Organocadmium chemistry
Organocadmium chemistry describes the physical properties, synthesis, reactions, and use of organocadmium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to cadmium chemical bond.[1] Cadmium shares group 12 with zinc and mercury and their corresponding chemistries have much in common. The synthetic utility of organocadmium compounds is limited.
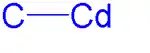
The simplest organocadmium compound is dimethylcadmium. It is a linear molecule with a C-Cd bond length of 213 pm.[2] Organocadmium compounds are typically sensitive to air, light, and moisture.
Synthesis
Dimethylcadmium and diethylcadmium were reported in 1917 by Erich Krause. In general, they are prepared by transmetalation or by an exchange reaction between an alkylating agent and a cadmium salt.[3]
According to one procedure, diethylcadmium is produced the reaction of cadmium bromide with two equivalents of the Grignard reagent ethylmagnesium bromide in diethyl ether. Diethylcadmium is a colorless oil with melting point −21 °C. Diphenylcadmium can be prepared by the reaction of phenyllithium with cadmium bromide. Diphenylcadmium is a solid with a melting point of 174 °C.
Fluoroalkyl and alkenyl derivatives
Following established trends, perfluorinated alkyl and alkenyl derivatives of cadmium exhibit improved thermal stability. The alkenyl derivatives are generated by the addition of iodotrifluoroethylene to cadmium metal.[4]
Reactions
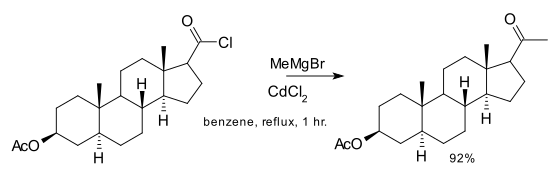
Organocadmium compounds are less nucleophilic than the organozincs. This reduced reactivity is demonstrated in the conversion of acyl chlorides to ketones with these reagents.[5] This reaction was reported by Henry Gilman in 1936 and was used until less toxic cuprates were available. The related Grignard reagent would react further, giving to the tertiary alcohol. Methyl cadmium was used in one of the steps leading to cholesterol total synthesis:[6]
Another synthetic use of an organocadmium is the reaction of diisoamylcadmium with β-carbomethoxypropionyl chloride to methyl 4-keto-7-methyloctanoate without reacting further with the ketone group or the ester group.[7]
This selectivity is observed provided that the reaction is carried out salt free.[8] When the cadmium reagent is generated in situ from a cadmium salt, the halide generates a more nucleophilic organocadmium reagent, an ate complex. The same salt effect can be observed with organozinc compounds.
Dimethylcadmium has been used to synthesize colloidal nanocrystals of II-VI materials such as cadmium selenide. Its toxic and volatile nature has led researchers to look elsewhere for cadmium precursors such as cadmium oxide.[9]
Toxicity
Cadmium compounds are toxic. Dimethylcadmium is toxic to the kidney, the liver, the central nervous system, and the respiratory organs when inhaled.[10] Cadmium compounds in general are considered to be carcinogen to humans by the IARC.[11]
References
- Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry Vol 5, Copper, Silver, Gold, Zinc, Cadmium, and Mercury W.A. Herrmann Ed. ISBN 3-13-103061-5
- Felix Hanke; Sarah Hindley; Anthony C. Jones; Alexander Steiner (2016). "The Solid State Structures of the High and Low Temperature Phases of Dimethylcadmium". Chemical Communications. 52 (66): 10144–10146. doi:10.1039/c6cc05851e. PMID 27457504.
- Erich Krause (1917). "Einfache Cadmiumdialkyle. (I. Mitteilung über organische Cadmium-Verbindungen.)". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 50 (2): 1813–1822. doi:10.1002/cber.19170500292.
- Burton, Donald J.; Yang, Zhen-Yu; Morken, Peter A. (1994). "Fluorinated organometallics: Vinyl, Alkynyl, Allyl, Benzyl, Propargyl and Aryl". Tetrahedron. 50 (10): 2993–3063. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)81105-4.
- David A. Shirley (2011). "The Synthesis of Ketones from Acid Halides and Organometallic Compounds of Magnesium, Zinc, and Cadmium". Org. Reactions: 28–58. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or008.02. ISBN 9780471264187.
- Woodward, R. B.; Sondheimer, Franz; Taub, David; Heusler, Karl; McLamore, W. M. (1952). "The Total Synthesis of Steroids". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 74 (17): 4223–51. doi:10.1021/ja01137a001.
- Cason, James; Proutyear=1948, Franklin S. (1948). "Methyl 4-Keto-7-Methyloctanoate". Organic Syntheses. 28: 75. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.028.0075.
- Jones, Paul R.; Desio, Peter J. (1978). "The less familiar reactions of organocadmium reagents". Chemical Reviews. 78 (5): 491–516. doi:10.1021/cr60315a001.
- Peng ZA, Peng X (2001). "Formation of high-quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals using CdO as precursor". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 123 (1): 183–4. doi:10.1021/ja003633m. PMID 11273619.
- Spiridonova EIa (1991). "[Experimental study of toxic properties of dimethylcadmium]". Gigiena Truda I Professional'nye Zabolevaniia (in Russian) (6): 14–7. PMID 1916391.
- "Cadmium and Cadmium compounds". Arsenic, Metals, Fibres and Dusts. International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2012. pp. 121–145. ISBN 9789283201359.