N-Propyl-L-arginine
N-Propyl-l-arginine, or more properly NG-propyl-l-arginine (NPA), is a selective inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS).[1]
- Zhang, Henry Q.; Fast, Walter; Marletta, Michael A.; Martasek, Pavel; Silverman, Richard B. (1997-11-01). "Potent and Selective Inhibition of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase by N ω -Propyl- l -arginine". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 40 (24): 3869–3870. doi:10.1021/jm970550g. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 9397167.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
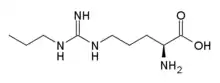
2-Amino-5-[(N'-propylcarbamimidoyl)amino]pentanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H20N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 216.285 g·mol−1 |
| log P | 0.389 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.512 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.485 |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids |
|
Related compounds |
Acecarbromal |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.