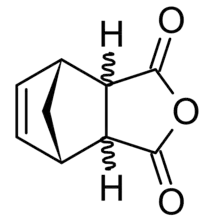
Nadic anhydride
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
24-oxatricyclo[5.2.1.02,6]dec-8-ene-3,5-dione | |
| Other names
5-Norbornene-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride Nadic acid anhydride Himic anhydride (exo) Carbic anhydride (endo) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.416 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 164.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Norbornene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Nadic anhydride, also known as 5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride, is an organic acid anhydride derivative of norbornene.
Stereochemistry
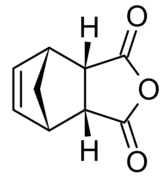
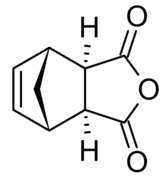
Nadic anhydride exhibits endo-exo isomerism. In the exo isomer, the acid anhydride group points in the same direction towards the bridging carbon of the norbornene, while in the endo isomer the acid anhydride group points in the opposite direction. These isomers are respectively named cis-5-norbornene-exo-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride (also known as himic anhydride) and cis-5-norbornene-endo-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride (also known as carbic anhydride).[1][2] Commercially available nadic anhydride is mainly the endo isomer, as this is the isomer predominantly made in the Diels-Alder reaction in its synthesis.[3]
 |  |
 | 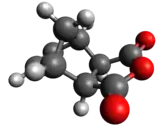 |
| endo | exo |
Preparation
In the patent for the Diels-Alder reaction, nadic anhydride was given as an example of the reaction, made by the condensation of maleic anhydride and cyclopentadiene, which gives mostly the endo isomer.[3] The endo isomer can be converted into the exo isomer by irradiation with UV light.[4]
Uses
Nadic anhydride is used in the synthesis of hydrogel polymers based on thiol-ene linkages.[5] The nadic anhydride is condensed with a multi-arm polyethylene glycol macromer to give a 3- or 4-armed polymer with norbornene ester ends, which can then react with thiol-containing monomers to form a hydrogel.
See also
References
- "cis-5-Norbornene-exo-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride". PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved January 19, 2023.
- "cis-5-Norbornene-endo-2,3-dicarboxylic anhydride". PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved January 19, 2023.
- United States US1944731A, Otto Diels & Kurt Alder, "Organic compound having hydrogenated ring systems and process of preparing it", published January 23, 1934
- Pandey, Bipin; Athawale, Asawar A.; Reddy, Ravinder S.; Dalvi, Pravinder S.; Kumar, Pradeep (1991). "A Remarkably Efficient Photochemical Methodology for Endo to Exo IsomerizatLon of Dials–Alder Cycloadducts". Chemistry Letters. 20 (7): 1173–1176. doi:10.1246/cl.1991.1173.
- Shih, Han; Lin, Chien-Chi (2013). "Visible-Light-Mediated Thiol-Ene Hydrogelation Using Eosin-Y as the Only Photoinitiator". Macromolecular Rapid Communications. 34 (3): 269–273. doi:10.1002/marc.201200605. PMID 23386583.