Paleoophiocordyceps
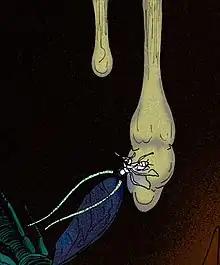
Paleoophiocordyceps coccophagus is an extinct parasitic fungus in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae from Cretaceous-aged Burmese amber.[1] P. coccophagus' morphology is very similar to the species of Ophiocordyceps. The only known specimen consists of two whip-like fruiting bodies emerging from the head of a male scale insect of an undescribed species very similar to the extinct species Albicoccus dimai.
| Paleoophiocordyceps | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Subdivision: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Paleoophiocordyceps Sung, et al., 2008 |
| Species: | P. coccophagus |
| Binomial name | |
| Paleoophiocordyceps coccophagus Sung, et al., 2008 | |
References
- Sung GH, Poinar GO Jr, Spatafora JW (2008). "The oldest fossil evidence of animal parasitism by fungi supports a Cretaceous diversification of fungal–arthropod symbioses". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 49 (2): 495–502. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2008.08.028. PMID 18817884.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.