Merocyanine
Merocyanines are a class of polymethine dyes which are clearly defined by set structural properties. Merocyanines belong to the group of dyes referred to as functional dyes, where their applications are not only determined by their colour, but also their valuable chemical properties.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Sodium 3-{(2Z)-2-[(2E)-4-(1,3-dibutyl-2,4,6-trioxo-1,3-diazinan-5-ylidene)but-2-en-1-ylidene]-1,3-benzoxazol-3(2H)-yl}propane-1-sulfonate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H32N3NaO7S | |
| Molar mass | 553.60 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
These dyes are usually intensely colored and have large extinction coefficients.
Merocyanine 540 was the first fluorescent dye used for measuring membrane potential,[1] while Brooker's merocyanine and related compounds are notable for their solvatochromatic properties.
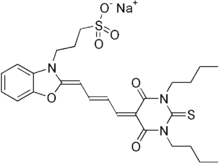 Merocyanine 540 differs from merocyanine I by the replacement of an oxygen atom with a sulfur atom
Merocyanine 540 differs from merocyanine I by the replacement of an oxygen atom with a sulfur atom
Definition
- Conventionally, merocyanine class includes streptocyanines and their analogues where both the nitrogen atom and carbonyl group (or any other electron-withdrawing group containing a multiple carbon-heteroatomic bond, e.g. amino group) can form part of a heterocyclic system. Like ionic cyanines, merocyanines contain two terminal heteroatoms and a polymethine chain in their chromophores.[2]
See also
References
- "AnaSpec | Custom Peptide Synthesis". Archived from the original on 2011-07-07.
- Kulinich, A V; Ishchenko, A A (2009). "Merocyanine dyes: synthesis, structure, properties and applications". Russian Chemical Reviews. 78 (2): 141–164. Bibcode:2009RuCRv..78..141K. doi:10.1070/RC2009v078n02ABEH003900.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.