Mississippi Chancery Courts
Mississippi Chancery Courts are courts of equity. They also have jurisdiction over family law, sanity hearings, wills, and constitutional law. In counties with no County Court, they have jurisdiction over juveniles. Typically, trials are heard without a jury, but juries are permitted. There are 20 districts.[1]
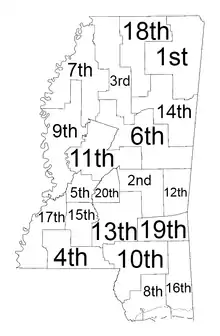
Map of Chancery Court districts
Elections
Judges in Mississippi Chancery Courts are elected every four years in a nonpartisan election.[2] Judges are required to have five years of experience as a practicing attorney, to be at least 26 years old, to have lived in Mississippi for at least five years, and to live within the court's district.[3]
Districts
Mississippi Chancery Courts are divided into the following 20 districts.[1]
| District | Counties covered |
|---|---|
| 1st | Alcorn, Itawamba, Monroe, Pontotoc, Prentiss, Lee, Tishomingo, Union |
| 2nd | Jasper, Newton, Scott |
| 3rd | Desoto, Grenada, Montgomery, Panola, Tate, Yalobusha |
| 4th | Amite, Franklin, Pike, Walthall |
| 5th | Hinds |
| 6th | Attala, Carroll, Choctaw, Kemper, Neshoba, Winston |
| 7th | Bolivar, Coahoma, Leflore, Quitman, Tallahatchie, Tunica |
| 8th | Hancock, Harrison, Stone |
| 9th | Humphreys, Issaquena, Sharkey, Sunflower, Warren, Washington |
| 10th | Forrest, Lamar, Marion, Pearl River, Perry |
| 11th | Holmes, Leake, Madison, Yazoo |
| 12th | Clarke, Lauderdale |
| 13th | Covington, Jefferson Davis, Lawrence, Simpson, Smith |
| 14th | Chickasaw, Clay, Lowndes, Noxubee, Oktibbeha, Webster |
| 15th | Copiah, Lincoln |
| 16th | George, Greene, Jackson |
| 17th | Adams, Claiborne, Jefferson, Wilkinson |
| 18th | Benton, Calhoun, Lafayette, Marshall, Tippah |
| 19th | Jones, Wayne |
| 20th | Rankin |
See also
- Courts of Mississippi
- The Summons, a novel about a Chancery Court judge
References
- "Chancery Court – About the Court". State of Mississippi Judiciary. Retrieved 27 December 2013.
- "Mississippi local trial court judicial elections, 2020". Ballotpedia. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- "Methods of Judicial Selection: Mississippi". Judicial Selection in the States. National Center for State Courts. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.