McClain County, Oklahoma
McClain County is a county located in south central Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, the population was 41,662.[1] Its county seat is Purcell.[2] The county was named for Charles M. McClain, an Oklahoma constitutional convention attendee.[3]
McClain County | |
|---|---|
 | |
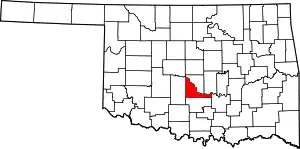 Location within the U.S. state of Oklahoma | |
 Oklahoma's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 35°00′N 97°26′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1907 |
| Seat | Purcell |
| Largest city | Newcastle |
| Area | |
| • Total | 580 sq mi (1,500 km2) |
| • Land | 571 sq mi (1,480 km2) |
| • Water | 9.6 sq mi (25 km2) 1.6% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 41,662 |
| • Density | 72/sq mi (28/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 4th |
| Website | mcclain-co-ok |
McClain County is part of the Oklahoma City, OK metropolitan statistical area.
History
The Chickasaw tribe began moving into this area in 1837, when the land had already been assigned to the Choctaws by the U.S. government. In 1855, the area became part of the Chickasaw Nation, after the two tribes officially separated. The present McClain County became part of Pontotoc County, Chickasaw Nation and remained so until Oklahoma attained statehood. Few Chickasaws lived here because of hostilities with western tribes (e.g., Kiowa). Major Richard Mason established Camp Holmes (also called Camp Mason) in 1835, near the present city of Lexington, while negotiating a treaty between the western tribes and the newly arrived Choctaws. Federal troops abandoned the camp in August 1835, after the Treaty of Camp Holmes was signed.[3]
Auguste Pierre Chouteau built a trading post at the Camp Holmes site, but it closed after Chouteau died in 1838. Randolph Marcy is credited with bringing the California Road through this area in 1849. The U.S. Army built Camp Arbuckle in 1850 to protect the road, but the troops were withdrawn to what is now Garvin County, Oklahoma in the following year.[3]
Jesse Chisholm also operated a trading post in this area around 1850. A group of Delaware Indians occupied the former camp, then known as Beaversville, but left before the outbreak of the Civil War.[3]
Montford T. Johnson, a rancher, moved to this area after the Civil War. He and Jesse Chisholm, who acted as the negotiator, obtained an agreement with the Chickasaw leaders to allow ranching on their land, provided no whites were employed. Thereafter, Johnson built a ranch and hired a Chickasaw freedman to operate it. He then established other ranches and hired another freedman to run those.[3]
The Southern Kansas Railway built a line south from Kansas to present McClain County in 1886–7, and the Gulf, Colorado and Santa Fe Railway (both of which were controlled by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, AT&SF) built a line north from Texas, meeting at and founding the town of Purcell. Eastern Oklahoma Railroad (later acquired by the AT&SF) laid tracks in 1900-04 from Newkirk to Pauls Valley, passing through eastern McClain County. In 1906 the Oklahoma Central Railway (sold to AT&SF in 1914) built a line that traversed McClain County from the southeast to the northwest. It ran through Byars and Purcell, and established Washington, Cole, and Blanchard.[3]
Purcell was a starting point for the Land Run of 1889. It also was at the dividing line between Indian Territory, where alcohol could not be sold, and Oklahoma Territory, where alcohol sale was legal. The town of Lexington, across the river from Purcell, had numerous saloons. In 1899, the Purcell Bridge Company built a toll bridge across the river, profiting from the alcohol trade.[3]
Geography
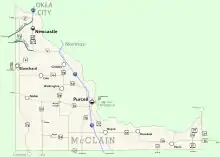
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 580 square miles (1,500 km2), of which 571 square miles (1,480 km2) is land and 9.6 square miles (25 km2) (1.6%) is water.[4] The county lies largely in the Red Bed Plains region of the Osage Plains. The western part of the county is hilly and covered with black jack oak trees, while the eastern part is level lowlands. The South Canadian River forms the northern border, The Washita River flows through the southwestern corner, and is fed by several McClain County creeks.[3]
Adjacent counties
- Cleveland County (north)
- Pottawatomie County (northeast)
- Pontotoc County (east)
- Garvin County (south)
- Grady County (west)
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1910 | 15,659 | — | |
| 1920 | 19,326 | 23.4% | |
| 1930 | 21,575 | 11.6% | |
| 1940 | 19,205 | −11.0% | |
| 1950 | 14,681 | −23.6% | |
| 1960 | 12,740 | −13.2% | |
| 1970 | 14,157 | 11.1% | |
| 1980 | 20,291 | 43.3% | |
| 1990 | 22,795 | 12.3% | |
| 2000 | 27,740 | 21.7% | |
| 2010 | 34,506 | 24.4% | |
| 2020 | 41,662 | 20.7% | |
| 2022 (est.) | 45,306 | [5] | 8.7% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790-1960[7] 1900-1990[8] 1990-2000[9] 2010-2019[10] | |||
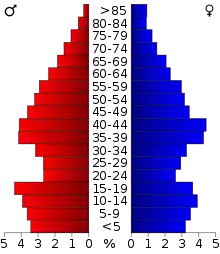
As of the 2010 United States census, there were 34,506 people, 12,891 households, and 9,785 families residing in the county. The population density was 59.5 people per square mile (23.0 people/km2). There were 13,996 housing units at an average density of 24 units per square mile (9.3/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 84.5% white, 0.7% black or African American, 6.4% Native American, 0.4% Asian, less than 0.1% Pacific Islander, 2.7% from other races, and 5.3% from two or more races. Seven percent of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. By 2020, its population was 41,662.[1]
There were 12,891 households, out of which 37.4% included children under the age of 18, 61.3% were married couples living together, 9.9% had a female householder with no husband present, 4.7% had a male householder with no wife present, and 24.1% were non-families. Individuals living alone accounted for 20.1% of households and individuals 65 years of age or older living alone accounted for 8.1%. The average household size was 2.66 and the average family size was 3.06.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 26.6% under the age of 18, 6.9% from 18 to 24, 25.7% from 25 to 44, 27.6% from 45 to 64, and 13.2% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38.2 years. For every 100 females, there were 98.5 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 95.4 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $56,126, and the median income for a family was $67,948. Males had a median income of $42,262 versus $32,821 for females. The per capita income for the county was $24,898. About 8% of families and 12% of the population were below the poverty line, including 11% of those under age 18 and 8% of those age 65 or over.
Politics
| Voter Registration and Party Enrollment as of June 30, 2023[11] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Number of Voters | Percentage | |||
| Republican | 17,631 | 64.84% | |||
| Democratic | 5,240 | 19.27% | |||
| Libertarian | 229 | 0.84% | |||
| Unaffiliated | 4,090 | 15.04% | |||
| Total | 27,190 | 100% | |||
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2020 | 15,295 | 79.51% | 3,582 | 18.62% | 359 | 1.87% |
| 2016 | 13,169 | 78.12% | 2,894 | 17.17% | 795 | 4.72% |
| 2012 | 11,112 | 77.67% | 3,194 | 22.33% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 2008 | 11,193 | 75.92% | 3,551 | 24.08% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 2004 | 10,041 | 72.85% | 3,742 | 27.15% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 2000 | 6,750 | 64.05% | 3,679 | 34.91% | 110 | 1.04% |
| 1996 | 4,363 | 46.22% | 3,753 | 39.76% | 1,323 | 14.02% |
| 1992 | 4,377 | 40.62% | 3,378 | 31.35% | 3,021 | 28.03% |
| 1988 | 4,771 | 56.44% | 3,594 | 42.52% | 88 | 1.04% |
| 1984 | 6,056 | 69.83% | 2,549 | 29.39% | 67 | 0.77% |
| 1980 | 4,284 | 56.87% | 2,990 | 39.69% | 259 | 3.44% |
| 1976 | 2,444 | 37.19% | 4,048 | 61.59% | 80 | 1.22% |
| 1972 | 4,241 | 73.16% | 1,350 | 23.29% | 206 | 3.55% |
| 1968 | 2,047 | 36.98% | 1,842 | 33.27% | 1,647 | 29.75% |
| 1964 | 1,638 | 31.05% | 3,638 | 68.95% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1960 | 2,547 | 51.85% | 2,365 | 48.15% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1956 | 2,081 | 41.11% | 2,981 | 58.89% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1952 | 2,326 | 42.08% | 3,201 | 57.92% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1948 | 908 | 20.83% | 3,451 | 79.17% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1944 | 1,492 | 31.08% | 3,301 | 68.76% | 8 | 0.17% |
| 1940 | 1,862 | 33.01% | 3,768 | 66.80% | 11 | 0.20% |
| 1936 | 1,191 | 22.47% | 4,092 | 77.21% | 17 | 0.32% |
| 1932 | 818 | 13.85% | 5,087 | 86.15% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 1928 | 2,399 | 55.07% | 1,913 | 43.92% | 44 | 1.01% |
| 1924 | 1,233 | 30.74% | 2,519 | 62.80% | 259 | 6.46% |
| 1920 | 1,733 | 40.32% | 2,315 | 53.86% | 250 | 5.82% |
| 1916 | 680 | 25.04% | 1,541 | 56.74% | 495 | 18.23% |
| 1912 | 583 | 25.63% | 1,273 | 55.96% | 419 | 18.42% |
Economy
The county economy has been based primarily on agriculture and cattle raising. Each town had its own cotton gin early in the 1900s. Purcell had a flour mill. Otherwise, there was little industrial activity. Many county residents commute to work in the Oklahoma City area. Mid-America Area Vo-Tech opened in 1971 to provide vocational education to students. Duke Energy North America built a power plant (which it sold to NRG Energy, Inc., that year) near Newcastle in 2001. The Chickasaw Nation operated a gaming casino at Newcastle.[3]
Education
K-12 schools
School districts include (all full K-12):[13]
- Alex Public Schools
- Asher Public Schools
- Blanchard Public Schools
- Bridge Creek Public Schools
- Dibble Public Schools
- Lindsay Public Schools
- Maysville Public Schools
- Newcastle Public Schools
- Norman Public Schools
- Paoli Public Schools
- Purcell Public Schools
- Stratford Public Schools
- Washington Public Schools
- Wayne Public Schools
Libraries
Pioneer Library System operates branch libraries in nine cities in Cleveland, McClain and Pottawatomie counties.[14] The Purcell Public Library at 919 N. 9th Street in Purcell is the only library in McClain County that is part of the Pioneer System.
Transportation
Major highways
The busiest highway in the county is Interstate 35, which enters the county on the north at Goldsby on the McCall Bridge. It then parallels the Canadian River through the county seat, Purcell. It eventually turns southward and leaves the county at its border with Garvin County.
Another important interstate highway is Interstate 44, which runs through the northwestern part of the county. The H.E. Bailey Turnpike Norman Spur connects this highway to the US-62/US-277/SH-9 intersection.
SH-9 enters McClain County via the McCall bridge, duplexed with I-35, and immediately turns due west, running along the northern edge of Goldsby until its intersection with U.S. Highway 62/U.S. Highway 277, south of Newcastle, Oklahoma. From this intersection the three highways continue southwest towards Blanchard and further on to Chickasha in Grady County.
County roads
Like many counties, McClain County contains an extensive network of county-maintained roads. They form a grid with parallel roads generally placed 1 mile apart.
To dispel confusion and assist the small cities introducing new 9-1-1 systems, the county road system was recently renamed and signed throughout the county. East–west roads are numbered, with 100th Street located along the southern edge of the county, and the numbers gradually increasing toward the northern tip of the county. North–south streets are named, generally indicating the name of the road in the Oklahoma City grid that the county road best aligns with. (e.g. Pennsylvania Avenue would, if extended northward, eventually connect with the street of the same name in Oklahoma City.)
Controversy
Contaminated water supply
In 2010, the EPA ordered local water utilities to begin the first nationwide tests for hexavalent chromium 6 (AKA The Erin Brockovich Chemical). From 2013 to 2015, utilities took more than 60,000 samples of drinking water and found chromium-6 in more than 75 percent of them.[15] The Purcell water supply tested positive for an average of 11.53ppb, 577 times the original recommendation from the scientists at the respected and influential California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment of 0.02ppb.[16]
Communities
Local landmarks
The following sites in McClain County are listed on the National Register of Historic Places:
- Hotel Love, Purcell
- McClain County Courthouse, Purcell
- James C. Nance Memorial Bridge (U.S. Highway 77/State Highway 39 Bridge over the Canadian River), Purcell/Lexington
References
- "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: McClain County, Oklahoma; United States". www.census.gov. Retrieved August 6, 2022.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- O'Dell, Larry. "McClain County," Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture, Oklahoma Historical Society, 2009. Accessed April 4, 2015.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 4, 2023.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on April 26, 2015. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved November 9, 2013.
- "Current Registration Statistics by County" (PDF). ok.gov. February 28, 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved August 6, 2022.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 29, 2018.
- "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: McClain County, OK" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved July 23, 2022. - Text list
- "Pioneer Library System to buy Borders bookstore building in Norman". NewsOK. The Oklahoman. September 27, 2011. Retrieved October 25, 2011.
- "Occurrence data unregulated contaminant monitoring rule #3".
- "U.S. EPA, Occurrence Data for the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule. April 2016".