Natangians
Natangians or Notangians (Prussian: Notangi; Polish: Natangowie; Lithuanian: Notangai; German: Natanger) was a Prussian clan, which lived in the region of Natangia, an area that is now mostly part of the Russian exclave Kaliningrad Oblast, whereas the southern portion lies in the Polish Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship.
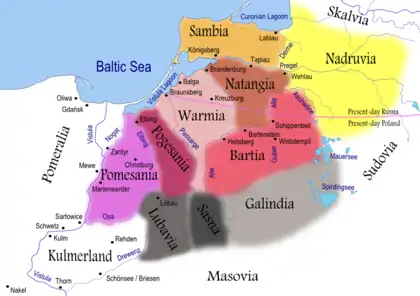 Natangians (in brown) and other Prussian clans in the 13th century | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| Extinct in 17th–18th century | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Languages | |
| Old Prussian, later also German | |
| Religion | |
| Prussian mythology (Paganism) | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other Prussians and Balts |
In the 13th century when the Teutonic Knights began their crusade against the Prussians, some 15,000 people might have lived in the area between the Pregolya and Łyna rivers.[1] The Natangian lands bordered with Sambia in the north, Warmia in the west and south, and Bartia in the southeast.[2] They likely spoke a West Baltic language, now extinct, similar to Old Prussian language.
History
Natangians are first mentioned in a 1238 treaty between the Knights and Duke Świętopełk II of Pomerania.[1] They were conquered by the Teutonic Knights around 1239–1240.[2] In order to prevent the Natangians from liberating themselves from Teutonic rule, the Teutonic Order erected the Kreuzburg Castle in Natangia.[2] The Treaty of Christburg of early 1249, which assured personal freedom to newly converted Christians, included Natangians. However, the treaty failed to address the underlying causes of the conflict, and Natangians massacred 54 knights in the Battle of Krücken in November 1249.[3] But the victory was short-lived, the Knights regained their strength in just two years and continued their crusade. In 1255 they built Königsberg (now Kaliningrad) at the mouth of Pregolya river, right on the border between Natangia and Sambia.
During the Great Prussian Uprising (1260–1274), the Natangians elected Herkus Monte, who was educated in Germany, as their chief. At first he was successful and defeated the Knights in the Battle of Pokarwis and Battle of Löbau. However, the rebels were unable to capture the brick castles built by the Knights and were defeated. Herkus, who had been one of the most prominent leaders of the Prussians, was captured and hanged in 1273. The Natangian nobles submitted to the Germans, who promised privileges and undisturbed ownership of their estates. Natangians, led by Sabynas and Stanta, rebelled for the last time in 1295.[1] In 1454, the region was incorporated by King Casimir IV Jagiellon to the Kingdom of Poland.[4] After the subsequent Thirteen Years' War, the longest of all Polish–Teutonic wars, since 1466, it formed part of Poland as a fief held by the Teutonic Order,[5] and after 1525 held by secular Ducal Prussia.
When German colonists settled in the area, the Natangians kept their local language and customs up until the 17th century. Later on, their identity disappeared by the end of the 17th century or the beginning of the 18th century as they merged with the German population, but the local populace still defined themselves as "Natangians" up to 1945 and even the local newspaper of Landsberg (Górowo Iławeckie) was called "Natanger Zeitung" after 1919. [6]
References
- Simas Sužiedėlis, ed. (1970–1978). "Notanga". Encyclopedia Lituanica. Vol. IV. Boston, Massachusetts: Juozas Kapočius. pp. 101–102. LCCN 74-114275.
- Słownik geograficzny Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich, Tom VI (in Polish). Warszawa. 1885. p. 931.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Urban, William (2000). The Prussian Crusade (2nd ed.). Chicago, Illinois: Lithuanian Research and Studies Center. p. 242. ISBN 0-929700-28-7.
- Górski, Karol (1949). Związek Pruski i poddanie się Prus Polsce: zbiór tekstów źródłowych (in Polish). Poznań: Instytut Zachodni. p. 54.
- Górski, p. 96–97, 214–215
- W. Reichermann, "Ut Noatange - Plattdütsche Spoasskes", Königsberg 1892, In Natangen - Ein Bildband, Kreisgemeinschaft Pr. Eylau, Verden 1986