New methylene blue
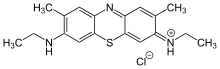
New methylene blue (also NMB) is an organic compound of the thiazine class of heterocycles. It is used as a stain and as an antimicrobial agent. It is classified as an azine dye, and the chromophore is a cation, the anion is often unspecified.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.026.833 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22N3S:SCl ZnCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 484.22 g/mol |
| Melting point | 239 °C (462 °F; 512 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Applications
NMB is a staining agent used in diagnostic cytopathology and histopathology, typically for staining immature red blood cells. It is a supravital stain.[2] It is closely related to methylene blue, an older stain in wide use.
Safety
New methylene blue is toxic. Skin contact or inhalation should be avoided.
See also
References
- Vennerstrom, Jonathan L.; Makler, Michael T.; Angerhofer, Cidy K.; Williams, Jean A. "Antimalarial dyes revisited: xanthenes, azines, oxazines, and thiazine" Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (1995), 39(12), 2671–7. doi:10.1128/AAC.39.12.2671.
- "Reticulocyte Count" (PDF). Prentice-Hall.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.