Nitrourea
Nitrourea is a strong high explosive compound[1] synthesized by the nitration of urea or by way of a dehydration reaction of urea nitrate.[2]
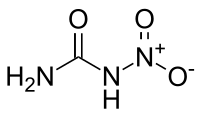 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Nitrourea | |
| Other names
N-Nitrocarbamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.314 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C1H3N3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 105.05 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.73 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 155°C (decomposition) |
| Soluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone Slightly soluble in benzene and chloroform |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | Medium |
| Friction sensitivity | Low |
| Detonation velocity | 6860 |
| RE factor | 1.01 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Urea nitrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "Nitrourea". CAMEO Chemicals. NOAA. 2.4.
- Ingersoll, A. W.; Armendt, B. F. (1925). "Nitrourea". Organic Syntheses. 5: 85.; Collective Volume, vol. 1, p. 417
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.