changes from northeast to southeast and at moonset from northwest to southwest. In a year of a major lunar standstill, solar eclipses occur in March at ascending node and in September at descending node, whereas lunar eclipses at descending node occur in March, lunar eclipses at ascending node occur in September. In a year of a minor lunar standstill the situation is reversed.
The times of lunar standstills appear to have had special significance for the Bronze Age societies who built the megalithic monuments in Britain and Ireland. It also has significance for some neopagan religions. Evidence also exists that alignments to the moonrise or moonset on the days of lunar standstills can be found in ancient sites of other ancient cultures, such as at Chaco Canyon in New Mexico, Chimney Rock in Colorado and Hopewell Sites in Ohio.
Major lunar standstill
A major lunar standstill occurs when the Moon's declination reaches a maximum monthly limit, stopping at 28.725° north or south. An eclipse season near the March equinox has solar and lunar eclipses at an odd-numbered saros, while another eclipse season near the September equinox has solar and lunar eclipses at an even-numbered saros. Between 1951 and 2050, these dates are 29 March 1969, 8 November 1987, 19 June 2006, 29 January 2025 and 10 September 2043.
Minor lunar standstill
A minor lunar standstill occurs when the Moon's declination reaches a minimum monthly limit, stopping at 18.134° north or south. An eclipse season near the March equinox has solar and lunar eclipses at an even-numbered saros, while another eclipse season near the September equinox has solar and lunar eclipses at an odd-numbered saros. Between 1951 and 2050, these dates are 7 December 1959, 19 July 1978, 27 February 1997, 10 October 2015 and 21 May 2034.
Origin of name
The term lunar standstill was apparently first used by engineer Alexander Thom in his 1971 book Megalithic Lunar Observatories.[2] The term solstice, which derives from the Latin solstitium: sol- (sun) + -stitium (a stoppage), describes the similar extremes in the Sun's varying declination. Neither the Sun nor the Moon stands still, obviously; what stops, momentarily, is the change in declination. The word tropic, as in Tropic of Capricorn, comes from ancient Greek meaning "to turn", referring to how ascending (or descending) motion turns to descending (or ascending) motion at the solstice.[3]
Informal explanation
As Earth rotates on its axis, the stars in the night sky appear to follow circular paths around the celestial poles. (This daily cycle of apparent movement is called diurnal motion.) All the stars seem fixed on a celestial sphere surrounding the observer. In the same way that positions on Earth are measured using latitude and longitude, the apparent places of stars on this sphere are measured in right ascension (corresponding to longitude) and declination (corresponding to latitude). If viewed from a latitude of 50° N on Earth, any star with a declination of +50° would pass directly overhead (reaching the zenith at upper culmination) once every sidereal day (23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds), whether visible at night or obscured in daylight.
Unlike the stars, the Sun and Moon do not have a fixed declination. Since Earth's rotational axis is tilted by about 23.5° with respect to a line perpendicular to its orbital plane (the ecliptic), the Sun's declination ranges from +23.5° at the June solstice to −23.5° at the December solstice, as the Earth orbits the Sun once every tropical year. Therefore, in June, in the Northern Hemisphere, the midday Sun is higher in the sky, and daytime then is longer than in December. In the Southern Hemisphere, the situation is reversed. This obliquity causes Earth's seasons.
The Moon's declination also changes, completing a cycle once every lunar nodal period of 27.212 days. Thus, lunar declination ranges from a positive value to a negative one in just under two weeks, and back. Consequently, in under a month, the Moon's altitude at upper culmination (when it contacts the observer's meridian) can shift from higher in the sky to lower above the horizon, and back.
Thus the Moon's declination varies cyclically with a period of about four weeks, but the amplitude of this oscillation varies over an 18.6 year cycle. A lunar standstill occurs at the points in this latter cycle when this amplitude reaches a minimum or a maximum.
The Moon differs from most natural satellites around other planets in that it remains near the ecliptic (the plane of Earth's orbit around the Sun) instead of Earth's equatorial plane. The Moon's maximum and minimum declination vary because the plane of the Moon's orbit around Earth is inclined by about 5.14° with respect to the ecliptic plane, and the spatial direction of the Moon's orbital inclination gradually changes over an 18.6-year cycle, alternately adding to or subtracting from the 23.5° tilt of Earth's axis.
Therefore, the maximum declination of the Moon varies roughly from (23.5° − 5° =) 18.5° to (23.5° + 5° =) 28.5°. At the minor lunar standstill, the Moon will change its declination during the nodal period from +18.5° to −18.5°, for a total range of 37°. Then 9.3 years later, during the major lunar standstill, the Moon will change its declination during the nodal period from +28.5° to −28.5°, which totals 57° in range. This range is enough to bring the Moon's altitude at culmination from high in the sky to low above the horizon in just two weeks (half an orbit).
Strictly speaking, the lunar standstill is a moving position in space relative to the direction of Earth's axis and to the rotation of the Moon's orbital nodes (lunar nodal precession) once every 18.6 years. The standstill position does not persist over the two weeks that the Moon takes to move from its maximum (positive) declination to its minimum (negative) declination, and it most likely will not exactly coincide with either extreme.
However, because the 18.6 year cycle of standstills is so much longer than the Moon's orbital period (about 27.3 days), the change in the declination range over periods as short as half an orbit is very small. The period of the lunar nodes precessing in space is slightly shorter than the lunar standstill interval due to Earth's axial precession, altering Earth's axial tilt over a very long period relative to the direction of lunar nodal precession. Put simply, the standstill cycle results from the combination of the two inclinations.
Apparent position of the Moon during standstill
The azimuth (horizontal direction) of moonrise and moonset varies according to the Moon's nodal period of 27.212 days, while the azimuth variation during each nodal period varies with the lunar standstill period (18.613 years).
For a latitude of 55° north or 55° south on Earth, the following table shows moonrise and moonset azimuths for the Moon's narrowest and widest arc paths across the sky. The azimuths are given in degrees from true north and apply when the horizon is unobstructed. Figures for a time midway between major and minor standstill are also given.
The arc path of the full Moon generally reaches its widest in midwinter and its narrowest in midsummer. The arc path of the new Moon generally reaches its widest in midsummer and its narrowest in midwinter. The arc path of the first quarter moon generally reaches its widest in midspring and its narrowest in midautumn. The arc path of the last quarter moon generally reaches its widest in midautumn and its narrowest in midspring.

Azimuth of full Moon on horizon
(as viewed from 55° north)Narrowest arc Widest arc Epoch Moonrise Moonset Moonrise Moonset Minor standstill 124° 236° 56° 304° Midway 135° 225° 45° 315° Major standstill 148° 212° 32° 328°
Azimuth of full Moon on horizon
(as viewed from 55° south)Widest arc Narrowest arc Epoch Moonrise Moonset Moonrise Moonset Minor standstill 124° 236° 56° 304° Midway 135° 225° 45° 315° Major standstill 148° 212° 32° 328°
For observers at the middle latitudes (not too near the Equator or either pole), the Moon is highest in the sky in each period of 24 hours when it reaches the observer's meridian. During the month, these culmination altitudes vary so as to produce a greatest value and a least value. The following table shows these altitudes at different times in the lunar nodal period for an observer at 55° north or 55° south. The greatest and least culminations occur about two weeks apart.
Altitude at culmination
(as viewed from 55° north or south)Epoch Greatest Least Minor standstill 53.5° 16.5° Midway 58.5° 11.5° Major standstill 63.5° 6.5°
The following table shows some occasions of a lunar standstill. The times given are for when the Moon's node passed the equinox—the Moon's greatest declination occurs within a few months of these times, depending on its detailed orbit.[4][5] However, the Moon is close to standstill for a year or so on either side of these dates.[2]
Effects on Earth
During a minor lunar standstill, the tidal forces (gravitational forces) of solar objects are more aligned. This leads to an increased amplitude in tides and tidal flooding at the 18.6 year interval.[1]
Detailed explanation
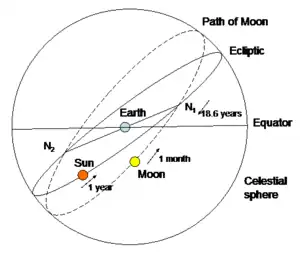
A more detailed explanation is best considered in terms of the paths of the Sun and Moon on the celestial sphere, as shown in the first diagram. This shows the abstract sphere surrounding the Earth at the center. The Earth is oriented so that its axis is vertical.
The Sun is, by definition, always seen on the ecliptic (the Sun's apparent path across the sky) while Earth is tilted at an angle of e = 23.5° to the plane of that path and completes one orbit around the Sun in 365.25636 days, slightly longer than one year due to precession altering the direction of Earth's inclination.
The Moon's orbit around Earth (shown dotted) is inclined at an angle of i = 5.14° relative to the ecliptic. The Moon completes one orbit around the Earth in 27.32166 days. The two points at which Moon crosses the ecliptic are known as its orbital nodes, shown as "N1" and "N2" (ascending node and descending node, respectively), and the line connecting them is known as the line of nodes. Due to precession of the Moon's orbital inclination, these crossing points, the nodes and the positions of eclipses, gradually shift around the ecliptic in a period of 18.59992 years.
Looking at the diagram, note that when the Moon's line of nodes (N1 & N2) rotates a little more than shown, and aligns with Earth's equator, (from front to back, N1, Earth, and N2, seem to be the same dot), the Moon's orbit will reach its steepest angle with the Earth's equator, and in 9.3 years (from front to back, N2, Earth, N1 seem to be the same dot) it will be the shallowest: the 5.14° declination (tilt) of the Moon's orbit either adds to (major standstill) or subtracts from (minor standstill) the inclination of earth's rotation axis (23.439°).
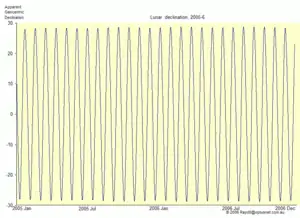
The effect of this on the declination of the Moon is shown in the second diagram. During the course of the nodal period, as the Moon orbits the Earth, its declination swings from –m° to +m°, where m is a number in the range (e – i) ≤ m ≤ (e + i). At a minor standstill (e.g., in 2015), its declination during the month varies from –(e – i) = –18.5° to +(e – i) = 18.5°. During a major standstill (e.g., in 2005–2006), the declination of the Moon varied during each month from about –(e + i) = –28.5° to +(e + i) = 28.5°.
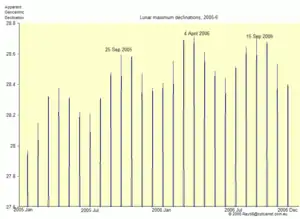
However, an additional subtlety further complicates the picture. The Sun's gravitational attraction on the Moon pulls it toward the plane of the ecliptic, causing a slight wobble of about 9 arcmin within a 6-month period. In 2006, the effect of this was that, although the 18.6-year maximum occurred in June, the maximum declination of the Moon was not in June but in September, as shown in the third diagram.
Other complications
Because the Moon is relatively close to the Earth, lunar parallax alters declination up to 0.95° when observed from Earth's surface versus geocentric declination, the declination of the Moon from the center of the Earth. Geocentric declination may be up to about 0.95° different from the observed declination. The amount of this parallax varies with latitude, hence the observed maximum of each standstill cycle varies according to position of observation.
Atmospheric refraction – the bending of the light from the Moon as it passes through the Earth's atmosphere – alters the observed declination of the Moon, more so at low elevation, where the atmosphere is thicker (deeper).
Not all the maxima are observable from all places in the world – the Moon may be below the horizon at a particular observing site during the maximum, and by the time it rises, it may have a lower declination than an observable maximum at some other date.
2006 standstill
| Events in Sydney, Australia | Date/time | RA | Dec | Az. | Elev | Lunar phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closest viewing of "true maximum" on Friday, 15 September during civil twilight | Thursday, 14 September 19:53 | 04:42:57.32 | +29:29:22.9 | 3° | 27° | 46% waning |
| Highest visible maximum during civil twilight | Tuesday, 4 April 07:49 | 06:03:11.66 | +29:30:34.5 | 350° | 26° | 38% waxing |
| Highest visible maximum during darkness | Tuesday, 4 April 09:10 | 06:05:22.02 | +29:27:29.4 | 332° | 21° | 39% waxing |
| Lowest visible minimum during civil twilight | Wednesday, 22 March 19:45 | 18:10:57.40 | −28:37:33.2 | 41° | 83° | 50% waning |
| Lowest visible minimum during darkness | Wednesday, 22 March 18:36 | 18:09:01.55 | −28:36:29.7 | 80° | 71° | 50% waning |
| Events in London, England | Date/time | RA | Dec | Az. | Elev | Lunar phase |
| Highest visible maximum during civil twilight | Friday, 15 September 05:30 | 06:07:12.72 | +28:19:52.6 | 150° | 64° | 42% waning |
| Highest visible maximum during darkness | Tuesday, 7 March 19:43 | 05:52:33.05 | +28:18:26.9 | 207° | 64° | 60% waxing |
| Lowest visible minimum during civil twilight | Friday, 29 September 17:44 | 17:49:08.71 | −29:31:34.4 | 186° | 9° | 43% waxing |
| Lowest visible minimum during darkness | Saturday, 2 September 20:50 | 18:15:08.74 | −29:25:44.0 | 198° | 7° | 70% waxing |
Note that all dates and times in this section, and in the table, are in UTC, all celestial positions are in topocentric apparent coordinates, including the effects of parallax and refraction, and the lunar phase is shown as the fraction of the Moon's disc which is illuminated.
In 2006, the minimum lunar declination, as seen from the centre of the Earth, was at 16:54 UTC on 22 March, when the Moon reached an apparent declination of −28:43:23.3. The next two best contenders were 20:33 on 29 September, at a declination of −28:42:38.3 and 13:12 on 2 September at declination −28:42:16.0.
The maximum lunar declination, as seen from the centre of the Earth, was at 01:26 on 15 September, when the declination reached +28:43:21.6. The next highest was at 07:36 on 4 April, when it reached +28:42:53.9
However, these dates and times do not represent the maxima and minima for observers on the Earth's surface.
For example, after taking refraction and parallax into account, the observed maximum on 15 September in Sydney, Australia, was several hours earlier, and then occurred in daylight. The table shows the major standstills that were actually visible (i.e. not in full daylight, and with the Moon above the horizon) from both London, UK, and Sydney, Australia.
For other places on the Earth's surface, positions of the Moon can be calculated using the JPL ephemeris calculator. During a major lunar standstill, the moon was on the 29th parallel because eclipses of odd numbered saros occurred near March Equinox and even numbered saros occurring near September Equinox. During a minor lunar standstill, the moon was on the 18th parallel because eclipses of even numbered saros occurred near March Equinox and odd numbered saros occurred near September Equinox.
References
- Machemer, Theresa (14 July 2021). "Moon's Wobbly Orbit and Rising Sea Levels Will Cause Record Flooding in the 2030s". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- Vincent, Fiona (2005). "A major 'lunar standstill'" (PDF). Journal of the British Astronomical Association. 115 (4): 220. Bibcode:2005JBAA..115..220V. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2014.
- Dictionary.com – tropic
- Vincent, Fiona. "Lunar standstills". What's in the sky?. Archived from the original on 19 November 2010.
- Vincent, Fiona. "More about lunar standstills". What's in the sky?. Archived from the original on 6 April 2013.
- Times of maxima and minima of lunar declination at culmination "Solar System Dynamics". Horizons. NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
External links
- Major Lunar Standstill 2006 A photographic digital mosaic of the 2006 event from Greece
- Lunar Standstill Season
- A webcamera at Calanais I (Lewis, Scotland) recording the lunar standstill events in 2005, 2006 and 2007
- A project to study the major standstill events in 2005, 2006 and 2007 at (pre-)historic buildings
- Major Lunar Standstill at Chimney Rock
