Minami-Hiyoshi Seamount
The Minami-Hiyoshi Seamount is an active seamount in the Bonin Islands of Japan.
| Minami-Hiyoshi Seamount | |
|---|---|
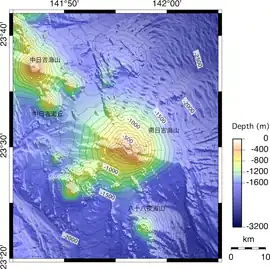 Bathymetry map of Minami-Hiyoshi | |
| Summit depth | −107 m (−351 ft)[1] |
| Height | ~1,300 m (4,265 ft) |
| Location | |
| Range | Izu-Ogasawara Ridge |
| Coordinates | 23°30′00″N 141°56′06″E[1] |
| Country | Japan |
| Geology | |
| Type | Stratovolcanoes |
| Last eruption | 1975 |
Geography
Located 1,350 km (839 mi) south of Tokyo and 155 km (96 mi) south of Iwo Jima, The main cone of the Hiyoshi complex, the Minami-Hiyoshi is a stratovolcano with a base diameter of 19 km (12 mi) with a height above the seabed around 1,300 m (4,265 ft).[2] The submarine volcano complex involves four submarine volcanic peaks; Kita-Hiyoshi, Naka-Hiyoshi, Minami-Hiyoshi and the Ko-Hiyoshi submarine volcanoes. This complex is geologically connected to the Izu-Mariana arc.[3]
Recent activity
In a report about the seismic activity of the volcano compiled in 2003, the active cone, Minami-Hiyoshi was reported to have "low activity" over the period of a month in 2001.[4] Other than that, Minami-Hiyoshi has had many periods of activity including 1975, 1976, 1977, 1978, 1992 and 1996.[1]
Gallery
 Activity at Minami-Hiyoshi in 10 January, 1977
Activity at Minami-Hiyoshi in 10 January, 1977 Rafts of volcanic rocks rising to the surface above the Minami-Hiyoshi volcano in 12 January, 1977
Rafts of volcanic rocks rising to the surface above the Minami-Hiyoshi volcano in 12 January, 1977
References
- "Minami-Hiyoshi Seamount". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 1 January 2023.
- "Minamihiyoshi Seamount" (in Japanese). Japan Coast Guard Hyrdographic and Oceanographic Department. Retrieved January 6, 2023.
- Petrova, V. V.; Rashidov, V. A. (2019). "Composition and Origin of Lavas from the Minami-Hiyoshi Submarine Volcano (Mariana Arc)". Doklady Earth Sciences. 485 (1): 238–241. Bibcode:2019DokES.485..238P. doi:10.1134/S1028334X19030140. S2CID 189995687. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- Nishizawa, A.; Ono, T.; Sasahara, N.; Hashiguchi, H.; Otani, Y. (2003). Ocean Bottom Seismographic Observation at Minami-Hiyoshi Seamount at the Northern End of the Mariana Arc (Report) (in Japanese). Japan Coast Guard Hydrographic and Oceanographic Department. p. 3-20. Retrieved January 7, 2023.