3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol
3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG, MOPEG) is a metabolite of norepinephrine degradation. In the brain, it is the principal norepinephrine metabolite. It is released into the blood and cerebrospinal fluid,[1] and a blood sample of it may therefore be an indication of recent sympathetic nervous system activity.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
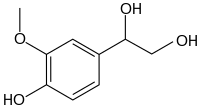
1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl) ethane-1,2-diol | |
| Other names
MHPG | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Methoxyhydroxyphenylglycol |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 184.18918 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Low levels of MHPG in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid are associated with anorexia nervosa and pathological gambling, indicating that norepinephrine may play a role in these behaviors.[2]
 Norepinephrine degradation. 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol is shown at right. Enzymes are shown in boxes.[3] |
References
- Increase in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma levels of 3-methoxy-4- hydroxyphenylglycol in acute stroke T Kanda, K Azuma, F Sakai and Y Tazaki. Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kitasato University, Sagamihara, Japan.
- "Pharmacologic Approaches to the Treatment of Pathological Gambling". Mental Health eJournal. 1998;3(3). Medscape.
- Figure 11-4 in: Rod Flower; Humphrey P. Rang; Maureen M. Dale; Ritter, James M. (2007). Rang & Dale's pharmacology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-06911-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.