Paleoshoreline
A paleoshoreline (ancient shoreline) is a shoreline that existed in the geologic past. (Paleo is from an ancient Greek word meaning "old" or "ancient".)[1] A perched coastline is an ancient (fossil) shoreline positioned above the present shoreline.
Tides cause the ocean to advance and recede in a very short time scale, in most places about twice per day. Weather conditions can also cause short-term variations. Coastlines can also move by coastal erosion without a change in sea level. However, "sea level" refers to the average level over a relatively long period (years). This average sea level can advance and recede over much longer periods (thousands or millions of years), causing paleoshorelines which may be difficult to identify.
Just off the coast of parts of North America, in the last 15,000 years sea level has varied from over 100 metres (330 ft) below, to as high as 10 metres (33 ft) above its present level. That entire time, humans have lived in North America.[2]
A lake may also have a paleoshoreline.[3][4]
Paleoshorelines have also been inferred on Mars;[5][6] see Burgsvik Beds and Martian dichotomy.
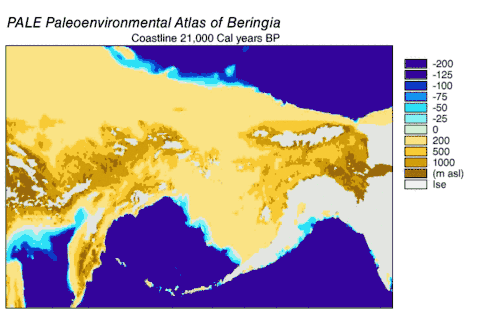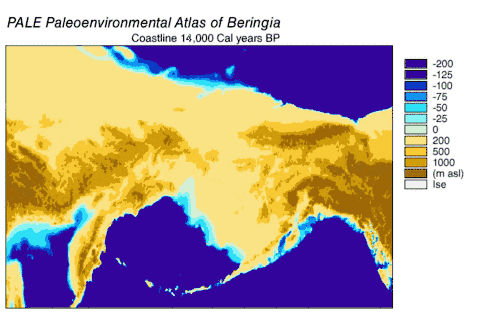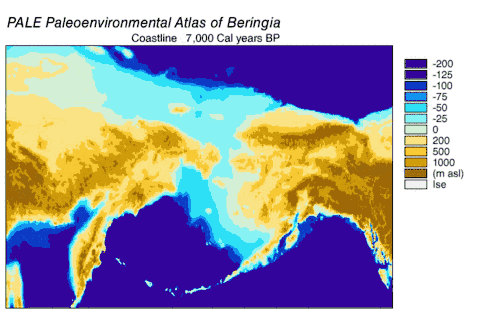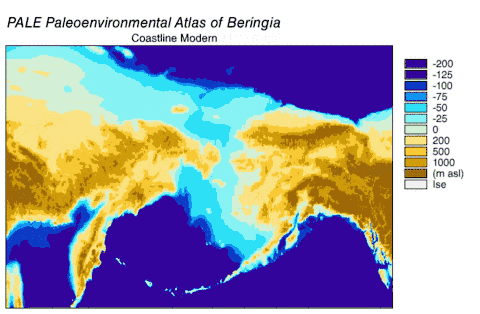
Scientific importance
Paleoshorelines capture valuable records of environmental change and can tell us about modern shelf ecosystems. These structures can indicate distributions of seabed features that are habitats of marine life; they may also reveal the location of coastal resources once used by humans, of archaeological significance.[7]
Examples
- The Bering Land Bridge once stood above water, and the commonest explanation of early human presence in the Americas is that the Native Americans came over this land bridge. Now it is under water.[2]
- Once Doggerland, an area of the North Sea, stood above water, connecting Great Britain to the rest of Europe.[8]
- In a sudden event, the 1700 Cascadia earthquake caused the coastline of what are now British Columbia, Washington, Oregon and north California to "drop several feet".[9]
- In Asia, the Yonaguni Monument, a submerged rock formation near the Ryukyu Islands, once stood above sea level; whether the formations are human-made is still argued.[10]
See also
References
- "paleo-". dictionary.com. Retrieved 2020-12-31.
- "Paleoshoreline Research".
- Komatsu, Goro (2001). "Paleoshoreline geomorphology of Böön Tsagaan Nuur, Tsagaan Nuur and Orog Nuur: the Valley of Lakes, Mongolia". Geomorphology. 39 (3–4): 83–98. Bibcode:2001Geomo..39...83K. doi:10.1016/S0169-555X(00)00095-7. Retrieved 2021-01-01.
- Egger, A.E. (December 2012). "Paleoseismology from Paleoshorelines: Combining Lidar Data and Geochronology to Resolve Displacement of Pleistocene Pluvial Shorelines along Normal Faults in the Northwestern Basin and Range". AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts. 2012. Bibcode:2012AGUFMPP11A2003E. Retrieved 2021-01-01.
- Erkeling, Gino (November 20, 2015). "Paleoshoreline". Encyclopedia of Planetary Landforms. pp. 1501–1507. Bibcode:2015epl..book.....H. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-3134-3_248. ISBN 9781461431343. Retrieved 2020-12-29.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - Ruiz, Javier (November 20, 2003). "Should Paleoshorelines of ancient Martian Oceans be close to present-day equipotential Surfaces?". Proceedings of the Third European Workshop on Exo-Astrobiology. 545: 281. Bibcode:2004ESASP.545..281R.
- Barrett, Katherine (June 7, 2017). "Paleoshorelines, Time capsules of the ocean's ancient shorelines". Oceanbites. Retrieved 2020-12-29.
- "Doggerland - The Europe That Was". Retrieved 2020-12-31.
- "Cascadia Subduction Zone". oregon.gov. Retrieved 2020-12-31.
- Ryall, Julian (19 September 2007). "Japan's Ancient Underwater "Pyramid" Mystifies Scholars". nationalgeographic.com. Retrieved 2020-12-31.
External links and references
- Paleoshoreline research
- Paleoshoerlines of Pacific islands
- Paleoshorelines off Australia
- Shelf sand supply determined by glacial-age sea-level modes, submerged coastlines and wave climate
- Paleoshorelines off Tonga
- Paleoshoreline evidence for postglacial tilting in Southern Manitoba
- Paleoshorelines of Florida, USA
- Submerged Shorelines in the Southern California Borderland
- Paleoshorelines of Mono Lake, California, USA