Mandelʹshtam (crater)
Mandelʹshtam is the remains of a large crater on the Moon's far side named after Leonid Mandelstam. Nearly attached to the northeast outer rim is the crater Papaleksi. To the south lies the crater Vening Meinesz.
 Oblique Lunar Orbiter 1 image, at the terminator | |
| Coordinates | 5.4°N 162.4°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 197 km |
| Depth | Unknown |
| Colongitude | 200° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Leonid I. Mandelʹshtam |
The outer rim of this crater has been battered into near ruin, with sections forming only an irregular circular rise in the surface. Much of the rim consists of clefts, small craters, and ridges. The satellite crater Mandelʹshtam R breaks across the rim to the west-southwest, and Mandelʹshtam Y is attached to the northern edge.
The interior floor of the crater has not escaped bombardment, and the central portion is overlain by Mandelʹshtam A, a respectable crater in its own right. Mandelʹshtam N lies on the interior along the south-southwestern inner edge. The northwestern floor and to a lesser degree the southeast floor are relatively level, and have suffered less impact damage than elsewhere.
The crater was named after Dutch geophysicist and geodesist Leonid I. Mandelʹshtam by the IAU in 1970.[1] Mandelʹshtam was known as Crater 220 prior to naming.[2]
The small crater Mandelʹshtam F to the east has a small ray system with several faint, streaky rays overlaying the floor of Mandelʹshtam.
 Lunar Orbiter 2 image. Mandelʹshtam A is in the center of Mandelʹshtam, and Mandelʹshtam R is similar in size to A and to the left, and it overlies the smaller Mandelʹshtam T.
Lunar Orbiter 2 image. Mandelʹshtam A is in the center of Mandelʹshtam, and Mandelʹshtam R is similar in size to A and to the left, and it overlies the smaller Mandelʹshtam T. Oblique Apollo 13 image
Oblique Apollo 13 image The floor of Mandelʹshtam, showing a typical highlands scarp at right. From Apollo 16.
The floor of Mandelʹshtam, showing a typical highlands scarp at right. From Apollo 16.
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Mandelʹshtam.
| Mandelʹshtam | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 5.7° N | 162.4° E | 64 km |
| F | 5.2° N | 166.2° E | 17 km |
| G | 4.5° N | 166.4° E | 29 km |
| N | 3.3° N | 161.6° E | 25 km |
| Q | 2.4° N | 158.8° E | 20 km |
| R | 4.5° N | 159.8° E | 57 km |
| T | 5.7° N | 160.4° E | 37 km |
| Y | 9.1° N | 161.8° E | 32 km |
 Oblique view of Mandelʹshtam F from Apollo 11. Mandelʹshtam F lies to the east of Mandelʹshtam itself and is adjacent to the larger but less obvious Mandelʹshtam G.
Oblique view of Mandelʹshtam F from Apollo 11. Mandelʹshtam F lies to the east of Mandelʹshtam itself and is adjacent to the larger but less obvious Mandelʹshtam G. Another view of Mandelʹshtam F from Apollo 10.
Another view of Mandelʹshtam F from Apollo 10. Oblique view of Mandelʹshtam R from Apollo 10.
Oblique view of Mandelʹshtam R from Apollo 10.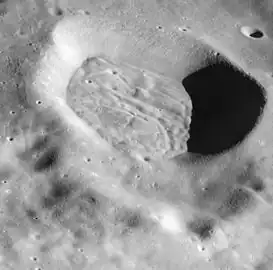 Mandelʹshtam Q from Apollo 16. The crater has a floor that is heavily lineated and grooved, but this structure is subdued rather than sharp and is contained wholly within the crater. The cracked floor is typical of a variety of craters that occur in the highlands away from the mare basins. (partial NASA caption)
Mandelʹshtam Q from Apollo 16. The crater has a floor that is heavily lineated and grooved, but this structure is subdued rather than sharp and is contained wholly within the crater. The cracked floor is typical of a variety of craters that occur in the highlands away from the mare basins. (partial NASA caption)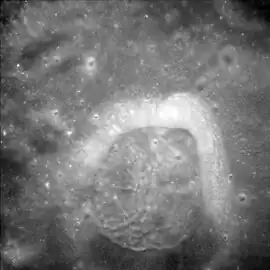 Mandelʹshtam Q from Apollo 11.
Mandelʹshtam Q from Apollo 11.
References
- Mandelʹshtam, Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature, International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN)
- Lunar Farside Chart (LFC-1A)
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763. S2CID 122125855.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.