Menefee Formation
The Menefee Formation is a lower Campanian geologic formation found in Colorado and New Mexico, United States.
| Menefee Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: | |
 Menefee Formation in road cut at Mesa Verde National Park, Colorado | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Mesaverde Group |
| Sub-units | Cleary Coal Member, Allison Member |
| Underlies | Cliff House Sandstone |
| Overlies | Point Lookout Sandstone |
| Thickness | 500 m (1,600 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | sandstone, shale |
| Other | coal< |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 37°19′37″N 108°14′56″W |
| Region | |
| Country | |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Menefee Mountain (37°19′37″N 108°14′56″W) |
| Named by | A.J.Collier |
| Year defined | 1919 |
 Menefee Formation (the United States)  Menefee Formation (Colorado) | |

Description
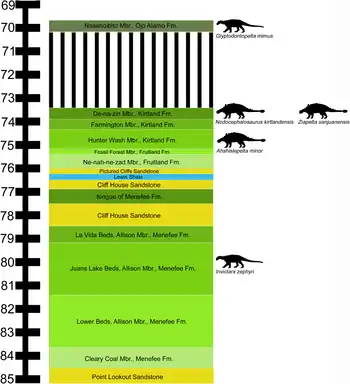
The Menefee Formation consists of fluvial sandstone, shale, and coal. Based on ammonite biostratigraphy, the age of the Menefee Formation can be constrained to 84.2-79 million years (Ma), based on the presence of Baculites perplexus in the overlying Cliff House Sandstone, and ammonites from the late Santonian in the underlying Point Lookout Sandstone.[1]
Named members include a lower Cleary Coal Member and an upper Allison Member.[2]
The Mesaverde Group in the San Juan Basin records a marine regression-transgression sequence of the western margin of the Western Interior Seaway. The Menefee Formation was deposited at the peak of the regression as coastal river delta and swamp sediments, and includes numerous coal beds.[2][3]
The formation is exposed at Chaco Canyon National Park, where many of the coal beds have been burned to produce distinctive red cinder outcrops.[4]
Fossils
The Menefee Formation includes fossils of turtles, fish and crocodiles and fragmentary evidence of hadrosaurs, ankylosaurs, and ceratopsian dinosaurs. Plant fossils include leaf impressions of palms, conifers, laurels, witchhazel, and camellia. The flora are suggestive of a moist subtropical environment.[5]
Vertebrate fauna
Several vertebrates have been recovered from the Menefee Formation, including intermediate remains of baenids, trionychids, and dromaeosaurids.[6]
| Dinosaurs reported from the Menefee Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
| Ankylosauria[7] |
Indeterminate[7] |
|
Numerous partial osteoderms.[7] |
Indeterminate Ankylosaur remains.[7] |
| |
| Dynamoterror[8] |
D. dynastes[8] |
|
Frontals, fragmentary vertebral centra, fragments of dorsal ribs, metacarpal, supraacetabular crest of an ilium, unidentifiable fragments of long bones and phalanxes.[8] |
A tyrannosaurid tyrannosaurine known from fragmentary remains.[8] | ||
| Hadrosauridae[7] |
Indeterminate[7] |
|
A proximal femur, a distal metatarsal, jaw fragments, a radius, an ulna, caudal vertebrae and a distal tibia.[7] |
Indeterminate hadrosaurid remains.[7] | ||
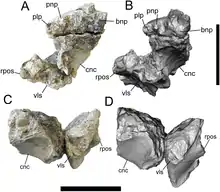
| Invictarx[9] |
I. zephyri[9] |
|
Dorsal rib fragments, dorsal vertebrae, distal end of humerus, distal end of ulna, proximal ends of radii, incomplete metacarpal, and numerous incomplete and complete osteoderms.[9] |
A nodosaurid, similar to Glyptodontopelta from the Ojo Alamo Formation.[9] | ||
| Menefeeceratops[10][6] | M. sealeyi[10] | A partial premaxilla, nearly complete postorbital horncore, squamosals, an incomplete parietal, jugal, predentary, dentary, a cervical vertebra, dorsal vertebrae, sacral vertebrae, dorsal ribs, ilium, radius, the proximal and distal portions of an ulna, metatarsal, femur, and the distal end of a fibula.[10][6] | The oldest recognized centrosaurine ceratopsid.[10][6] | |||
| Ornatops[1] |
O. incantatus[1] |
|
A partial premaxilla, postorbital, squamosal, quadrates, skull roof, braincase, partial dorsal vertebrae, dorsal rib, ossified tendons, scapula, proximal end of a humerus, ulna lacking the proximal end, radius lacking the proximal end, metacarpals, and incomplete pubis and ischium.[1] |
The first brachylophosaurin reported from New Mexico and the southernmost occurrence of the clade.[1] | ||
| cf. Saurornitholestes[7] |
cf. S. sp[7] |
|
A fragmentary tooth.[7] |
A saurornitholestine dromaeosaurid represented by a single, isolated tooth.[7] | ||
| Tyrannosauridae[7] |
Indeterminate[7] |
|
A scapula, metatarsal, shaft of anterior thoracic rib, postorbital and lateral tooth.[7] |
Indeterminate tyrannosaurid remains.[7] | ||
| Crocodilians reported from the Menefee Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
| Crocodylia[6] |
Indeterminate[6] |
|
A jaw fragment, teeth and scutes.[6] | Indeterminate crocodylian remains.[6] |
| |
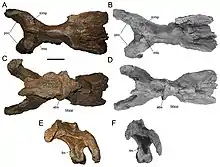
| Brachychampsa[11] |
B. sealeyi[11] |
|
A partial skull, associated partial right mandible, partial ramus of the left mandible, and a nearly complete osteoderm.[11] |
Mandible preserves bite marks which may have been inflicted by another alligatorioid.[11] | ||
| Deinosuchus[12] |
D. sp[12] |
|
[Six] osteoderms, caudal vertebrae, and a fragmentary tooth.[12] |
One of the earliest occurrences of the genus on the Laramidian continent and all of North America.[12] | ||
| Turtles reported from the Menefee Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images | |
| Baenidae[7] |
Indeterminate[7] |
|
Carapace fragments and plastron fragments.[7] |
|||
| Testudines[6] |
Indeterminate[6] |
|
A very fragmentary partial carapace and plastron.[6] |
|||
| Trionychidae[7][6] |
A nearly complete costal, carapace fragments and plastron fragments.[7][6] |
Indeterminate trionychid remains.[7][6] | ||||
Economic geology
The Menefee Formation has been extensively mined for coal since the early 20th century.[13] The Monero field in Rio Arriba County, New Mexico, was mined from the 1880s into the early 1920s to support the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, but while the coal is of good quality, the coal beds are relatively thin and the terrain is rugged. Remaining reserves are around 13.5 million tons, inadequate for economic exploitation in the 21st century.[14]
History of investigation
The Menefee Formation was first described by W.H.Holmes in 1877 during the Hayden Survey as the "Middle Coal Group" of the Mesaverde Formation.[15] A.J. Collier redesignated this unit in 1919 as the Menefee Formation and raised the Mesaverde Formation to group rank.[13]
See also
References
- McDonald et al. 2021.
- Lucas et al. 2005.
- Fillmore 2011.
- Scott, O'Sullivan & Weide 1984.
- National Park Service 2015.
- Williamson 1997.
- Hunt & Lucas 1993.
- McDonald, Wolfe & Dooley 2018.
- McDonald & Wolfe 2018.
- Dalma et al. 2021.
- Williamson 1996.
- Mohler, McDonald & Wolfe 2021.
- Collier 1919.
- Hoffman 1991.
- Holmes 1877.
Bibliography
- Collier, A.J. (1919). "Coal south of Mancos, Montezuma County, Colorado". U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin. 691-K: K293–K310. doi:10.3133/b691K.
- Dalma, S. G.; Lucas, S. G.; Jasinski, S. E.; Lichtig, A. J.; Dodson, P. (2021). "The oldest centrosaurine: a new ceratopsid dinosaur (Dinosauria: Ceratopsidae) from the Allison Member of the Menefee Formation (Upper Cretaceous, early Campanian), northwestern New Mexico, USA". PalZ. 95 (2): 291–335. doi:10.1007/s12542-021-00555-w. S2CID 234351502.
- Fillmore, Robert (2011). Geological evolution of the Colorado Plateau of eastern Utah and western Colorado, including the San Juan River, Natural Bridges, Canyonlands, Arches, and the Book Cliffs. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press. pp. 224, 247–248. ISBN 978-1-60781-004-9.
- Hoffman, Gretchen K. (February 1991). "Geology and quality of Menefee Formation coals, Monero coal field, Rio Arriba County, New Mexico" (PDF). New Mexico Geology. 13 (1). Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- Holmes, W.H. (1877). "Report [on the San Juan District, Colorado]". U.S. Geological and Geographical Survey of the Territories (Hayden), Annual Report. 9: 237–276.
- Hunt, Adrian P.; Lucas, Spencer G. (1993). "Cretaceous vertebrates of New Mexico". In Lucas, S.G.; Zidek, J. (eds.). Dinosaurs of New Mexico. New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin, 2. Albuquerque, New Mexico: New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science. pp. 77–91.
- Lucas, Spencer G.; Spielmann, Justin A.; Braman, Dennis R.; Brister, Brian S.; Peters, Lisa; McIntgosh, William C. (2005). "Age of the Cretaceous Menefee Formation, Gallina Hogback, Rio Arriba County, New Mexico" (PDF). New Mexico Geological Society Field Conference Series. 56. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- McDonald, AT; Wolfe, DG (2018). "A new nodosaurid ankylosaur (Dinosauria: Thyreophora) from the Upper Cretaceous Menefee Formation of New Mexico". PeerJ. 6: e5435. doi:10.7717/peerj.5435. PMC 6110256. PMID 30155354.
- McDonald, A.T.; Wolfe, D.G.; Dooley, A.C., Jr. (2018). "A new tyrannosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Upper Cretaceous Menefee Formation of New Mexico". PeerJ. 6: 6:e5749. doi:10.7717/peerj.5749. PMC 6183510. PMID 30324024.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - McDonald, A. T.; Wolfe, D. G.; Freedman Fowler, E. A.; Gates, T. A. (2021). "A new brachylophosaurin (Dinosauria: Hadrosauridae) from the Upper Cretaceous Menefee Formation of New Mexico". PeerJ. 9: e11084. doi:10.7717/peerj.11084. PMC 8020878. PMID 33859873.
- "Menefee Formation". Chaco Canyon National Historical park. National Park Service. 2015. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- Mohler, B.F.; McDonald, A.T.; Wolfe, D.G. (2021). "First remains of the enormous alligatoroid Deinosuchus from the Upper Cretaceous Menefee Formation, New Mexico". PeerJ. 9: e11302. doi:10.7717/peerj.11302. PMC 8080887. PMID 33981505.
- Scott, G.R.; O'Sullivan, R.B.; Weide, D.L. (1984). "Geologic map of the Chaco Culture National Historical Park, northwestern New Mexico [includes chapter on archaeology by W.B. Gillespie]". U.S. Geological Survey Miscellaneous Investigations Series Map. I-1571. Retrieved 21 April 2021.
- Williamson, TE (1996). "Brachychampsa sealeyi, sp. nov., (Crocodylia, Alligatoroidea) from the Upper Cretaceous (lower Campanian) Menefee Formation, northwestern New Mexico". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 16 (3): 421–431. doi:10.1080/02724634.1996.10011331.
- Williamson, TE (1997). "A new Late Cretaceous (early Campanian) vertebrate fauna from the Allison Member, Menefee Formation, San Juan Basin, New Mexico". In Lucas, SG; Estep, JW; Williamson, TE; Morgan, GS (eds.). New Mexico's Fossil Record 1. Albuquerque: New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 11. pp. 51–59. Retrieved 21 April 2021.