Medway NHS Foundation Trust
Medway NHS Trust is an NHS foundation trust based in Kent which runs Medway Maritime Hospital.
| Medway NHS Foundation Trust | |
|---|---|
| Type | NHS foundation trust |
| Established | 1 November 1993 |
| Headquarters | Windmill Road Gillingham ME7 5NY |
| Hospitals | Medway Maritime Hospital |
| Staff | 4,382 FTE (2019/20)[1] |
| Website | www |
History
The trust was established as Medway NHS Trust on 1 November 1993, and became operational on 1 April 1994.[2]
A proposed merger with Dartford and Gravesham NHS Trust was called off in September 2013.[3]
Special measures
In July 2013 as a result of the Keogh Review the Trust was put into special measures by Monitor.[4] In November 2013 it was threatened that Monitor would remove the management because of its failure to address problems.[5] It was put into a buddying arrangement with East Kent Hospitals University NHS Foundation Trust.[6]
In December 2013 the Trust was one of 13 hospital trusts named by Dr Foster Intelligence as having higher than expected mortality indicator scores for the period April 2012 to March 2013 in their Hospital Guide 2013[7] and in June 2014, the Daily Telegraph highlighted "six figure sums" paid to "dozens of managers" at a time when the "failing hospital" was short of some 120 nurses.[8] The Telegraph quoted the £200,000 package for a 2-day week of chairman Christopher Langley who is entitled to £17,000 flat rate expenses, and banker Robert Griffiths who is paid the annual equivalent of £540,000 to act as "treasurer".[8] The Care Quality Commission (CQC) made a further inspection in July 2014 and rated it as inadequate. Particular problems were identified in the casualty department where staff "felt under siege", with up to 16 ambulances queuing outside and patients waited for more than 24 hours on at least ten occasions during the year.[9] The CQC imposed conditions on the running of the Accident and Emergency Department that all patients arriving at the Department must be assessed by a clinician within 15 minutes. A system must be established to record each patient's arrival, registration and time of first clinical assessment and the Trust is required to report on a weekly basis every time this standard is failed; and provide details about the patients affected, how long each one waited for an initial assessment, the reason why they waited longer than 15 minutes, and if there were consequences.[10]
In an effort to improve performance the Trust was given support first by University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust and then by Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust.[11]
In March 2017 the trust came out of special measures after an inspection that showed substantial improvements had been made.[12] In April 2017 32% of patients with suspected cancer had to wait longer than 2 weeks to see a specialist though 93% should see a cancer specialist within that time.[13]
Performance
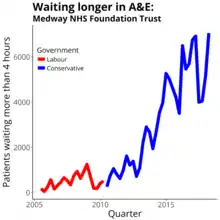
The Trust was one of 26 responsible for half of the national growth in patients waiting more than four hours in accident and emergency over the 2014/5 winter.[14]
In 2014/5 the Trust was given a loan of £22.5 million by the Department of Health which was to be paid back within five years.[15]
The Trust spent 13.3% of its total turnover on agency staff in 2014/5 – the biggest proportion of any NHS Trust in England.[16]
In March 2016 the Trust was rated as having a poor reporting culture in the Learning from Mistakes League.[17] Ten thousand patients were said to have waited more than 18 weeks for their first out-patient appointment, a situation that was expected to continue for at least a year.[18] The Trust had the second worst rating in the English inpatient experience survey,[19] and ended 2015/6 in deficit of £52.5 million.[20]
The Trust had a deficit of £62 million in 2017-18, £24.3 million worse than planned, and with loans from the Department of Health and Social Care of £217 million, £11.2 million more than its assets. The Trust expects a deficit of £46.8 million in 2018/9 with no prospect of repaying its loans.[21]
In January 2019 seven out of 92 patients (8%) referred for investigation of breast symptoms were seen by a specialist within two weeks. The target is 93% [22]
Mark Reckless
During the 2014 Rochester and Strood by-election Mark Reckless, the UKIP candidate produced a leaflet attacking the Conservative Party for failing NHS patients, featuring a picture of him, taken when he was a Conservative MP, with Dr Phillip Barnes, the acting Chief Executive of the Trust. Shena Winning, the Chair of the Trust, complained to Reckless, pointing out that public bodies cannot be associated with politically-biased information that could be seen to give any party an electoral advantage and that he had not asked permission to use the picture. Winning required that the leaflet be withdrawn and a public retraction.[23]
History
Dr Helen Mair was District Medical Officer for the Trust in the 1980s.[24]
See also
References
- "ANNUAL REPORT AND ACCOUNTS 2019/20" (PDF). Medway NHS Foundation Trust. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
- "The Medway National Health Service Trust (Establishment) Order 1993". legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
- "Dartford and Medway hospital trusts pull out of merger". BBC News. 15 September 2013. Retrieved 9 November 2013.
- "Keogh review: Hospital death rates". BBC News. 16 July 2013. Retrieved 9 November 2013.
- "Medway NHS Foundation Trust told to improve or face management changes". Kent News. 28 November 2013. Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- "'Buddy' trusts could double their money under bonus scheme". Health Service Journal. 23 July 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
- "Dr Foster identifies 13 trusts with high mortality ratios". Health Service Journal. 6 December 2013. Retrieved 7 December 2013.
- Laura Donnelly (28 June 2014). "Hospital dangerously short of nurses pays out six-figure sums to managers". Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 29 June 2014. Retrieved 29 June 2014.
- "Medway Maritime Hospital dubbed worst in country after special measures revealed it as failing". Kent Online. 24 November 2014. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- "Strict conditions imposed on Medway following multiple inspections". Health Service Jpurnal. 26 November 2014. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- "Leading foundation trust buddies with Medway". Health Service Journal. 10 March 2015. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- "Medway NHS Foundation Trust out of special measures after four years". BBC News. 17 March 2017. Retrieved 17 March 2017.
- Under-strain NHS fails to ensure cancer patients seen quickly enough The Guardian
- "26 trusts responsible for half of national A&E target breach". Health Service Journal. 1 April 2015. Retrieved 3 May 2015.
- "11 trusts whose DH bailouts were converted to loans". Health Service Journal. 2 September 2015. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- "Agency spending: the real picture". Health Service Journal. 26 November 2015. Retrieved 23 December 2015.
- "Trusts ranked in 'learning from mistakes' league". Health Service Journal. 9 March 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- "Kent CCG looks to Calais staff to reduce waiting times". Health Service Journal. 11 April 2016. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- "Survey analysis: Trusts scoring worst across patient experience survey". Health Service Journal. 17 June 2016. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- "Analysis: The trusts whose finances fell furthest despite 'urgent action'". Health Service Journal. 2 June 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- "Trust in 'negative equity' questions whether it is 'going concern'". Health Service Journal. 3 May 2018. Retrieved 26 June 2018.
- "Trust hits waiting time target in just 8pc of cases". Health Service Journal. 9 April 2019. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- "NHS Demands Mark Reckless Withdraw 'Misleading' Ukip Leaflet". Huffington Post. 10 November 2014. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- "Munks Roll Details for Helen Elizabeth Mair". munksroll.rcplondon.ac.uk. Retrieved 27 July 2019.