McDermitt Caldera
The McDermitt Caldera is a large, oval-shaped caldera west of McDermitt in southeastern Oregon and northern Nevada in the United States. It is about 28 miles (45 km) long north–south and 22 miles (35 km) wide east–west.[3] The western part of the caldera is in the Trout Creek Mountains, and the northern part is in the Oregon Canyon Mountains.[3][4] The highest point of the McDermitt Caldera is Jordan Meadow Mountain at 6,816 feet (2,078 m), which is part of the Montana Mountains of Humboldt County, Nevada.[1][5]
| McDermitt Caldera | |
|---|---|
 Location of the caldera in Oregon and Nevada  McDermitt Caldera (Nevada) | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Jordan Meadow Mountain |
| Elevation | 6,816 ft (2,078 m)[1] |
| Coordinates | 41°51′01″N 118°02′12″W[2] |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 28 mi (45 km) north–south[3] |
| Width | 22 mi (35 km) east–west[3] |
| Geography | |
| Location | Harney County, Oregon Malheur County, Oregon Humboldt County, Nevada |
| Range coordinates | 42°00′05″N 117°59′48″W |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | 19 million years (Miocene) |
| Mountain type | Caldera |
| Last eruption | 16.39 ± 0.02 million years ago (Miocene) |
McDermitt Caldera is possibly the oldest of a sequence of calderas formed by the Yellowstone hotspot.[6] The caldera was preceded by a lava dome that had been built by volcanic eruptions of rhyolite starting about 19 million years ago.[3][4] This lava dome collapsed into a caldera in an eruption between 16.37 and 16.41 million years ago.[6] A lake subsequently formed in the caldera, and it deposited varved sediments, diatomite, opal, carbonaceous material, and mafic lavas.[7]
Significant ore deposits are buried in the caldera, including mercury and uranium, which were mined at more than eight sites in the caldera during the 20th century. Mercury at these mines was extracted in large amounts, and it came mostly from cinnabar.[3][8] The McDermitt Mine, located on the eastern edge of the caldera in Nevada, was the last active mercury mine in the United States before it shut down in 1992.[9] Uranium was discovered in the caldera in 1953, and it was extracted mainly from a rhyolite brecciated fault zone at the Moonlight mine on the caldera's southwestern edge.[3][7][10] The uranium ore minerals include uraninite and coffinite. The age of the uranium formation is assumed to be the same as the caldera tuff, which is approximately 16.1 million years.[7] Other deposits in the caldera contain ores of antimony, cesium, and lithium[11][12] (potentially, one of the biggest mines in the world).[13]
The Thacker Pass lithium deposit, located within the caldera, is a prospect that in 2017 was said to be the most significant lithium-clay resource in the U.S.[14]

 Location of Aurora uranium deposit at McDermitt caldera margin
Location of Aurora uranium deposit at McDermitt caldera margin Cross-section showing Aurora uranium deposit in McDermitt caldera
Cross-section showing Aurora uranium deposit in McDermitt caldera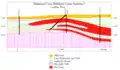 Schematic cross-section of Aurora uranium deposit ore zones
Schematic cross-section of Aurora uranium deposit ore zones
See also
References
- Rytuba, James J.; Glanzman, Richard K. (1978). "Relation of Mercury, Uranium, and Lithium Deposits to the McDermitt Caldera Complex, Nevada-Oregon" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. p. 8. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- "Jordan Meadow Mountain". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. 12 December 1980. Retrieved 7 March 2021.
- Rytuba, James J. (1976). "Geology and Ore Deposits of the McDermitt Caldera, Nevada–Oregon" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- Rytuba, James J.; Conrad, Walter K. (1981). Goodell, P. C.; Waters, A. C. (eds.). "Petrochemical Characteristics of Volcanic Rocks Associated with Uranium Deposits in the McDermitt Caldera Complex". Studies in Geology. 178: 63–72. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- "Jordan Meadow Mountain - 6,816' Nevada". Listsofjohn.com. Retrieved 17 June 2018.
- Henry, Christopher D.; Castor, Stephen B.; Starkel, William A.; Ellis, Ben S.; Wolff, John A.; Laravie, Joseph A.; McIntosh, William C.; Heizler, Matthew T. (17 July 2017). "Geology and evolution of the McDermitt caldera, northern Nevada and southeastern Oregon, western USA". Geosphere. 13 (4): 1066–1112. Bibcode:2017Geosp..13.1066H. doi:10.1130/GES01454.1. ISSN 1553-040X.
- Nash, J. Thomas (2010). "Volcanogenic Uranium Deposits: Geology, Geochemical Processes, and Criteria for Resource Assessment" (PDF). USGS Open-File Report 2010-1001. United States Geological Survey. pp. 17–22. Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- Orr, Elizabeth L.; Orr, William N. (1999). Geology of Oregon (5th ed.). Dubuque, Iowa: Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. p. 93. ISBN 978-0-7872-6608-0. OCLC 42944922.
- "Mercury" (PDF). United States Geological Survey. January 2012. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- Dahlkamp, Franz J. (2010). Uranium Deposits of the World: USA and Latin America. Vol. 2. Springer. pp. 282, 290. ISBN 978-3-540-78559-0.
- Rytuba, James J.; McKee, Edwin H. (30 September 1984). "Peralkaline ash flow tuffs and calderas of the McDermitt Volcanic Field, southeast Oregon and north central Nevada". Journal of Geophysical Research. 89 (B10): 8616–8628. Bibcode:1984JGR....89.8616R. doi:10.1029/JB089iB10p08616.
- Borden, Buddy; Harris, Tom (November 2017). "Economic and Fiscal Impacts From New Lithium Mine and Lithium Processing Operations in Humboldt County, Nevada" (PDF). University of Nevada, Reno. Retrieved 7 March 2020.
- Alessio Ricchiardi. "EV batteries, the largest lithium deposit discovered | Now the world balance is changing".
- Bradley, Dwight C.; Stillings, Lisa L.; Jaskula, Brian W.; Munk, LeeAnn; McCauley, Andrew D. (2017). "Lithium" (PDF). In Schulz, Klaus J.; DeYoung, Jr., John H.; Seal II, Robert R.; Bradley, Dwight C. (eds.). Critical Mineral Resources of the United States—Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply (Report). Professional Paper. United States Geological Survey. doi:10.3133/pp1802K. ISSN 2330-7102.
- "Kleinite". Mindat.org. Hudson Institute of Mineralogy. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
External links
 Media related to McDermitt Caldera at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to McDermitt Caldera at Wikimedia Commons