Methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane
Methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine is a Wittig reagent used for the homologization of aldehydes, and ketones to extended aldehydes, a organic reaction first reported in 1958. The reagent is generally prepared and used in situ. It has blood-red color, indicative of destabilized ylides.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methoxymethylidene(triphenyl)-λ5-phosphane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H19OP | |
| Molar mass | 306.345 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Preparation
The reagent can be prepared in two steps from triphenylphosphine. The first step is P-alkylation with chloromethyl methyl ether.
- PPh3 + CH3OCH2Cl → [CH3OCH2PPh3]Cl
In the second step, the resulting phosphonium salt is deprotonated.
- [CH3OCH2PPh3]Cl + LiNR2 → CH3OCH=PPh3 + LiCl + HNR2
In place of chloromethyl methyl ether, a mixture of methylal and acetyl chloride can be used.
Uses
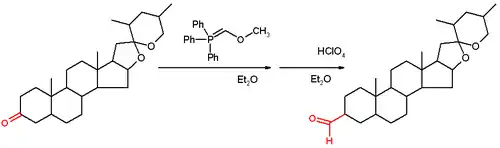
This reagent reacts with a ketone or aldehyde in a Wittig reaction to give an enol ether, which can be converted to the aldehyde by acid-induced hydrolysis.
The initial report of the reaction demonstrated its use on the steroid tigogenone.
It was later used in the Wender Taxol total synthesis and the Stork quinine total synthesis.
References
- ^ A new aldehyde synthesis Samuel G. Levine J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1958; 80(22); 6150–6151. doi:10.1021/ja01555a068