Niğde Province
Niğde Province (Turkish: Niğde ili) is a province in the southern part of Central Anatolia, Turkey. Its area is 7,234 km2,[2] and its population is 365,419 (2022) of which 170,511 live in the city of Niğde.[1]. The population was 348,081 in 2000 and 305,861 in 1990. Neighbouring provinces are Kayseri, Adana, Mersin, Konya, Aksaray and Nevşehir.
Niğde Province
Niğde ili | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Location of the province within Turkey | |
| Country | Turkey |
| Seat | Niğde |
| Government | |
| • Vali | Cahit Çelik |
| Area | 7,234 km2 (2,793 sq mi) |
| Population (2022)[1] | 365,419 |
| • Density | 51/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| Time zone | TRT (UTC+3) |
| Area code | 0388 |
| Website | www |
The province is surrounded on three sides by mountain ranges: the Taurus Mountains, Mount Hasan, and the Melendiz Mountains.
Districts
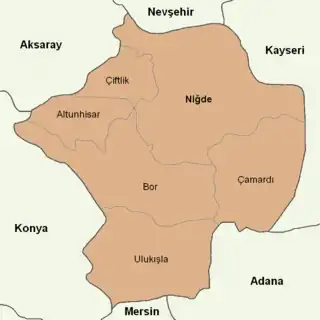
Niğde province is divided into 6 districts (capital district in bold):
Some of the towns within these districts are Bademdere, Bahçeli, Çiftehan, Darboğaz, Fertek and Kemerhisar.
Etymology
Known in antiquity as Nakita or Nahita the name derived from the Iranian goddess Anahita. It has mutated through Nekidâ, Nekide, Nikde and lastly to Niğde by the republican regime of Turkey.
History

The area has been settled since the Neolithic period of 8000-5500 BC, as proved excavations of burial mounds höyük in the district of Bor, and tin mines on the district of Çamardı -Keste. The area was later settled by the Hittites, who lived here for a thousand years up until 800BC. The name Nig˘de first occurs in written sources in the form na-hi-ti-ia in a Luwian inscription of king Saruanis from Andaval as was pointed out by Ignace Gelb (Hittite Hieroglyphs II [1935] pp. 17–18). Then came Assyrians and Phrygians, Greeks, Armenians, Persians, Alexander the Great, Romans, who built the city of Tyana with its palaces and waterworks.
Roman rule persisted from the Eastern capital of Byzantium until the area was occupied by the Seljuk Turks from 1166 onwards. By the early 13th century Niğde was one of the largest cities in Anatolia and a number of impressive mosques and tombs date from this period. The area was brought within the Ottoman Empire in 1471 and thus passed into the territory of the Turkish Republic in the 1920s.
In 2016, archaeologists discovered in Kınık Mound, an archeological site located in Yeşilyurt village of Altunhisar district at Niğde province, a temple dating back to the late Persian era. In 2018, they discovered an ancient Hellenistic temple and a bull statue made from ceramics.[3]
Niğde today

Niğde benefits from its rich agriculture, its apples are particularly famous, and its location between the wealthy regions of Konya and Adana on the Mediterranean coast. Also because the province is near the tourist attractions of Cappadoccia it is close to the airports of Kayseri and Nevşehir.
As well as apples important crops include potatoes, cabbages, grain and sugar beet. Niğde is Turkey's biggest potato growing region and has the most apple trees (although newer plantings in other provinces are achieving greater production).
Meat and dairy are also important activities along with beekeeping and more recently trout farms.
The country's second largest solar farm is in the province.[4]
Niğde has a rich tradition of folk culture including song and dance and the famous proverb (the Turkish equivalent of "the early bird catches the worm") - "Bor's eastern market is over, ride your donkey to Niğde".[5] Another Niğde tradition is to plum someone (Erikletmek) meaning if you have visitors sit them in the garden and fill them up with plums (or other fruit) so you don't have to give them dinner.
As recently as 2020, a 1,600 year-old octagonal church was discovered in the excavations of the ancient city of Tyana.[6]
Places of interest

.jpg.webp)


The Aladağlar and Bolkar mountain ranges in the Taurus mountains are popular for winter sports, climbing and trekking through the high meadows and mountain villages. The mountains are particularly attractive when the hills are covered in spring flowers.
- The Aladaglar mountains in particular are one of the most popular climbing venues in Turkey. Although the Aladaglar mountains border on their namesake Aladağ District, in Adana Province, they are generally reached from the villages of Demirkazık and Çukurbağ in Çamardı.
- The Bolkar mountains have a 7 km ski-run and a crater lake.
- The Melendiz Mountains (Melendiz Dağlar) have an elevation of 2963 meters, or (9721 feet).[7]
Niğde is part of Cappadocia and does attract some tourists to its historical sites, although nothing like as many as the centre of the area in Nevşehir. Sites of historical importance in Niğde include many churches, mosques and underground cities (safe-havens cut deep down into the soft volcanic rock). Another important site is the ancient city of Tyana and a number of Roman waterways in the district of Bor.
An important underground city and ancient monastery is located in Gümüşler, Niğde, called Gümüşler Monastery.
In Ulukışla, Öküz Mehmet Pasha Complex, a külliye is a 17th-century structure.
Niğde also has a number of mineral hot-springs and other attractions, so with a little investment in hotels and other infrastructure the province could attract more tourists than at present.
Churches
- Andaval Church
- Aktaş Church Mosque (Greek Church)
- Fertek Church Mosque
- Prodromos Church
- Yeşilyurt Altunhisar Antik Roma Kilisesi
- Hançerli Church
- Hasaköy Church, formerly known as Aya Makrina
- Konakli, formerly known as St. Basil (St. Demetrius of Misthi) Church
- Kumulca Church Mosque
- Kurdunus (Hamamlı) Church
- Küçükköy Church
- Narli Lake Chapel
- Yeşil Burç Church Mosque
- Dikiltaş (Obelisk) Church
- Balli Church
References
- "Address-based population registration system (ADNKS) results dated 31 December 2022, Favorite Reports" (XLS). TÜİK. Retrieved 19 September 2023.
- "İl ve İlçe Yüz ölçümleri". General Directorate of Mapping. Retrieved 19 September 2023.
- Ancient Hellenistic temple unearthed in central Turkey
- https://balkangreenenergynews.com/turkeys-second-largest-solar-power-plant-is-taking-shape/
- Geçti Bor'un pazarı sür eşeğini Niğde'ye
- "1,600-year-old octagonal church found in Central Anatolia". hurriyetdailynews.com. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- Peakbagger. "Melendiz Daği, Turkey". Retrieved 2004-11-01.
External links
- (in Turkish) Niğde governor's official website
- (in Turkish) Niğde municipality's official website
- (in English) Niğde weather forecast information
- (in English) Niğde University's official website
