Ensconsin
Ensconsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAP7 gene.[5][6]
| MAP7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | MAP7, E-MAP-115, EMAP115, microtubule associated protein 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 604108 MGI: 1328328 HomoloGene: 20851 GeneCards: MAP7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function
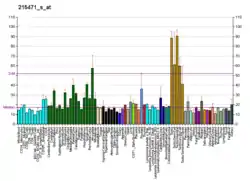
The product of this gene is a microtubule-associated protein that is predominantly expressed in cells of epithelial origin. Microtubule-associated proteins are thought to be involved in microtubule dynamics, which is essential for cell polarization and differentiation. This protein has been shown to be able to stabilize microtubules, and may serve to modulate microtubule functions. Studies of the related mouse protein also suggested an essential role in microtubule function required for spermatogenesis.[6]
In addition, MAPs also play a role in regulating cellular transport. MAP7 is a necessary cofactor to activate and subsequently transport cargos by Kinesin-1. [7] [8]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000135525 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000019996 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Masson D, Kreis TE (October 1993). "Identification and molecular characterization of E-MAP-115, a novel microtubule-associated protein predominantly expressed in epithelial cells". The Journal of Cell Biology. 123 (2): 357–371. doi:10.1083/jcb.123.2.357. PMC 2119845. PMID 8408219.
- "Entrez Gene: MAP7 microtubule-associated protein 7".
- Hooikaas PJ, Martin M, Mühlethaler T, Kuijntjes GJ, Peeters CA, Katrukha EA, et al. (April 2019). "MAP7 family proteins regulate kinesin-1 recruitment and activation". The Journal of Cell Biology. 218 (4): 1298–1318. doi:10.1083/jcb.201808065. PMC 6446838. PMID 30770434.
- Monroy BY, Tan TC, Oclaman JM, Han JS, Simó S, Niwa S, et al. (April 2020). "A Combinatorial MAP Code Dictates Polarized Microtubule Transport". Developmental Cell. 53 (1): 60–72.e4. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2020.01.029. PMC 7181406. PMID 32109385.
- Monroy BY, Sawyer DL, Ackermann BE, Borden MM, Tan TC, Ori-McKenney KM (April 2018). "Competition between microtubule-associated proteins directs motor transport". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 1487. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03909-2. PMC 5902456. PMID 29662074.
- Ferro LS, Fang Q, Eshun-Wilson L, Fernandes J, Jack A, Farrell DP, et al. (January 2022). "Structural and functional insight into regulation of kinesin-1 by microtubule-associated protein MAP7". Science. 375 (6578): 326–331. doi:10.1126/science.abf6154. PMID 35050657.
- Suzuki M, Hirao A, Mizuno A (December 2003). "Microtubule-associated [corrected] protein 7 increases the membrane expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (51): 51448–51453. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308212200. PMID 14517216.
Further reading
- Masson D, Kreis TE (November 1995). "Binding of E-MAP-115 to microtubules is regulated by cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation". The Journal of Cell Biology. 131 (4): 1015–1024. doi:10.1083/jcb.131.4.1015. PMC 2200015. PMID 7490279.
- Fabre-Jonca N, Viard I, French LE, Masson D (February 1999). "Upregulation and redistribution of E-MAP-115 (epithelial microtubule-associated protein of 115 kDa) in terminally differentiating keratinocytes is coincident with the formation of intercellular contacts". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 112 (2): 216–225. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00500.x. PMID 9989799.
- Bulinski JC, Odde DJ, Howell BJ, Salmon TD, Waterman-Storer CM (November 2001). "Rapid dynamics of the microtubule binding of ensconsin in vivo". Journal of Cell Science. 114 (Pt 21): 3885–3897. doi:10.1242/jcs.114.21.3885. PMID 11719555.
- Penttilä TL, Parvinen M, Paranko J (June 2003). "Microtubule-associated epithelial protein E-MAP-115 is localized in the spermatid manchette". International Journal of Andrology. 26 (3): 166–174. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2605.2003.00406.x. PMID 12755995.
- Vanier MT, Deck P, Stutzmann J, Gendry P, Arnold C, Dirrig-Grosch S, et al. (August 2003). "Expression and distribution of distinct variants of E-MAP-115 during proliferation and differentiation of human intestinal epithelial cells". Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton. 55 (4): 221–231. doi:10.1002/cm.10124. PMID 12845596.
- Suzuki M, Hirao A, Mizuno A (December 2003). "Microtubule-associated [corrected] protein 7 increases the membrane expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (51): 51448–51453. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308212200. PMID 14517216.
- Sood R, Bader PI, Speer MC, Edwards YH, Eddings EM, Blair RT, et al. (2004). "Cloning and characterization of an inversion breakpoint at 6q23.3 suggests a role for Map7 in sacral dysgenesis". Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 106 (1): 61–67. doi:10.1159/000078563. PMID 15218243. S2CID 39067023.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G, Nigg EA, Körner R (April 2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 103 (14): 5391–5396. Bibcode:2006PNAS..103.5391N. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP (October 2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nature Biotechnology. 24 (10): 1285–1292. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243. S2CID 14294292.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (November 2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–648. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983. S2CID 7827573.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.