Myrichthys tigrinus
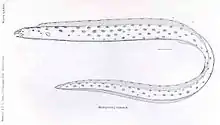
The spotted snake eel (Myrichthys tigrinus), also known as the tiger snake eel or the spotted tiger snake eel,[1] is an eel in the family Ophichthidae (worm/snake eels).[2] It was described by Charles Frédéric Girard in 1859. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Chile, Costa Rica, Colombia, El Salvador, Ecuador, Mexico, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Panama, Honduras, and Peru.[3] It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 60 metres (0 to 197 ft), and inhabits benthic sediments of mud and sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 74 centimetres (29 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 60 centimetres (24 in).[2]
| Myrichthys tigrinus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Anguilliformes |
| Family: | Ophichthidae |
| Genus: | Myrichthys |
| Species: | M. tigrinus |
| Binomial name | |
| Myrichthys tigrinus Girard, 1859 | |
The spotted snake-eel is of no commercial interest to fisheries.[2] Due to its wide distribution in the eastern Pacific, its lack of known threats and lack of observed population decline, the IUCN redlist currently lists the species as Least Concern.[3]
References
- Common names of Myrichthys tigrinus at www.fishbase.org.
- Myrichthys tigrinus at www.fishbase.org.
- Myrichthys tigrinus at the IUCN redlist.
