Obafluorin
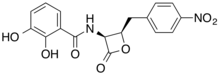
Obafluorin is a β-lactone antibiotic with the molecular formula C17H14N2O7.[1][2] Obafluorin is produced by the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens.[3] Obafluorin is a inhibitor of serine hydroxymethyltransferase.[4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3-dihydroxy-N-[(2R,3S)-2-[(4-nitrophenyl)methyl]-4-oxooxetan-3-yl]benzamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H14N2O7 | |
| Molar mass | 358.306 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Scott, Thomas A.; Batey, Sibyl F.; Wiencek, Patrick; Chandra, Govind; Alt, Silke; Franklyn, Christopher S.; Wilkinson, Barrie (17 July 2019). "Self-immunity guided identification of threonyl-tRNA synthetase as the molecular target of obafluorin, a β-lactone antibiotic". bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/704981. S2CID 201196822.
- Tymiak, Adrienne A.; Culver, Catherine A.; Malley, Mary F.; Gougoutas, Jack Z. (December 1985). "Structure of obafluorin: an antibacterial β-lactone from Pseudomonas fluorescens". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 50 (26): 5491–5495. doi:10.1021/jo00350a010.
- Wells, J. Scott; Trejo, William H.; Principe, Pacifico A.; Sykes, Richard B. (1984). "Obafluorin, a novel β-lactone produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Taxonomy, fermentation and biological properties". Journal of Antibiotics. 37 (7): 802–803. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.37.802. PMID 6432765.
- Prasad, Neha (18 April 2015). "Obafluorin: A Potential Inhibitor of Serine Hydroxymethyl Trasferase [sic]". Undergraduate Research Symposium Posters.
Further reading
- "Next antibiotic may come from dirt bacteria". Futurity. 2 August 2019.
- Scott, Thomas A.; Heine, Daniel; Qin, Zhiwei; Wilkinson, Barrie (26 June 2017). "An L-threonine transaldolase is required for L-threo-β-hydroxy-α-amino acid assembly during obafluorin biosynthesis". Nature Communications. 8 (1): 15935. doi:10.1038/ncomms15935. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 5490192. PMID 28649989.
- Herbert, Richard B.; Knaggs, Andrew R. (1992). "Biosynthesis of the antibiotic obafluorin from D-[U-13C]glucose and p-aminophenylalanine in Pseudomonas fluorescens". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1 (1): 103–107. doi:10.1039/P19920000103. ISSN 1364-5463.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.