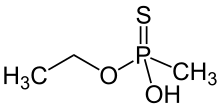
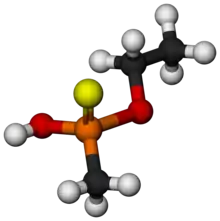
O-Ethyl methylphosphonothioic acid
O-Ethyl methylphosphonothioic acid (EMPTA) is an organophosphate compound. A dual-use chemical, it has constructive uses in the synthesis of pesticides and pharmaceuticals, and it is also a precursor in the synthesis of nerve agents such as Agent VM and Agent VX. The detection of EMPTA is cited as a major influence in the United States' 1998 decision to destroy the Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory in Sudan.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
O-Ethyl hydrogen methylphosphonothioate | |
| Other names
Methyl-phosphonothioic acid O-ethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.755 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9O2PS | |
| Molar mass | 140.14 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Claudine McCarthy (2005). "EMPTA (O-Ethyl methylphosphonothioic acid)" (Google Books excerpt). In Eric Croddy, James J. Wirtz (ed.). Weapons of mass destruction: an encyclopedia of worldwide policy, technology, and history. Bloomsbury Academic. pp. 123–124. ISBN 1-85109-490-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.