Niger Delta Basin (geology)
The Niger Delta Basin, also referred to as the Niger Delta province, is an extensional rift basin located in the Niger Delta and the Gulf of Guinea on the passive continental margin near the western coast of Nigeria[1] with suspected or proven access to Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea and São Tomé and Príncipe. This basin is very complex, and it carries high economic value as it contains a very productive petroleum system. The Niger delta basin is one of the largest subaerial basins in Africa. It has a subaerial area of about 75,000 km2, a total area of 300,000 km2, and a sediment fill of 500,000 km3.[1] The sediment fill has a depth between 9–12 km.[2] It is composed of several different geologic formations that indicate how this basin could have formed, as well as the regional and large scale tectonics of the area. The Niger Delta Basin is an extensional basin surrounded by many other basins in the area that all formed from similar processes. The Niger Delta Basin lies in the south westernmost part of a larger tectonic structure, the Benue Trough. The other side of the basin is bounded by the Cameroon Volcanic Line and the transform passive continental margin.[2]
Basin formation
The Niger Delta Basin was formed by a failed rift junction during the separation of the South American plate and the African plate, as the South Atlantic began to open. Rifting in this basin started in the late Jurassic and ended in the mid Cretaceous. As rifting continued, several faults formed many of them thrust faults. Also at this time syn-rift sands and then shales were deposited in the late Cretaceous. This indicates that the shoreline regressed during this time. Concurrently, the basin had been undergoing extension resulting in high angle normal faults and fault block rotation. At the beginning of the Paleocene there was a significant shoreline transgression.[2] During the Paleocene, the Akata Formation was deposited, followed by the Agbada Formation during the Eocene. This loading caused the underlying shale Akata Formation to be squeezed into shale diapirs. Then in the Oligocene the Benin formation was deposited, which is still being deposited today. The overall basin is divided into a few different zones due to its tectonic structure.[1] There is an extensional zone, which lies on the continental shelf, caused by the thickened crust. Moving basinward is a transition zone, and a contraction zone, which lies in the deep sea part of the basin.
Lithology
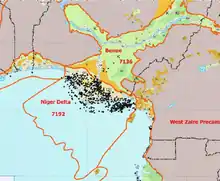
The sediment fill in the Niger Delta basin is characterized by three major depobelts. These three cycles show that the basin experienced an overall regression throughout time as the sediments go from deep sea mud sized grains to fluvial denser sand sized grains. The lithologies of the area experience changes due to several factors. The sediment provenance from the onshore highlands which feed into the delta control the mineralogy of the grains. Additionally, the impact of sea level on sediment deposition is well known; relative sea level will control the basinward extent of lithologies (see sequence stratigraphy). Volcanic activity in the area may also result in thin deposits of ash (bentonite). The early Cretaceous sediments are thought to be from a tide-dominated system that were deposited on a concave shoreline, and throughout time the shoreline became convex and it is currently a wave-dominated system.
- Basement
The oceanic basement rock is the oldest rock in the basin and is basaltic in composition. Also closer to the coast Precambrian continental basement crops out onshore.
- Cretaceous
There is a section of rock in this basin from the middle to late Cretaceous which is poorly understood due to its significant burial depth. It is believed to be composed of sediments from a tide-dominated coastline,[1] and there are believed to be several layers of shales, although their distribution is unconstrained.
- Akata Formation
The Akata Formation is Paleocene in age. It is composed of thick shales, turbidite sands, and small amounts of silt and clay. The clay content resulted in it being a ductile shale formation which was squeezed into shale diapirs in the basin. The Akata Formation formed during lowstands in relative sea level and anoxic conditions. This formation is estimated to be up to 7,000 meters thick.[1]
- Agbada Formation
The Agbada Formation dates back to Eocene in age. It is a marine facies defined by both freshwater and deep sea characteristics. This is the major oil and natural gas-bearing facies in the basin. The hydrocarbons in this layer formed when this layer of rock became subaerial and was covered in a marsh-type environment rich in organic content. It is estimated to be 3,700 meters thick.[1]
- Benin Formation
The Benin Formation is Oligocene and younger in age. It is composed of continental flood plain sands and alluvial deposits. It is estimated to be up to 2,000 meters thick.[1]
Tectonic structures
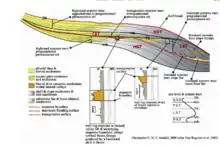
The tectonic structures in the Niger Delta Basin are typical of an extensional rift system, but the added shale diapirism due to loading makes this basin unique. The main method of deformation is gravitational collapse of the basin, although the older faulting and deformation in the basin are related to the continental breakup and rifting of the African plate and South American plates.[1] The overall basin is divided into a few different zones due to its tectonic structure. There is an extensional zone, which lies on the continental shelf, that is caused by the thickened crust. There is a transition zone, and then there is a contraction zone, which lies in the deep sea part of the basin.
- Basin inversion
Basin inversion is caused by uplift and/or compression in this basin. The compression is caused by the toe detachment of the shale diapirs. Basin inversion forms anticline structures, which serve as a great oil trap. Clay smears in the sediments seal the formations so oil does not escape out.[1]
- Basinward dipping reflectors
Basinward dipping reflectors are a common feature of extensional type rift basins. As fault blocks extend they rotate to dip towards the center of the basin. At the top of these fault blocks sub basins can form.
- Shale diapirs
The shale diapirs are from the Akata Formation. This structure is formed due to the improper dehydration of the formation and the over pressuring by the overlying and denser Agbada Formation.[1]
- High-angle normal faulting
High-angle normal faulting is a feature of the extensional portion of the rifting in this basin. It is considered a growth fault and the feature lies closer towards the basins edge and transitions to the toe detachment faulting as you continue down the basin.[3]
Oil and Gas
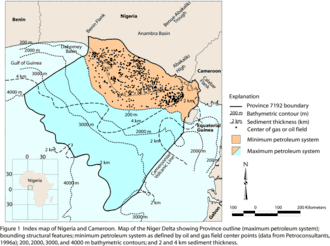
The Niger Delta is the twelfth largest province in the world by known oil and gas resources.[4] The Niger Delta Basin produces around 2 million barrels of oil per day. The entire system is predicted to contain 34.5 billion barrels of oil and 94 trillion feet3 of natural gas. This area is still very heavily explored by oil companies today. It is one of the largest oil producers in the world.[1]
Oil Pollution
Environmental issues in the Niger Delta are caused by its petroleum industry.[5][6][7] The delta covers 20,000 km2 (7,700 sq mi) within wetlands of 70,000 km2 (27,000 sq mi) formed primarily by sediment deposition. Home to 20 million people and 40 different ethnic groups, this floodplain makes up 7.5% of Nigeria's total land mass.[8] It is the largest wetland and maintains the third-largest drainage basin in Africa.[9] The Delta's environment can be broken down into four ecological zones: coastal barrier islands, mangrove swamp forests, freshwater swamps, and lowland rainforests. Fishing and farming are the main sources of livelihoods for majority of her residents.[10]
This incredibly well-endowed ecosystem contains one of the highest concentrations of biodiversity on the planet, in addition to supporting abundant flora and fauna, arable terrain that can sustain a wide variety of crops, lumber or agricultural trees, and more species of freshwater fish than any ecosystem in West Africa.[11]
The advent of oil production has also negatively impacted the Niger Delta region due to unprecedented oil spillage which has been ongoing for the past 5 decades making the region one of the most polluted in the world.[12][13] The heavy contamination of the air, ground and water with toxic pollutants is often used as an example of ecocide.[14][15][16][17] It is estimated that while the European Union experienced 10 incidences of oil spills in 40 years, Nigeria recorded 9,343 cases within 10 years.[18] The carelessness of the oil industry has also precipitated this situation, which can perhaps be best encapsulated by a 1983 report issued by the NNPC, long before popular unrest surfaced:[19]
- We witnessed the slow poisoning of the waters of this country and the destruction of vegetation and agricultural land and good water source by oil spills which occur during petroleum operations. But since the inception of the oil industry in Nigeria, more than fifty years ago, there has been no concerned and effective effort on the part of the government, let alone the oil operators, to control environmental problems associated with the industry.[20]
In July 1979, an incident on the coastal zone of the Forcado tank 6 terminal spilled 570 thousand barrels of oil into the Forcados estuary, affecting the sea species and surrounding swamp forest.[4] In January 1980, the Funiwa No.5 Well in Funiwa Field spilled 421 thousand barrels of oil into the ocean, damaging 836 acres of mangrove forest.[4] In 1983, 5 000 barrels were spilled causing high mortality in crabs, fish and shrimps.[4] Until 1999, an average of 240 thousand barrels of crude oil was spilled in the zone every year.[4]
See also
References
- Tuttle, Michele; Charpentier, Ronald; Brownfield, Michael. "The Niger Delta Petroleum System: Niger Delta Province, Nigeria, Cameroon, and Equatorial Guinea, Africa". United States Geologic Survey. United States Geologic Survey. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- fatoke, oluwaseyi adedamola (2010). sequence stratigraphy of the pliocene-pleistocene strata and shelf-margin deltas of the eastern niger delta, nigeria (ph.d.). university of houston.
- Short, K.C.; Staeuble, A.J. "Outline of geology of Niger delta". AAPG Bulletin. 51 (5): 761–799. doi:10.1306/5d25c0cf-16c1-11d7-8645000102c1865d.
- Tuttle, Michele L. W.; Brownfield, Michael E.; Charpentier, Ronald R. "Niger Delta (Akata-Agbada) Petroleum System OF99-50H, Chapter A". pubs.usgs.gov. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- "Oil and the environment - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". www.eia.gov. Retrieved 2022-05-31.
- Albert, Oshienemen N.; Amaratunga, Dilanthi; Haigh, Richard P. (2018). "Evaluation of the Impacts of Oil Spill Disaster on Communities and Its Influence on Restiveness in Niger Delta, Nigeria". Procedia Engineering. 212: 1054–1061. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2018.01.136.
- "'This place used to be green': the brutal impact of oil in the Niger Delta". the Guardian. 2019-12-06. Retrieved 2022-03-20.
- P.C. Nwilo & O. T. Badejo: Impacts of Oil spills along the Nigerian coast The Association for Environmental Health and Sciences, 2001
- "Conserving and restoring wetlands in Nigeria's Niger River Delta". Wetlands International. Retrieved 2022-02-26.
- Adebayo, Bukola (2019-03-27). "Major new inquiry into oil spills in Nigeria's Niger Delta launched". CNN. Retrieved 2022-03-12.
- "oil spill in Nigeria". 6 January 2012.
- Donatus, Peter (2016-10-15). "Shell's Nigeria ecocide is creating a refugee crisis". www.greenleft.org.au. Retrieved 2023-07-06.
- "UNEP Ogoniland Oil Assessment Reveals Extent of Environmental Contamination and Threats to Human Health". UNEP. 2017-08-07. Retrieved 2023-07-06.
- "'Ecocide' movement pushes for a new international crime: Environmental destruction". NBC News. 2021-04-07. Retrieved 2023-07-06.
- "Fighting ecocide in Nigeria". theecologist.org. 5 February 2014. Retrieved 2023-07-06.
- "UNPO: Ogoni: An Ecocide in the Making?". unpo.org. Retrieved 2023-07-06.
- "How an ecocide law could prevent another Nigerian oil disaster". The Guardian. 2011-08-22. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2023-07-06.
- Albert,Amaratunga, Haigh (Nov 29,2017) "Evaluation of the Impacts of oil spill Disaster on communities and its influence on Restiveness in Niger Delta, Nigeria."
- Osemwengie, Garrick (2010-03-05). "As Goodluck would have it:Theophilus Danjuma ! His $500 Million Booty & $100 million Donation to Charity". Sahara Reporters. Retrieved 2022-03-20.
- Vidal, John (2010-05-30). "Nigeria's agony dwarfs the Gulf oil spill. The US and Europe ignore it". The Observer. Retrieved 27 July 2010. government's National Oil Spill Detection and Response Agency (Nosdra) says that between 1976 and 1996 alone, more than 2.4m barrels
- Ayanlade, Proske (August 31, 2015)."Assessing wetland degradation and loss of ecosystem services in the Niger Delta, Nigeria."
- Ayanalde,Proske (August 31, 2015). "Assessing wetland degradation and loss of ecosystem services in the Niger Delta, Nigeria."
External links
- The Niger Delta Petroleum System: Niger Delta Province, Nigeria, Cameroon, and Equatorial Guinea, Africa, United States Geological Survey, 1999
- Regional Geology and Petroleum Prospectivity, Nigeria - São Tomé and Príncipe Joint Development Zone (JDZ)