Mayo Kébbi
The Mayo Kébbi is a river in Central and West Africa. The river rises in Chad, then flows west into the Bénoué River.[1] Mayo-Kébbi Prefecture in Chad is named for it. The Mayo Kébbi is the major outlet for Lake Fianga, shared between Cameroon and Chad.[2]
| Mayo Kébbi | |
|---|---|
 | |
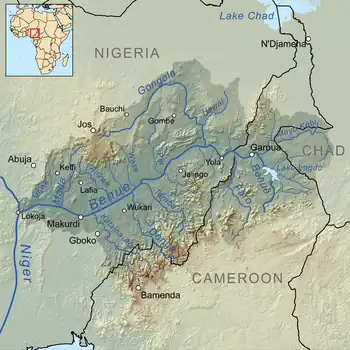 Catchment of the Bénoué River | |
| Location | |
| Countries |
|
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | |
• location | in the Bénoué River |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Niger River |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Mayo Louti, Mayo Oulu |
In the past, the Mayo Kébbi served as the outlet of the paleolake Mega-Chad.[3] The presence of African manatees in the inflows of Lake Chad is evidence of this, since the manatee is otherwise only in rivers connected to the Atlantic Ocean (i.e. it is not possible that it evolved separately in an enclosed Chad Basin).[4] The grand scale of the Mayo Kébbi river course, is also evidence of earlier overflow from Mega-Chad; the upstream catchment of today is far too small to have dug such a large channel.[5]
Pollution
According to research carried out in 2017, the Mayo Kébbi river is being polluted by heavy metals such as: Cu, Cd, Pb, Fe, Mn, As, Zn, Ni and Cr and some sediments are being dropped in the river of which some are very toxic to the lives of the acquatic animals.[6]
References
- https://www.globalforestwatch.org/dashboards/country/TCD/14/?category=forest-change&location=WyJjb3VudHJ5IiwiVENEIiwiMTQiXQ%3D%3D&map=eyJjZW50ZXIiOnsibGF0Ijo4Ljc1ODMxODg2MTMzNjI5NywibG5nIjoxNS45Mjg0OTk5OTk5NzQ1MDR9LCJ6b29tIjo2LjYzMzkzMTM3Njc1NzUyMiwiY2FuQm91bmQiOmZhbHNlLCJkYXRhc2V0cyI6W3siZGF0YXNldCI6InBvbGl0aWNhbC1ib3VuZGFyaWVzIiwibGF5ZXJzIjpbImRpc3B1dGVkLXBvbGl0aWNhbC1ib3VuZGFyaWVzIiwicG9saXRpY2FsLWJvdW5kYXJpZXMiXSwiYm91bmRhcnkiOnRydWUsIm9wYWNpdHkiOjEsInZpc2liaWxpdHkiOnRydWV9LHsiZGF0YXNldCI6Ik5ldC1DaGFuZ2UtU1RBR0lORyIsImxheWVycyI6WyJmb3Jlc3QtbmV0LWNoYW5nZSJdLCJvcGFjaXR5IjoxLCJ2aXNpYmlsaXR5Ijp0cnVlLCJwYXJhbXMiOnsidmlzaWJpbGl0eSI6dHJ1ZSwiYWRtX2xldmVsIjoiYWRtMSJ9fV19&showMap=true&widget=treeLossRanked
- https://www.tripadvisor.com/Tourism-g3657391-Mayo_Kebbi_Est_Region-Vacations.html
- Leblanc et al. (2006). "Reconstruction of megalake Chad using shuttle radar topographic mission data". Palaeogeography, palaeoclimatology, palaeoecology 239, pp. 16–27 ISSN 0031-0182 1872-616X
- https://www.tripadvisor.com/Tourism-g3657436-Mayo_Kebbi_Ouest_Region-Vacations.html
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Map-showing-the-location-of-Mayo-Kebbi-Ouest-region-provided-by-Google-Map_fig1_326300461
- Tchakounté, Jacqueline; Eglinger, Aurélien; Toteu, Sadrak Félix; Zeh, Armin; Nkoumbou, Charles; Mvondo-Ondoa, Joseph; Penaye, Joseph; de Wit, Martin; Barbey, Pierre (2017-09-01). "The Adamawa-Yadé domain, a piece of Archaean crust in the Neoproterozoic Central African Orogenic belt (Bafia area, Cameroon)". Precambrian Research. 299: 210–229. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2017.07.001. ISSN 0301-9268.