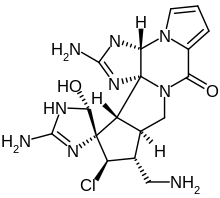
Palau'amine
Palau'amine is a toxic alkaloid compound synthesized naturally by Stylotella agminata, a species of sea sponge found in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The name of the molecule derives from the island nation of Palau, near which the sponges are found.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3aR,4′R,5′S,10aS,11S,12S,13aS,13bR)-2,2′-Diamino-11-(aminomethyl)-12-chloro-5′-hydroxy-1,1′,3a,5′,10a,11,12,13a-octahydro-8H,10H-spiro[cyclopenta[3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]imidazo[4,5-b]pyrrolo[1,2-d]pyrazine-13,4′-imidazol]-8-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C438976 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H22ClN9O2 | |
| Molar mass | 419.87 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
The substance was first isolated and described in 1993.[1] Containing nine nitrogen atoms, the molecule is considered highly complex. The precise atomic structure was pinned down in 2007,[2] and two years later the molecule was synthesized in the lab of Phil Baran at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California.[3][4] Early efforts towards its synthesis were directed at a misassigned structure featuring a cis- rather than trans-5/5 ring fusion, an error that was made because the trans-5/5 ring system is some 6 kcal/mol less stable than the cis-configured system.[5]
Biomimetic synthesis
Based on the hypothesized biosynthesis of palau'amine, a proposed pathway to this dimeric pyrrole-imidazole alkaloid includes a key oxidation of a β-ketoester with manganese(III) acetate to initiate a cascade radical cyclization, producing an ageliferin skeleton.[6]
Biological effects
Palau'amine is a proteasome inhibitor.[7]
References
- Kinnel, Robin B.; Gehrken, Henning Peter; Scheuer, Paul J. (1993). "Palau'amine: a cytotoxic and immunosuppressive hexacyclic bisguanidine antibiotic from the sponge Stylotella agminata". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 115 (8): 3376–3377. doi:10.1021/ja00061a065.
- Halford, Bethany (2007). "Sponge Alkaloids: Palau'amine Reconsidered". Chemical & Engineering News. 85 (10): 12. doi:10.1021/cen-v085n010.p012a.
- Seiple, Ian B.; Su, Shun; Young, Ian S.; Lewis, Chad A.; Yamaguchi, Junichiro; Baran, Phil S. (2010). "Total Synthesis of Palau'amine". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 49 (6): 1095–8. doi:10.1002/anie.200907112. PMC 3367661. PMID 20041464.
- Madrigal, Alexis (2010-01-14). "Bizarre Sea Sponge Compound Finally Synthesized by Humans". Wired. Retrieved 2010-01-15.
- Usami, Yoshihide (2009-07-13). "Recent Synthetic Studies Leading to Structural Revisions of Marine Natural Products". Marine Drugs. 7 (3): 314–330. doi:10.3390/md7030314. ISSN 1660-3397. PMC 2763102. PMID 19841716.
- Ma Z, Lu J, Wang X, Chen C (Jan 7, 2011). "Revisiting the Kinnel–Scheuer hypothesis for the biosynthesis of palau'amine". Chem Commun. 47 (1): 427–9. doi:10.1039/c0cc02214d. PMC 2999656. PMID 20848010.
- Lansdell, T. A; Hewlett, N. M; Skoumbourdis, A. P; Fodor, M. D; Seiple, I. B; Su, S; Baran, P. S; Feldman, K. S; Tepe, J. J (2012). "Palau'amine and Related Oroidin-alkaloids Dibromophakellin and Dibromophakellstatin Inhibit the Human 20S Proteasome". Journal of Natural Products. 75 (5): 980–5. doi:10.1021/np300231f. PMC 3367325. PMID 22591513.