Olibanic acid
Olibanic acid is an organic compound that is naturally found in frankincense. Even though it is present in smaller concentrations than other components, it has a highly potent odor and is believed to be one of the key components responsible for the distinctive smell of frankincense. Both the (1S,2S)-(+)-trans and (1S,2R)-(+)-cis enantiomers are present and have similar but not identical "old church"-like odors.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
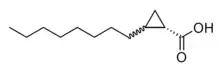
2-octylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O2 | |
| Molar mass | 198.306 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Cerutti-Delasalle C, Mehiri M, Cagliero C, Rubiolo P, Bicchi C, Meierhenrich UJ, Baldovini N (October 2016). "The (+)-cis- and (+)-trans-Olibanic Acids: Key Odorants of Frankincense". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 55 (44): 13719–13723. doi:10.1002/anie.201605242. hdl:2318/1609095. PMID 27699963.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.