Palazzo Antonini, Udine
Palazzo Antonini also known as Palazzo Palladio and Palazzo Antonini-Maseri (after 2018), is a palazzo in Udine, northern Italy. It was designed by Italian Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio in the middle of the 16th century for the Antonini family, owner of various other palaces in Udine.

The present owner is the University of Udine.
History
The beginning of construction on the Palazzo Antonini is traditionally said to date to 1556, contemporaneous with the construction of the Bollani arch, another work by Palladio in Udine. The patron was Floriano Antonini, a young and ambitious member of one of the most high-profile families of Udine aristocracy. Antonini did not hesitate to resurrect erudite traditions by minting a foundation medal for the Palazzo, probably desiring to demonstrate that sophisticated taste was not the exclusive prerogative of aristocratic circles in the capital of the Serenissima, Venice.[1] In 1559, the palace was already partially inhabitable, but in 1563 building works were still in progress.
In the following century, at least two campaigns of works heavily altered the building's appearance, going so far as to replace all the windows, except those to the right of the loggia on the back façade, as well as the internal staircases. In 1709, Martino Fischer executed the decorative ornaments, thereby contributing to the definitive transformation of the original Palladian interiors. In essence, all that remains of Palladio's project are the plan (less the stairs) and the building's basic volumes, the front and back loggias (whose pediments were never executed), and the components of the "Hall of the four columns".
The architect Valentino Presani supervised a reorganisation of the entire building during the 19th century. During this reorganisation, Odorico Politi painted the neoclassical-styled fresques in the rooms facing the garden (1818 ca.).[2]
The garden was supervised by Pietro Quaglia da Polcenigo and Giuseppe Rho.[3] One of the first California redwoods arrived in Italy was planted in the garden in 1867 and is still living today.[4]
In the 1930s, the building became the location of the Treasury of the Bank of Italy.
The 1976 Friuli earthquake left the building partially damaged, so the paintings were removed from the walls and placed on wooden supports.
In 2009, the Bank of Italy left the building to the local Museum network Civici Musei di Udine.[5] So the paintings were placed in the local art gallery (Biblioteca d'Arte dei Civici Musei).
For some years, it seemed impossible to find a proper placement for the building. In 2018, dr Attilio Maseri, famous cardiologist based in Udine, purchased it and donated it to the University of Udine.[6] After the donation, the building was officially renamed "Palazzo Antonini-Maseri".[7]
Architecture
This project opens the section in the I quattro libri dell'architettura (1570) dedicated to city palaces although, as was the opposite case in the Villa Pisani at Montagnana and the Villa Cornaro at Piombino, the Palazzo Antonini was actually a rather ambivalent building: it is truly an urban palace which assumes the typology of a suburban villa. In this respect, one must bear in mind that the palace rose on the borders of the urban centre, in an open area with gardens, just like the Palazzo Chiericati or the Palazzo Civena.
The design of its façades facing the street incorporates engaged Ionic half-columns, fashioned from blocks of stone, which forecast those at the Villa Sarego at Santa Sofia. A thick web of openings transforms the loggia onto the street into a sort of diaphragm transparent to the light. The entire edifice seems to be strapped by continuous bands of stone, from the plinth of engaged columns to the entablature, right up to the band corresponding to the upper frieze, where the small unframed windows of the granary open.
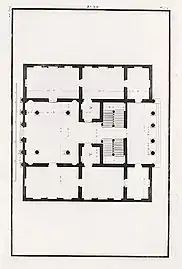 Floor plan (drawing by Ottavio Bertotti Scamozzi, 1781)
Floor plan (drawing by Ottavio Bertotti Scamozzi, 1781)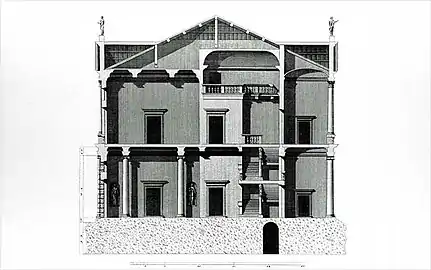 Cross section (drawing by Ottavio Bertotti Scamozzi, 1781)
Cross section (drawing by Ottavio Bertotti Scamozzi, 1781)
References
- Palazzo Antonini, Banca d'Italia website (in Italian)
- Palazzo Antonini, Banca d'Italia website (in Italian)
- Progettato da Andrea Palladio è l'edificio più prestigioso della famiglia Antonini, Udine Vicina, 2015 (in Italian)
- Progettato da Andrea Palladio è l'edificio più prestigioso della famiglia Antonini, Udine Vicina, 2015 (in Italian)
- Palazzo Antonini, Banca d'Italia website (in Italian)
- Palazzo Palladio appartiene all'Università di Udine, University of Udine, 2019 (in Italian)
- Palazzo Palladio appartiene all'Università di Udine, University of Udine, 2019 (in Italian)
External links
- Palazzo Antonini in the CISA website (source for the first revision of this article, with kind permission)
- Historical photo of the interior
