Orthoacetic acid
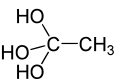
Orthoacetic acid or ethane-1,1,1-triol is an hypothetical organic compound with formula C
2H
6O
3 or H3C-C(OH)3. It would be an ortho acid with the ethane backbone.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethane-1,1,1-triol[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 78.067 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Orthoacetic acid is believed to be impossible to isolate, since it would readily decompose into acetic acid and water. It may have a fleeting existence in aqueous solutions of acetic acid.[2]
Orthoacetate anions
The three hydroxyls of CH3C(OH)3 could be deprotonated, leading successively to CH3C(OH)2(O–) (dihydrogenorthoacetate), CH3C(OH)(O–)2 (hydrogenorthoacetate), and finally CH3C(O–)3 (orthoacetate).
Orthoacetate esters
There are many stable organic compounds with the trivalent moiety H3CC(OR)3, which are formally esters of orthoacetic acid and called orthoacetates. They include trimethyl orthoacetate and triethyl orthoacetate, which are commercially available.
See also
References
- "Ethane-1,1,1-triol - PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- Yamabe, Shinichi (2003). "A computational study of interactions between acetic acid and water molecules". Journal of Computational Chemistry. 24 (8): 939–947. doi:10.1002/jcc.10178. PMID 12720314. S2CID 6096517.