Pancharatha
A Hindu temple is a pancharatha when there are five ratha (on plan) or paga (on elevation) on the tower of the temple (generally a shikhara).[1] The rathas are vertical offset projection or facets. The name comes from the sanskrit Pancha (=five) and Ratha (=chariot), but the link with the concept of chariot is not clear.

Drawing of a pancharatha building
There are also temples with three rathas (triratha), seven rathas (saptaratha) and nine rathas (navaratha).[1]
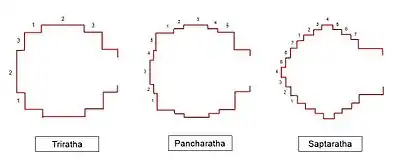
Triratha, Pancharatha and Saptaratha
Examples of pancharatha temples
- Lingaraja Temple in Bhubaneswar
- Lakshmana Temple in Khajuraho
- Rajarani Temple in Bhubaneswar
- Jagannath Temple in Puri, Odisha
- Jagannath Temple in Baripada, Odisha
- Jagannath Temple in Nayagarh, Odisha
- Isanesvara Siva Temple in Bhubaneswar
- Mukteswar Temple in Bhubaneswar
- Brahmani temple in Baleswar, Odisha
Pancharatha temples
 Isanesvara Siva Temple in Bhubaneswar
Isanesvara Siva Temple in Bhubaneswar Jagannath Temple in Baripada
Jagannath Temple in Baripada Lingaraja Temple in Bhubaneswar
Lingaraja Temple in Bhubaneswar
Notes
- "Temple Architecture of Orissa". Archived from the original on 2012-10-13. Retrieved 2012-10-05.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.