Mytilene
Mytilene (/ˌmɪtɪˈliːni/; Greek: Μυτιλήνη, romanized: Mytilíni [mitiˈlini] ⓘ) is the capital of the Greek island of Lesbos, and its port. It is also the capital and administrative center of the North Aegean Region, and hosts the headquarters of the University of the Aegean. It was founded in the 11th century BC.
Mytilene
Μυτιλήνη | |
|---|---|
 Clockwise from top: Panoramic view of the City of Mytilene, Archaeological Museum of Mytilene, Statue of Liberty, Characteristic samples of urban architecture, the seafront and Harbor of Mytilene, Church of Saint Therapon, and Lesbos Regional Unit Administration. | |
 Seal | |
 Mytilene Location within the region  | |
| Coordinates: 39°6′N 26°33′E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | North Aegean |
| Regional unit | Lesbos |
| Municipality | Mytilene |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Stratis Kytelis |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 566.7 km2 (218.8 sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 107.46 km2 (41.49 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 8 m (26 ft) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • Municipality | 58.285[2] |
| • Municipal unit | 37,890 |
| • Municipal unit density | 350/km2 (910/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Mytilenian |
| Community | |
| • Population | 29,656 (2011) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 811 00 |
| Area code(s) | 22510 |
| Vehicle registration | MY |
| Website | www.mytilene.gr |
Mytilene is one of the two municipalities on the island of Lesbos, created in 2019; the other is West Lesbos.[3] Mytilene is built on the southeast edge of the island. It is the seat of a metropolitan bishop of the Eastern Orthodox Church.
History



As an ancient city, lying off the east coast, Mytilene was initially confined to a small island just offshore that later was joined to Lesbos, creating a north and south harbor. The early harbors of Mytilene were linked during ancient times by a channel 700 m long and 30 m wide. The Roman writer Longus speaks of white stone bridges linking the two sides. The Greek word εὔριπος eúripos is a commonly-used term when referring to a strait. The strait allowed ancient warships called triremes, with three tiers of rowers or more. The boats that passed were ca. 6 m wide plus oars and had depth of 2 m.
The areas of the city that were densely populated connected the two bodies of land with marble bridges. They usually followed a curved line. The strait begins at the old market called Apano Skala. It was also close to Metropolis Street and ended at the Southern Harbor. One could argue that the channel transversed what is now called Ermou Street. Over time the strait began to collect silt and earth. There was also human intervention for the protection of the Castle of Mytilene. The strait eventually filled with earth.[4]
Mytilene contested successfully with Mithymna in the north of the island for the leadership of the island in the seventh century BC and became the centre of the island's prosperous eastern hinterland. Her most famous citizens were the poets Sappho and Alcaeus and the statesman Pittacus (one of the Seven Sages of Greece). The city was famed for its great output of electrum coins struck from the late sixth through mid-fourth centuries BC.[5]
The Mytilenean revolt against Athens in 428 BC was overcome by an Athenian expeditionary force. The Athenian public assembly voted to massacre all the men of the city and to sell the women and children into slavery but the next day in the Mytilenian Debate changed its mind. A fast trireme sailed the 186 nautical miles (344 km) in less than a day and brought the decision to cancel the general massacre, but a thousand citizens were executed for taking part in the rebellion.
Aristotle lived on Mytilene for two years, 337–335 BC, with his friend and successor, Theophrastus (a native of the island), after being the tutor to Alexander, son of King Philip II of Macedon.[6][7]
The Romans, among whom was a young Julius Caesar, successfully defeated Mytilene in 81 BC at the Siege of Mytilene.[8] Although Mytilene supported the losing side in most of the great wars of the first century BC, her statesmen succeeded in convincing Rome of her support of the new ruler of the Mediterranean and the city flourished in Roman times.
In AD 56, Luke the Evangelist, Paul the Apostle and their companions stopped there briefly on the return trip of Paul's third missionary journey (Acts 20:14), having sailed from Assos (about 50 km (31 mi) away). From Mytilene they continued towards Chios (Acts 20:15).
The novel Daphnis and Chloe by Longus, is set in the country around it and opens with a description of the city.
Scholar and historian Zacharias Rhetor, also known as Zacharias of Mytilene was from Mytilene and lived from 465 to around 536. He was made Bishop of Mytilene and may have been a Chalcedonian Christian. He either died or was deposed between 536 and 553.[9]
The city of Mytilene was also home to 9th century Byzantine saints who were brothers, Archbishop George, Symeon Stylites, and David the Monk. The Church of St. Symeon, Mytilene venerates one of the three brothers.
Catching the eye of the Empress Zoë Porphyrogenita, Constantine IX Monomachos was exiled to Mytilene on the island of Lesbos by her second husband, Michael IV the Paphlagonian. The death of Michael IV and the overthrow of Michael V in 1042 led to Constantine being recalled from his place of exile and appointed as a judge in Greece.[10]
Lesbos and Mytilene had an established Jewish population since ancient times. In 1170, Benjamin of Tudela found ten small Jewish communities on the island.[11]
In the Middle Ages, it was part of the Byzantine Empire and was occupied for some time by the Seljuqs under Tzachas in 1085. In 1198, the Republic of Venice obtained the right to commerce from the city's port.
In the 13th century, it was captured by the Emperor of Nicaea, Theodore I Laskaris. In 1335, the Byzantines, with the help of Ottoman forces, reconquered the island, then property of the Genoese nobleman Domenico Cattaneo. In 1355, emperor John V Palaiologos gave it to the Genoese adventurer Francesco Gattilusio, who married the emperor's sister, Maria. They renovated the fortress in 1373, and it remained in Genoese hands until 1462, when it was besieged and captured by the Ottoman sultan Mehmed the Conqueror.
As part of the wider Great Turkish War, the Battle of Mytilene took place off the coast of Mytilene in 1690 when Venetian sailing ships attacked Ottoman and Barbary flagships. Resulting in a victory for the Venetians.[12]
Mytilene along with the rest of Lesbos remained under Ottoman control until the First Balkan War in 1912, when in November it was captured by the Kingdom of Greece.
Geography and climate
Mytilene is located in the southeastern part of the island, north and east of the Bay of Gera. It has a land area of 107.46 square kilometres (41.49 sq mi)[13] and a population of 36,196 inhabitants (2001). With a population density of 336.8/km2 it is by far the most densely populated municipal unit in Lesbos. The next largest towns in the municipal unit are Vareiá (pop. 1,254), Pámfila (1,247), Mória (1,207), and Loutrá (1,118). The Greek National Road 36 connects Mytilene with Kalloni. Farmlands surround Mytilene, the mountains cover the west and to the north. The airport is located a few kilometres south of town.
Municipal units
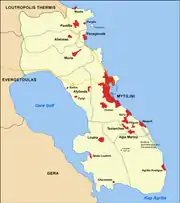
The municipality, as created in 2019, consists of the following six subdivisions:[3]
- Agiasos
- Evergetoulas
- Gera
- Loutropoli Thermis
- Mytilene
- Plomari
Province
The province of Mytilene (Greek: Επαρχία Μυτιλήνης) was one of the provinces of the Lesbos Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipal units Mytilene, Agiasos, Evergetoulas, Gera, Loutropoli Thermis, Mantamados and Polichnitos.[14] It was abolished in 2006.
Climate
Mytilene has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen: Csa) with hot, dry summers and cool, rainy winters.
| Climate data for Mytilene | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.2 (68.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
28.0 (82.4) |
31.0 (87.8) |
35.0 (95.0) |
40.0 (104.0) |
39.5 (103.1) |
38.2 (100.8) |
36.2 (97.2) |
30.8 (87.4) |
27.0 (80.6) |
22.5 (72.5) |
40.0 (104.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.1 (53.8) |
12.6 (54.7) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
23.9 (75.0) |
28.5 (83.3) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.2 (86.4) |
26.7 (80.1) |
21.7 (71.1) |
17.2 (63.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
20.9 (69.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 9.5 (49.1) |
9.9 (49.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
15.6 (60.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.1 (79.0) |
22.9 (73.2) |
18.5 (65.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
11.3 (52.3) |
17.6 (63.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
7.0 (44.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
11.2 (52.2) |
15.2 (59.4) |
19.3 (66.7) |
21.6 (70.9) |
21.4 (70.5) |
18.5 (65.3) |
14.8 (58.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
8.7 (47.7) |
13.7 (56.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.4 (24.1) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
4.0 (39.2) |
8.4 (47.1) |
11.0 (51.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
16.3 (61.3) |
10.9 (51.6) |
5.2 (41.4) |
1.4 (34.5) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 129.9 (5.11) |
97.2 (3.83) |
75.1 (2.96) |
46.8 (1.84) |
21.2 (0.83) |
6.0 (0.24) |
2.3 (0.09) |
4.1 (0.16) |
10.7 (0.42) |
38.2 (1.50) |
93.7 (3.69) |
145.4 (5.72) |
670.6 (26.40) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 9.0 | 8.1 | 6.5 | 4.8 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 3.3 | 6.8 | 10.0 | 54.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 71.0 | 69.8 | 57.5 | 63.9 | 62.6 | 57.3 | 56.0 | 57.4 | 59.5 | 66.1 | 71.0 | 72.0 | 64.5 |
| Source 1: Hellenic National Meteorological Service[15] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA[16] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Town population | Municipality population |
|---|---|---|
| 1981 | 24,991 | – |
| 1991 | 23,971 | 33,157 |
| 2001 | 27,247 | 36,196 |
| 2011 | 29,656 | 37,890 |
| 2021 | – | 58.285 |
Districts

- Agorá
- Chalikas (upper and lower)
- Chrisomallousa
- Epano Skala
- Kallithea
- Kamares
- Ladadika
- Lagada
- Pyrgélia
- Sourada
- Lazaretto/Vounaraki
Main streets
- Ermou Street
- Elyti Avenue
- Kountourioti Street
- Theofrastou Street
- Ellis Street
- Vernardaki
- Vournazon
- Eftalioti
- Myrivili
Economy

Mytilene has a port with ferries to the nearby islands of Lemnos and Chios and Ayvalık and at times Dikili in Turkey. The port also serves the mainland cities of Piraeus, Athens and Thessaloniki. One ship, named during the 2001 IAAF games in Edmonton Aeolus Kenteris, after Kostas Kenteris, used to serve this city (his hometown) with 6-hour routes from Athens and Thessaloniki. The main port serving Mytilene on the Greek mainland is Piraeus.
The city produces ouzo. There are more than 15 commercial producers on the island.
The city exports also sardines harvested from the Bay of Kalloni, olive oil, ladotyri cheese and woodwork.
Landmarks and urban architecture

The town of Mytilene has a large number of neoclassical buildings, public and private houses. Some of them are the building of the Lesbos Prefecture, the old City Hall, the Experimental Lyceum and various mansions and hotels all over the town.
The Baroque church of Saint Therapon dominates at the port with its impressive style.
- Ancient Theatre of Mytilene[17]
- Archaeological Museum of Mytilene
- Castle of Mytilene
- Church of Saint Symeon, Mytilene
- Catholic Church of Theotokos, where part of the relics of Saint Valentine are kept [18]
- Çarşı Hamam ("Market Bath")
- Ecclesiastical Byzantine Museum of Mytilene[19]
- Folk Art Museum of Mytilene[20]
- Monastery of Agios Raphael[21]
- Museum of Costume and Embroidery of Lesvos
- Sappho Square, where the statue of the Ancient Greek poet Sappho is located [22]
- Statue of Liberty (Mytilene)
- Theofilos Museum[23]
- Yeni Mosque, Mytilene
- Valide Mosque, Mytilene
- The Roman aqueduct of Mória[24]
- Teriade Meseum[25]
- Agora of Ermou street[26]
- Stoa of Mytilene, Hellinistic stoa in the area of Epano skala [27]
Archaeology


.jpg.webp)

Archaeological investigations at Mytilene began in the late 19th century when Robert Koldewey (later excavator of Babylon) and a group of German colleagues spent many months on the island preparing plans of the visible remains at various ancient sites like Mytilene. Significant excavations, however, do not seem to have started until after the First World War when in the mid-1920s Evangelides uncovered much of the famous theatre (according to Plutarch it was the inspiration for Pompey's theatre in Rome in 55 BC, the first permanent stone theatre in Rome) on the hill on the western side of town. Subsequent work in the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s by various members of the Archaeological Service revealed more of the theatre, including a Roman conversion to a gladiatorial arena. Salvage excavations carried out by the Archaeological Service in many areas of the city have revealed sites going back to the Early Bronze Age although most have been much later (Hellenistic and Roman). Particularly significant is a large stoa over a hundred metres long recently dug on the North Harbour of the city. It is clear from various remains in different parts of the city that Mytilene was indeed laid out on a grid plan as the Roman architect Vitruvius had written.
Archaeological excavations carried out between 1984 and 1994 in the Castle of Mytilene by the University of British Columbia and directed by Caroline and Hector Williams revealed a previously unknown sanctuary of Demeter and Kore of late classical/Hellenistic date and the burial chapel of the Gattelusi, the medieval Genoese family that ruled the northern Aegean from the mid-14th to mid-15th centuries of our era. The Demeter sanctuary included five altars for sacrifices to Demeter and Kore and later also to Cybele, the great mother goddess of Anatolia. Among the discoveries were thousands of oil lamps, terracotta figurines, loom weights and other dedications to the goddesses. Numerous animal bones, especially of piglets, also appeared. The Chapel of St. John served as the church of the castle and as a burial place for the Gattelusi family and its dependents. Although conversion to a mosque after the Ottoman capture of the city in 1462 resulted in the destruction of many graves, some remained. The great earthquake of February 1867 damaged the building beyond repair and it was demolished; the Ottomans built a new mosque over the ruins to replace it later in the 19th century.
Other excavations done jointly with the 20th Ephorate of Prehistoric and Classical Antiquities near the North Harbour of the city uncovered a multiperiod site with remains extending from a late Ottoman cemetery (including a "vampire" burial, a middle aged man with 20 cm (8 in) spikes through his neck, middle and ankles) to a substantial Roman building constructed around a colonnaded courtyard (probably a tavern/brothel in its final phase in the mid-4th century AD) to remains of Hellenistic structures and debris from different Hellenistic manufacturing processes (pottery, figurines, cloth making and dyeing, bronze and iron working) to archaic and classical levels with rich collections of Aeolic grey wares. A section of the late classical city wall runs across the site which was close to the channel that divided the mainland from the off shore island part of the city. Considerable remains of the two moles that protected the large North Harbour of the city are still visible just below or just breaking the surface of the sea; it functioned as the commercial harbour of the ancient city although today it is a quiet place where a few small fishing boats are moored.
The city has two excellent archaeological museums, one by the south harbour in an old mansion and the other two hundred metres further north in a large new purpose built structure. The former contains the rich Bronze Age remains from Thermi, a site north of Mytilene dug by the British in the 1930s as well as extensive pottery and figurine displays; the former coach house accommodates ancient inscriptions, architectural pieces, and coins. The latter museum is especially rich in mosaics and sculpture, including the famous late Roman mosaic floor from the "House of Menander" with scenes from plays by that Athenian 4th-century BC playwright. There are also mosaics and finds from other Roman mansions excavated by the Greek Archaeological Service under the direction of the archeologist Aglaia Archontidou-Argyri.
Education

There are 15 primary schools in Mytilene, along with seven lyceums, and eight gymnasiums. There are six university schools with 3671 undergraduates, the largest in the University of the Aegean. Here also is the Headquarters, the Central Library and the Research Committee of Aegean University. The University of Aegean is housed in privately owned buildings, in rented buildings located in the city centre and in modern buildings on the University Hill.
Refugee camps
By 2015, the city of Mytilene had become a primary entry point for refugees and migrants who seek to pass through Greece to resettle elsewhere in Europe. In 2015, over half a million people arrived in Lesbos.[28] The number of individuals coming through Lesbos has dwindled since the signing of the EU-Turkey deal which restricted the number of refugees that could legally resettle in Europe.[29] As of July 2017, seventy to eighty refugees were still arriving in Greece daily despite the deal and "many of them on Lesbos", according to Daniel Esdras, the chief of the International Organization for Migration.[30]
- Mória Reception & Identification Centre (in Greek : Κέντρο Υποδοχής και Ταυτοποίησης Μόριας), better known as Mória Refugee Camp, or just "Mória", was the biggest refugee camp in Europe.[31] It was located outside the village of Moria (Greek: Μόρια Mória). Enclosed by barbed wire and a chain-link fence, the military camp served as a European Union hotspot camp. It burned down and was permanently closed in September 2020. A new closed reception centre will be built in 2021 at Vastria near Nees Kydonies.[32]
- Kara Tepe Refugee Camp is a camp which has been transformed into a living space for around 700 refugees classified as vulnerable.[33] It will be replaced by a new closed reception centre at Vastria near Nees Kydonies in 2021.[32]
- Pipka camp or Lesbos Solidarity, once a children's holiday camp, aims to support the most vulnerable refugees who pass through Mytilene: families with children, the disabled, women who are pregnant, and the injured. The camp focuses on humanitarian aid and on providing for the various needs of refugees, including food, medical help, clothing, and psychological support.[34]
Sporting clubs
- Aiolikos F.C., football club
- Sappho Lesvou F.C., women's football club
Media
Radio
| Frequency | Name | Year of establishment |
|---|---|---|
| 88,2 MHz | Love Mitilini | 2003 |
| 90,0 MHz | Radio Mytilini | 1989 |
| 91,6 MHz | Rythmos Radio | 2005 |
| 92,3 MHz | First Program | 1938 |
| 92,8 MHz | Aeolos FM 92.8 | 1989 |
| 93,2 MHz | Astra FM 93,2 | 2000 |
| 93,3 MHz | Voice of the Church | 2000 |
| 94,3 MHz | Second Program | 1952 |
| 97,2 MHz | Third Program | 1954 |
| 97,6 MHz | Local 9.72 Mytilini | 1990 |
| 98,6 MHz | Best FM Lesvos | 1992 |
| 99,0 MHz | On the Island 99 FM | 2019 |
| 99,4 MHz | ERT Aegean | 1989 |
| 103,0 MHz | ERT Aegean | 1989 |
| 104,4 MHz | ERT Aegean | 1989 |
| 104,8 MHz | Piraeus Church | 1988 |
| 105,8 MHz | Piraeus Church | 1988 |
| 105,9 MHz | Second Program | 1952 |
| 106,4 MHz | Third Program | 1954 |
| 107,4 MHZ | Piraeus Church | 1988 |
| 107,9 MHz | ERT Sports | 1993 |
TV
A regional television station operates from the city of Mytilene; Aeolos TV.[35]
Notable Mytilenians
Ancient

- Alcaeus (6th century BC), Greek poet.[42]
- Sappho, Ancient Greek Lyric Poet. Plato called her "wise" and "Tenth Muse".
- Pittacus (c. 640–568 BC), one of the Seven Sages of Greece.
- Hellanicus (mid-5th century BC), Greek historian.[43]
- Theophrastus, Ancient Greek philosopher, student of Aristotle.
- Laomedon of Mytilene (4th BC), general of Alexander the Great
- Chares (4th century BC), Greek historian and chamberlain to Alexander the Great.[44]
- Scamon (4th century BC), Greek historian and son of Hellanicus.[45]
- Praxiphanes (4th century BC), Greek philosopher.[46]
- Epicurus, Greek philosopher.[47]
- Aeschines, Greek rhetorician.[48]
- Eunicus, Greek sculptor and silversmith.
- Hermarchus (3rd century BC), Greek philosopher.[49]
- Diophanes (2nd century BC), Greek rhetorician.[50]
- Lesbonax (1st century BC), Greek sophist and rhetorician.
- Archytas of Mytilene, Greek musician
- Crinagoras (70 BC-18 AD), Greek epigrammatist and ambassador, poet of "Palatine Poetry".
- Theophanes, middle of 1st century BC, Greek statesman, close friend of Pompey the Great.[51]
- Potamon (1st century AD), Greek rhetorician.[52]
Medieval
- Santa Thomais (910–1030), nun, philanthropist and healer
- Christopher of Mytilene (11th century), Greek poet.[53]
Modern
- Hayreddin Barbarossa ( 1478–1546), Ottoman admiral
- Oruç Reis (1478–1518), Ottoman bey
- Saint Parthenios (1600–1657), Patriarch of Constantinople and religious martyr
- Palaiologos Lemonis, member of Filiki Etaireia
- Dimitrios Skambas (1992–present), Greek-American financier, youngest Partner at Bannockburn Global Forex in NYC. Parents from Pamfila, Lesvos.
- Theophilos Hatzimihail (c.1870–1934), Greek painter
- P. M. Kourtzis, shipowner, founder of Aegean Steamship Company (1883)
- Gregorios Bernardakis, philologist
- Demetrios Bernardakis, playwright
- Stratis Myrivilis (1892–1969), Greek writer
- Odysseas Elytis (1911–1996), Greek poet, Nobel Laureate in 1979
- Argyris Eftaliotis (1849–1923) (née Cleanthis Michailidis), Greek writer
- Fotis Kontoglou (Aivali/Kydonies, origin from Mytilene) (1895–1965) Greek writer and painter.
- Georgios Jakobides, painter
- Hermon di Giovanno (c. 1900–1968), Greek painter
- Nikos Fermas (1905–1972), Greek actor
- Irini Mouchou (born 1987), triathlete
- Giorgos Mouflouzelis (1912–1991), Greek composer of rebetiko
- Panagiotis Polychronis (1854–1941), Greek artist: photographer, lithographist and painter.
- Leo Rapitis (1906–1957), Greek singer
- Konstantinos Kenteris (born 1973), Greek athlete
- Alexis Panselinos (1903–1984), Greek writer
- Sophocles Vournazos (1853–1889), Greek philanthropist and founder of Mytilene's academic buildings.
- Tériade (1889–1983), Greek art critic, patron, and publisher
- Ahmed Djemal Pasha (1872–1922), Ottoman military leader, perpetrator of the Armenian genocide
- Tamburi Ali Efendi (1836–1902), Turkish musician
- Nicholas Kampas (1857–1932), Greek poet
- Argyris Adalis, architect
- Nicholas Athanasiadis (1904–1990), Greek theatre writer, literature writer, poet.
- Ioannis Hatzidaniel (1850–1912), Greek painter and photographer.
- Solon Lekkas, singer of traditional music from Asia Minor.
- Giannis Bournellis, comedian, actor.
- Christos Touramanis, particle physicist
- Giorgos Vourgoutzis, (born 1991), football player
- Michalis Pavlis (born 1989), football player and coach
- Anastasios Chatzigiovanis, football player
Fictional
- Lysimachus, in Shakespeare's Pericles, Prince of Tyre
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Consulates
In the past the city hosted consulates from different European countries. Currently hosts consulates from the following countries:
Gallery
 Exhibits at the Archaeological Museum of Mytilene
Exhibits at the Archaeological Museum of Mytilene Church of St. Therapon by night
Church of St. Therapon by night The city hall
The city hall Hotel Pyrgos
Hotel Pyrgos Panoramic view
Panoramic view.jpg.webp) Zoodochos Pigi church
Zoodochos Pigi church
.jpg.webp) Street of Mytilene
Street of Mytilene.jpg.webp) Traditional wood carving
Traditional wood carving.jpg.webp) A chapel
A chapel Hotel Olympias
Hotel Olympias Cathedral of Saint Athanasios
Cathedral of Saint Athanasios Belltower of St Athanasius
Belltower of St Athanasius Building of Theofilos art association
Building of Theofilos art association.jpg.webp) Mytilene in snow
Mytilene in snow
See also
References
- "Απογραφή Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2011. ΜΟΝΙΜΟΣ Πληθυσμός" (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority.
- "lesvos pop 2021".
- "Τροποποίηση του άρθρου 1 του ν. 3852/2010" [Amendment of Article 1 of l. 3852/2010] (in Greek). Government Gazette. p. 1164.
- Harbor of Mytilene Archived 2014-08-08 at the Wayback Machine accessed July 31, 2014
- "Mytilene - Asia Minor Coins - Photo Gallery". www.asiaminorcoins.com. Archived from the original on 2018-12-23. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- Bio of Theophrastus accessed December 11, 2007
- Grade Saver bio on Aristotle accessed December 11, 2007
- Thorne, James (2003). Julius Caesar: Conqueror and Dictator. The Rosen Publishing Group. p. 34. ISBN 978-0-8239-3595-6.
- The Syriac Chronicle Known as That of Zachariah of Mitylene accessed July 31, 2014
- Finlay George "History of the Byzantine Empire from 716 – 1057" William Blackwood & Sons, 1853
- Before The Deluge: Jews Of The Mediterranean Islands (Part I) accessed July 31, 2014
- Candiani, Guido (2018-01-02). "A New Battle Fleet: The evolution of the Ottoman sailing navy, 1650–1718, revealed through Venetian sources". The Mariner's Mirror. 104 (1): 18–26. doi:10.1080/00253359.2018.1411096. ISSN 0025-3359. S2CID 165635839.
- "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-21.
- "Detailed census results 1991" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. (39 MB) (in Greek and French)
- "HNMS". Archived from the original on 2010-12-16. Retrieved 2011-04-03. – Hellenic National Meteorological Service
- "MITILINI Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved January 29, 2013.
- "Greeka".
- "Tripadvisor".
- "AegeanVacation".
- "Folk art".
- "Iera Moni".
- "Sappho square".
- "Theofilos".
- "Roman aqueduct". 19 March 2021.
- "Teriade".
- "Ermou".
- "Stoa". 22 February 2017.
- "Refugee Flows to Lesvos: Evolution of a Humanitarian Response". migrationpolicy.org. 2016-01-28. Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- "Q&A: EU-Turkey refugee deal explained". Middle East Eye. Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- (www.dw.com), Deutsche Welle. "Violence becoming commonplace in Moria refugee camp | Germany Guide for Refugees | DW | 21.07.2017". DW.COM. Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- "LESVOS ISLAND - GREECE". UNHCR.
- "Λέσβος / Ετοιμάζουν κλειστή δομή για τους πρόσφυγες στη Βάστρια". Αυγή (in Greek). 2020-11-30. Retrieved 2020-12-16.
- "Lesvos refugee camp transformed by activities, classes, Anthi Pazianou | Kathimerini". Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- "lesvossolidarity.org". www.lesvossolidarity.org. Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- "Aeolos TV".
- "Aeolos".
- "Stonisi".
- "Emprosnet".
- "Lesvosnews".
- "Lesvospost".
- "kalloninews".
- D. Gerber, Greek Lyric I: Sappho and Alcaeus (1982).
- Hellanikos von Mytilene, Die Fragmente der Griechischen Historiker no. 4.
- Chares von Mytilene, Die Fragmente der Griechischen Historiker no. 125.
- Skamon of Mytilene, Brill's New Pauly no. 476.
- F. Wehrli, Phainias von Eresos, Chamaileon, Praxiphanes (1945).
- "Epicurus". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. 2018.
- Diogenes Laertius 2.64.
- F. Longo Aurrichio, Ermarcho. Frammenti (1988).
- Plutarch, Vit. Ti. Gracch. 8.5.
- Theophanes of Mytilene, Brill's New Jacoby no. 188.
- Potamon of Mytilene, Die Fragmente der Griechischen Historiker continued Part IV no. 1085.
- E. Follieri, I calendari in metro innografico di Cristoforo Mitileneo(1980).
- "Αδελφοποιημένες Πόλεις". mytilene.gr (in Greek). Mytilene. Retrieved 2020-01-09.
External links
- Official website (in Greek)
- Calendar of Lesvos
- Tourist Guide of Mytilene-Lesvos (in Greek, English, and Turkish)




.jpg.webp)

