Methylmagnesium chloride
Methylmagnesium chloride is an organometallic compound with the general formula CH3MgCl. This highly flammable, colorless, and moisture sensitive material is the simplest Grignard reagent and is commercially available, usually as a solution in tetrahydrofuran.
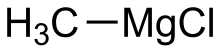 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
chlorido(methyl)magnesium | |
| Other names
(chloromagnesio)methane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.573 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3MgCl | |
| Molar mass | 74.79 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Reacts with water | |
| Solubility | soluble in diethyl ether and THF |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Flammable, Reacts with water |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H225, H250, H260, H314 | |
| P210, P222, P223, P231+P232, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P334, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P335+P334, P363, P370+P378, P402+P404, P403+P235, P405, P422, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −17 °C (1 °F; 256 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Phenylmagnesium bromide, Dibutylmagnesium |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Synthesis and reactions
Relative to the more commonly encountered methylmagnesium bromide[1] and methylmagnesium iodide, methylmagnesium chloride offers the advantages of low equivalent weight and low cost. It is prepared by the reaction of methyl chloride and magnesium in ethyl ether.[2]
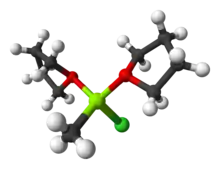
As with most Grignard reagents, methylmagnesium chloride is highly solvated by ether solvents via coordination from two oxygen atoms to give a tetrahedrally bonded magnesium center.
Like methyllithium, it is the synthetic equivalent to the methyl carbanion synthon. It reacts with water and other protic reagents to give methane, e.g.,:
- CH3MgCl + ROH → CH4 + MgCl(OR)
When treated with dioxane, ether solutions of methylmagnesium chloride reacts to give the insoluble coordination polymer with the formula MgCl2(dioxane)2. Remaining in the solution is the dioxane adduct of dimethylmagnesium. This conversion exploits the Schlenk equilibrium, which is driven to the right by the precipitation of the magnesium halide:[3]
- 2 CH3MgCl + 2 dioxane → (CH3)2Mg + MgCl2(dioxane)2
See also
Further reading
- Sakai, Shogo; Jordan, K. D. (1982). "Ab initio study of the structure and vibrational frequencies of the Grignard reagent methylmagnesium chloride". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 104 (14): 4019. doi:10.1021/ja00378a047.
References
- Raymond Paul; Olivier Riobé; Michel Maumy (1976). "(E)-4-Hexen-1-ol". Org. Synth. 55: 62. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.055.0062.
- E. R. Coburn (1947). "3-Penten-2-ol". Org. Synth. 27: 65. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.027.0065.
- Fischer, Reinald; Görls, Helmar; Meisinger, Philippe R.; Suxdorf, Regina; Westerhausen, Matthias (2019). "Structure–Solubility Relationship of 1,4‐Dioxane Complexes of Di(hydrocarbyl)magnesium". Chemistry – A European Journal. 25 (55): 12830–12841. doi:10.1002/chem.201903120. PMC 7027550. PMID 31328293.
