Oxo-Diels–Alder reaction
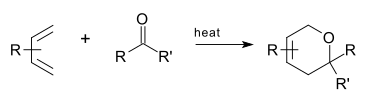
An oxo-Diels–Alder reaction (also called an oxa-Diels–Alder reaction) is an organic reaction and a variation of the Diels–Alder reaction in which a suitable diene reacts with an aldehyde to form a dihydropyran ring. This reaction is of some importance to synthetic organic chemistry.
| Oxo-Diels–Alder reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Otto Diels Kurt Alder |
| Reaction type | Cycloaddition |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000310 |
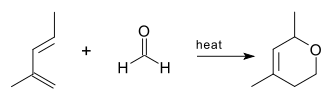
The oxo-DA reaction was first reported in 1949[1] using a methylpentadiene and formaldehyde as reactants.
Asymmetric oxo-DA reactions (including catalytic reactions) are well known.[2] Many strategies rely on coordinating a chiral Lewis acid to the carbonyl group.
References
- A Diels–Alder Type Reaction with Formaldehyde Thomas L. Gresham, Thomas R. Steadman J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1949, 71 (2), pp 737–738 doi:10.1021/ja01170a101
- Tetrahedron Report number 869 Asymmetric hetero-Diels–Alder reactions of carbonyl compounds Helene Pellissier Tetrahedron 65 (2009) 2839–2877 doi:10.1016/j.tet.2009.01.068
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.