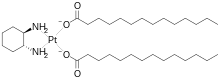
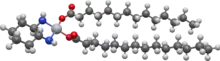
Miriplatin
Miriplatin (INN; trade name Miripla) is a drug used to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). It is a lipophilic platinum complex that is used in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE).[1][2] Miriplatin was approved by Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency in 2009.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Miripla |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C34H68N2O4Pt |
| Molar mass | 764.012 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- "Miriplatin". Inxight Drugs. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health.
- Ikeda M, Kudo M, Aikata H, Nagamatsu H, Ishii H, Yokosuka O, et al. (February 2018). "Transarterial chemoembolization with miriplatin vs. epirubicin for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomized trial". Journal of Gastroenterology. 53 (2): 281–290. doi:10.1007/s00535-017-1374-6. PMC 5846877. PMID 28766016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.