Minkébé National Park
Minkébé National Park (French: Parc National de Minkébé) is a national park in the extreme northeast of Gabon. It covers an area of 7,570 km2.[1] The WWF recognized it as an area needing protection as early as 1989 and has been actively working towards protecting the forest since 1997. The park was established as a provisional reserve in 2000 but the Minkébé National Park itself was officially recognized and established by the Gabonese government in August 2002.[2] It is recognized as a critical site for conservation by the IUCN and has been proposed as a World Heritage Site.
| Minkébé National Park | |
|---|---|
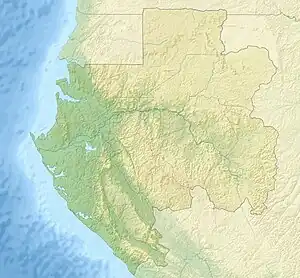 | |
| Location | Gabon |
| Coordinates | 1°40′47.18″N 12°45′34.21″E |
| Area | 7,570 km2 |
| Established | 2000 (provisional) August 2002 (National Park) |
| Governing body | National Agency for National Parks |
History and management
The Fang people once inhabited the Minkébé area but on becoming a protected area the park now has no permanent human population. The name Minkébé derives from the Fang word minkegbe, which means 'valleys' or 'ditches'. Historically, the park was under former French army control in the 1920s.
In 1997, the WWF initiated a management program and established two main centres of forest command, one at Oyem, the other at Makokou. A central camp was also installed at the mouth of the river Nouna to manage the protected area.[3]
Since 1997, the park has received funds from DGIS (Netherlands Development Cooperation) and CARPE (USAID), and the WWF has worked with other groups to build up ways in which to manage and protect the biodiversity in the park. The park has received donors from the European Union, CARPE, UNESCO and the French Global Environment Facility (FFEM).
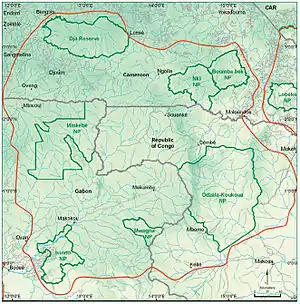
The WWF has attempted to create a complex of protected areas in the interzone between Gabon, Republic of the Congo and Cameroon and the Minkebe was intended to become a part of a conservation process on a much broader geographical scale. This interzone is considered one of the most biologically rich forests in Africa and is ecologically a part of the Northwest Congolian Lowland Forest ecoregion, one of WWF's main global ecoregions.[4] This work at a regional level in the interzone between Cameroon, Republic of the Congo and Gabon is known as the Dja- Odzala-Minkébé Tri-National (TRIDOM), where each of the countries have committed themselves to cooperating, implementing and managing the interzone in order to promote conservation and sustainable development. The TRIDOM zone covers 140,000 km2 which equates to approximately 7.5% of the Congo Basin's forests.[2]
Although much of the protected area is unspoiled with human intervention, logging of Gabonese redwood trees has increased considerably in recent years where roads have been built and there are two logging concessions in the area which could threaten the park in the future. Other threats to the park include low scale gold mining and hunting for crocodile skin, ivory or meat to sell in the cities of Gabon although this is relatively low. Hunting management is being implemented by a protocol signed within Gabon, between the Gabonese Ministry of Forestry Economy, the Governorate of the Woleu-Ntem Province, Bordamur and the villages in which are directly involved. The protocol acknowledges the interests of conservationists, loggers and local communities on matters relating to hunting and fishing. There is also a management strategy towards hunting activities in the north-eastern periphery of the park between the Ministry of Forestry Economy, the Ministry of Mines, and local representatives.[2]
In 2007, it was reported that a Chinese company had filed to exploit the second-largest iron ore deposit in the world, near the Minkebe National Park. To clear for the mining, it would involve removing a large area of the surrounding forest, and an estimated 350 miles (560 km) of railway, up to 40,000 Chinese laborers, and a hydroelectric dam would be needed to make it possible. This could seriously threaten the future of the conservation area, and the WWF are working with the Chinese and other mining companies in Gabon to attempt to provide a solution.[5]
Geography
The Minkebe forest itself covers 30,000 km2 in the wider area. There exists a wide diversity of habitats, from inselberg forest, herbaceous swamps, inundated river forest to secondary forest. The landscape of the park is dominated by isolated rock domes overlooking the surrounding forest and trees of many hundreds of years old are to be found. An abundance of marshy areas break the forest cover. The Minkébé forest has four main rivers and there are also areas of grassland with elephant tracks. Accessibility to the park in many places is extremely limited due to the distinct lack of infrastructure in the park which has helped to protect the area and leave much of it unspoiled by human interference.
Wildlife


The forest elephant is particularly important to the park and is believed by the WWF to contain one of the largest populations in Africa.[4] The lesser forest in the park is inhabited by elephants, gorillas, and various small carnivores, porcupines, squirrels, african golden cats, leopards, giant pangolins, duikers and red river hog. The primary forest is inhabited by creatures such as mandrill, black colobus and chimpanzee. The western lowland gorilla, chimpanzee, black colobus, mandrill and golden potto have all been listed on the IUCN Red List.[4] The riparian areas of the Minkébé forest provide for creatures who require a water habitat, including the dwarf crocodile, spotted-necked otter, crested mangabey, sitatunga, and water chevrotain. The swampy areas interspersed with vegetation also includes habitat for parrots and python. The park contains some animals which are rare in Gabon including the bongo and the giant forest hog.
Although the park itself is not permanently inhabited by humans, populations of Baka pygmy, Fang, Kota and Kwèl ethnic groups live in the forest region and possess a rich cultural and superstitious heritage, The Kota mask, the forest spirit, Baka Edzengui, and the Kwel Deke dance are of cultural note in the region.
Species of bird, including the spot-breasted ibis (Bostrychia rara) and Rachel's malimbe (Malimbus racheliae), are fairly common in the park, and the tree species Sterculia subviolacea is found in the national park and not found elsewhere in Gabon.
See also
References
- Operation Loango Archived 2008-05-17 at the Wayback Machine
- "Gabon decouverte - CDK". www.compagniedukomo.com. Archived from the original on 2008-08-28. Retrieved 2008-06-18.
- Gabon National Parks, Retrieved on June 18, 2008
- "WWF conservation projects around the world". Archived from the original on 2020-12-19. Retrieved 2008-06-18.
- "Funding and Financial Overview - WWF". World Wildlife Fund. Archived from the original on 2008-10-03. Retrieved 2008-06-18.