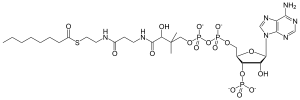
Octanoyl-CoA
Octanoyl-coenzyme A is the endpoint of beta oxidation in peroxisomes. It is produced alongside acetyl-CoA and transferred to the mitochondria to be further oxidized into acetyl-CoA.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3′-O-Phosphonoadenosine 5′-{(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-[(3-{[2-(octanoylsulfanyl)ethyl]amino}-3-oxopropyl)amino]-4-oxobutyl dihydrogen diphosphate} | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methyl} O3-{(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-[(3-{[2-(octanoylsulfanyl)ethyl]amino}-3-oxopropyl)amino]-4-oxobutyl} dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | |
| MeSH | octanoyl-coenzyme+A |
PubChem CID |
|
| Properties | |
| C29H50N7O17P3S | |
| Molar mass | 893.732 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
- Caprylic acid, the eight-carbon saturated fatty acid known by the systematic name octanoic acid.
References
- Grevengoed TJ, Klett EL, Coleman RA (2014-07-17). "Acyl-CoA metabolism and partitioning". Annual Review of Nutrition. 34 (1): 1–30. doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-071813-105541. PMC 5881898. PMID 24819326.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.