Parischnogaster nigricans serrei
Parischnogaster nigricans serrei is a hover wasp subspecies in the family Vespidae, and it is predominantly found in the Java region of Indonesia. Its nest cells are of conical structure, linearly attached to a string-like substratum. The nests are typically found in places open to human interactions, such as gardens, trees, or forests around villages. There is a clear dominance hierarchy within colonies, which often affects the behavioral activities of its members. The wasp’s most common predators are Vespa tropica, also known as the great banded hornet. P. nigricans serrei defends itself by flying away or giving out alarm calls.
| Parischnogaster nigricans serrei | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Vespidae |
| Genus: | Parischnogaster |
| Species: | P. nigricans |
| Subspecies: | P. n. serrei |
| Trinomial name | |
| Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Buysson, 1905) | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Taxonomy and phylogenetics
Studies investigating the biology and social behavior of subfamily Stenogastrinae wasps have begun since the early 20th century, but some of their unusual morphological and ethological traits make it hard for them to have a specific systematic allocation in the phylogenetic tree. These wasps also vary a significant degree in terms of social organization since there are some species that show a rather primitive social life while some display complex, socially dependent behaviors. Consequently, Van der Vecht classifies them as members of the subfamily of the family Eumenidae, while Carpenter considers them to be included in the family Vespidae along with Euparaginae, Masarinae, Eumeninae, Polistinae and Vespinae.[1] Therefore, studying subfamily Stenogastrinae species has long been regarded as a way to investigate the evolution of social life in Hymenoptera due to the wide spectrum of eusociality displayed in their wasps.[2]
Description and identification
Morphology
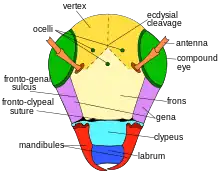
Parischnogaster wasps are typically 10mm long with a sub-triangular shaped head. P. nigricans serrei has a pretty uniform facial coloration, though females have more evident facial markings than males. Regarding species-specific exocrine glands, tegumental glands are clustered around the anterior part of the third gastral tergum. Additionally, male wasps have three white stripes on their tergites, which is associated with patrolling and mating behavior, but females do not display such morphological features.[3] Males of the species can be differentiated from Parischnogater jacobsoni, their closest cousin, because male P. nigricans serrei wasps lack a knife-like spine in the center of the clypeus.[4]
Nesting
The wasp often cohabits with humans; its nests are typically found in gardens, on trees, or remains of forests around villages. Its nest structure is also rather simple; it typically has conical cells attached in a linear fashion along a string-like substructure. Materials used are exclusively of plant origin, and abandoned cells are often recycled for building new cells or enlarging existing, active cells. The nest substructure can be made up of a wide variety of materials. Some nests have been found to be attached onto plant stems, lichens, veins of dead leaves, roots, or even iron threads, cords, and electric wires. It is easy to find conical cells in pairs, and they are typically built in slight rotation relative to the previous one.[2]
Distribution and habitat
Parischnogaster nigricans serrei has been identified in the village of Tegallega, near Bogor, and in the western part of the Java Island of Indonesia. It is not disturbed by human interactions, so its nests are often found close to civilization and human dwellings.[2] This kind of habitat choice is rather unique of P. nigricans serrei (along with Parischnogaster mellyi), since Stenogastrinae species are rarely populated in areas disturbed by human contact and civilization.[5]
Colony cycle
There are five distinct stages in the colony cycle of P. nigricans serrei: The pre-emergence period can be subdivided into two stages (foundation and initial nest), and the post-emergence period into three stages (young colony, middle-aged colony, and mature colony).[1]
- Foundation: It often marks the period between the start of the first cell by a foundress and its closure. Nests are typically found by a foundress who waits a few days before laying its first egg, and after doing so, she builds an ant guard a few centimeters above the first cell. Foundresses frequently reuse old, abandoned nests, and this leads to a number of foundresses living in the same nest for a short period of time.
- Initial nest: When the first larva fully matures, the foundress closes the cell with identical material as the ones the original walls are made with. During this stage, the foundress limits her foraging activity and stops collecting nest material, and thus spends more time on the nest.
- Young colony: After approximately 45–50 days from the start of the foundation stage, the first imago, which is usually a female, appears on the nest. During the first week, the foundress is the one foraging and acquiring food, but afterwards, the role reverses and the daughter is the one who forages and spends a considerable amount of time away from the nest. Female imagines (plural form of imago) that emerge later in the stage help their mother foundress rearing the brood, usually through active foraging.
- Middle-aged colony: The first male usually appears after 3 to 5 females emerge in a nest. At least the first male in a given colony is a direct offspring of the foundress, and it emerges around the same time the first female emerges. The males are also very loyal to their native nests and are typically aggressive in soliciting food from the foragers.
- Mature colony: This stage can be defined as a point in time in which there is a break in growth in cell number (and thus the population on the nest). Therefore, an equilibrium between the number of emerging and disappearing individuals is established. If there are either fewer females than males present on a given nest, the number of cells is greater than 24, or the total number of adults is more than 10, one can say that a certain colony of P. nigricans serrei is mature.
Behavior
Elementary behaviors
Elementary behaviors described in this section pertain to behavioral activities that are common to both males and females in a given colony.[3]
- Resting: Males and females spends about half of the time resting, being completely inactive with their bodies slightly raised or flattened against the substructure of the nest. Abdominal regions are distended or slightly bent, wings are low and joined, and antennae are wide apart. Rarely do the wasps rest inside the cells, but commonly do so in between cells and ant guards. Alpha females prefers resting in the vicinity of the central cells and in the zone near the ant guards. Desire for such positions could be related to nest defense.[6]
- Grooming: In some nests, grooming activity is predominantly seen around the time of sunset. P. nigricans serrei typically clean their entire body, usually beginning with hind legs, abdomen, and wings.[6]
- Flight: Flight of any Parischnogaster species features complicated hovering and quick changes in terms of flight direction. With such high motility, females are able to forage small prey from webs and males can perform their aerial ritual by displaying their three abdominal stripes. Their legs are also kept very closely to their body and the abdomen is fully extended during a typical flight.[3]
Extranidal behaviors
Extranidal behavior described in this section pertains to particular behavioral activities that specifically occur outside the nest that are common in both adult males and females in a given colony. Foraging and patrolling also constitute extra behavior, but they are discussed in more detail in patrolling behavior and diet and foraging activity.[2]
- Pulp Collection: Pulp is collected mainly for constructing nests, and this kind of activity is present in foundation, young and middle-aged colonies, but not very much in initial and mature colonies. This is partly due to the fact that nest construction is absent in initial nest stage and mature colonies typically reuse and recycle old cell material. Pulp collection activity reaches its peak in early morning, and it often occurs after water collection.
- Rest outside of the Nest: Female and male wasps also often rest outside of nests on roots or leaves. Various individuals interact with each other but no particular behavior has been recorded.
- Defecation: Wasps of subfamily Stenogastrinae defecate by rubbing the tip of their abdomen to the nest substructure, leaving the feces there. Since no fecal remnants are found in nests, one can assume that this activity happens externally. This extranidal defecation has been considered to be helpful in maintaining nest cleanliness and hygiene.[2]
Patrolling behavior
Patrolling activity is one of the characteristic behavioral features of P. nigricans serrei, and similar to P. mellyi; displaying their abdominal white stripes while hovering is frequently observed.[7] However, unlike P. mellyi, they hover vertically the majority of the time instead of making horizontal shifts. A male wasp is able to switch around between multiple landmarks, and this can lead to conflicts with other male patrollers. If a landmark is already taken by a male, the newcomer hovers a couple inches behind the owner, and the owner responds by quickly distending its gaster. This display of the gaster often results in the newcomer leaving the landmark, but it can also lead to start of a contest. A typical contest usually involves a tandem flight where the two males ascend, suddenly changing position (the owner goes behind and vice versa), displaying their abdominal stripes, and eventually clashing until one of them surrenders and leaves the landmark. Towards the end of the daily period of patrolling, fewer males are left hovering the landmark, and usually those who remain till the very end are the ones who won the most contests. Male P. nigricans serrei leave their nests around 1pm, and a typical patrolling session ends around two hours after departure.[3]
Ant guard construction
Ant guards are special umbrella-like structures that are built for defending against ants. Ant guard development begins around the first couple days, after the construction of the first cell, and it is typically built from material excreted from the tip of a female gaster. Small droplets of the guard material are collected on the hind legs, and they are rubbed against the extremity of the distended abdomen. Afterwards, the droplets are transferred to the middle legs, and ultimately to the mouth of the wasp. The female then applies the substance onto the nest by licking and simultaneously moving it around the structure of the guard without losing contact. This entire sequence, which lasts around 30–40 seconds, is repeated for 10–30 minutes and only takes places in the late afternoon before sunset.[8]

Social organization
A female typically founds a colony and eventually surrounds herself with four males. Those males are very loyal to the nest and aggressively attack any other males that attempt to approach the nest. Most of their time is spent protecting the cell and grooming. While interactions between individuals within a given nest differ in intensity, both males and females usually tend to avoid interacting with each other.[9] However, even with the limited interactions among individuals, there is a wide range in the degree of aggression the wasps express. While dominant individuals walk on the nest in a straight line, with their abdomen fully distended, subordinates contrastingly give in to the dominants and move around the nest. Studies have shown the existence of a distinct social caste organization in P. nigricans serrei through a clear differentiation between a rather aggressive dominant alpha female and a subordinate female in the majority of mature colonies. A close-to linear dominance hierarchy has been observed in respect to the degree of aggression. Only alpha females show aggression towards other nest mates, which are quieter and more reserved in interacting with each other. Multiple research studies have shown a positive correlation both between female ovarian development (in terms of head width and mean oocyte length) and hierarchical status and between time spent on the nest and hierarchical position.[6] In other words, while the dominant alpha female has the most developed ovaries and is present in the nest for the majority of the time, subordinate females have smaller ovaries and are often absent from the nest, typically engaging in foraging activities.[9]
Caste differentiation
Caste differentiation refers to the process of phenotypic variation between reproductively active and inactive individuals. Such differentiation can be further divided into imaginal (behavioral or physiological differences) or pre-imaginal (morphological differentiation before maturation), but as of now, pre-imaginal differences have not been found in hover wasp species. All females are typically totipotent, meaning that all females in a given colony have an equal potential of mating, developing ovaries and laying eggs. However, in the case of P. nigricans serrei, females can vary in terms of the timing of fertilization and the onset of ovarian development.[3] For instance, while the role of a sterile worker is temporary, fertilized females can continue foraging while still having small ovaries. The trend of females with large ovaries mating sooner could be how sterile workers evolved when the period of virginity endured indefinitely.[1] Such differentiation can be regarded as a “demographic predisposition” for a more complicated sociality in P. nigricans serrei. In other words, it would have been more beneficial for the colony to have those with delayed reproductive activity to function as helpers of the nest rather than have them to wait for full ovarian development and found their own colonies.
Division of labor
There exists a division of labor in respect to one’s position in the dominance hierarchy. Typical behaviors of an alpha female include egg-laying, aggression, and protection of the nest against predators. Subordinates, however, focus primarily on foraging for their colony. Additionally, dominant females devote most of their time to resting in their nest, but often showed patrolling and inspecting behaviors in the morning. On the other hand, subordinates would inspect the cells in the evening as they return to the nest from foraging. Both females contributed equally in terms of larval feeding, ant guard building, and nest construction.[6]
With larvae (larval care)
Cell inspection, which includes care for larvae, is one of the most common activities of Parischnogaster males and female wasps. Larvae usually feed on liquid drops regurgitated by females. The females acquire these drops from solid food, which includes various arthropods caught from spider webs, that is then chewed on by adult females for a considerable amount of time. At the start of an adult-larva interaction, a female contacts the larva along its ventral bend with its mouthparts and the larva responds to her solicitations of either food or care by opening themselves up like sphincters. Unlike other social wasps, adult P. nigricans serrei wasps barely use their antennae by keeping them apart and only touch the sides of the larva. Food pellets are typically placed inside the larva, which remains curled up without any stimulation from the parent. Adult wasps without food can stimulate larvae in the same fashion and larvae will react in the same way by relaxing and opening up. In this case, the adult wasps can remove the food pallets if they have not been eaten by the larvae and may eat them themselves, or transport them to another larva.[3][10]
Abdominal secretion collection and oviposition
Parischnogaster nigricans serrei exhibit similar egg deposition behaviors as other Parishnogaster species such as P. alternata. Abdominal secretion from the Dufour’s gland is characterized by egg-sized white, jelly-like droplets, and it has been observed to play an important role during oviposition (attaching the egg to the bottom of the cell). The wasp collects this gelatinous material while placing its posterior and middle legs on the nest with its gaster bent towards the mouth. The anterior legs are then used to roll these droplets into a bolus that emerges at the tip of its gaster, and the gaster is moved back and forth towards the mouth. Such movement is more frequent at the initial stage of the collection but gradually slows down as the size of the bolus increases. When the collection is complete, the wasp places the bolus in the bottom of the cell.
Egg laying in the Stenogastrinae hover wasps is quite unique, and it consists of three distinct phases: In the first stage, as discussed before, the female ventrally bends her gaster towards the mouth and collects the abdominal secretion. After some time, the wasp emits an egg with its mandibles and places it in the cell by adhering it to the patch of the secretion. The wasp then collects more gelatinous secretions and adds it on top of the egg so they can be used as a source of food for the larva.[9]
Individual life history
A typical colony of P. nigricans serrei starts with a female, and a male usually emerges as a fourth or a fifth adult in a given colony. All females mate roughly around 20 to 50 days after emerging into a nest, and fertilized females tend to have more developed ovaries than unfertilized ones in the same age range. This could potentially mean that females with more developed ovaries search for mating possibilities earlier or that mating leads to faster ovarian development. However, there is a general trend of bigger ovary size with greater age. A graphical model created by Turillazi for P. nigracians serrei showed the emergence of three to four females before the production of a first male, and the females departed from the colony as soon as their ovaries were fully developed. From field data and dissection studies, it is estimated that this process takes around 80 days. This model also predicts the full development of a colony to be completed in around 450 days. However, this data needs to be modified with other external factors by taking issues into consideration, such as predation and social factors that can affect the leaving and staying of female wasps.[3]
Interaction with other species
Diet and foraging activity
A number of Stenogastrinae species have shown foraging behaviors through plucking small arthropod preys off of spider webs; this holds true for P. nigricans serrei as well. Females can hover the webs without touching the threads and can pick the prey with their legs and mandibles. Their prey usually consists of flies, mosquitoes, termites, and spiders. In captivity, P. nigricans serrei have been reported to have easily plucked off small crickets or flies (typically Drosophilae), which were attached to the windows of a cage with drops of honey when they were captured. P. nigricans serrei also cut the prey up into small pieces with their mandibles when it was too big, and they often have shown chewing/ cutting behavior during flight, even before reaching the nest. Foraging behavior reaches its peak around mid-morning, decreases in the afternoon, and increases again before off-the-nest activities end. Maximum foraging activity typically occurs in middle-aged colonies and minimally in young, initial colonies. Additional sources of nourishment include eggs and larvae in nests of conspecifics (including Parischnogaster mellyi) that are left unguarded by foundresses.[2]
Predation
It has been observed that the Greater Banded Hornet, Vespa tropica, often preys on colonies of P. nigricans serrei by destroying cells to remove fully grown larvae and pupae. Adult P. nigricans serrei do not show resistance to such attacks and often abandon the colony, returning when the raid ceases. Additionally, nests with high larval and pupal populations exhibit a higher rate of consecutive attacks by the hornets. Predation by ants has also been observed, but the damage caused by ant raids are not as severe or as frequent as those by hornets.[1]
Defense
The main defense mechanism against vertebrate predators is flight; the wasps rarely sting. After leaving the nest, P. nigricans serrei return when it is apparent that everything is calm and the nest is clear of any predators by hovering before landing. On the other hand, they defend themselves against ants and conspecific predators by eliciting alarm reactions. Soon after detecting an ant on a nest, the wasps begin buzzing their wings, patrolling the nest, and then move quickly towards the ant, grasp it, and throw it to the ground. Nest patrolling and wing buzzing typically continue after the ant is gone. Additionally, when a conspecific predator approaches a nest, it has been observed that females will leave their nest to contact the nonresidents in flight and then quickly return to the colony for protection.[6]
References
- Turillazzi, S (1985). "Colonial cycle of Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Du Buysson) in West Java (Hymenoptera Stenogastrinae)". Insectes Sociaux. 32 (1): 43–60. doi:10.1007/bf02233225. S2CID 3257651.
- Turillazzi, S (1983). "Extranidal behaviour of Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Du Buysson) (Hymenoptera, Stenogastrinae)". Zeitschrift für Tierpsychologie. 63: 27–83. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0310.1983.tb00738.x.
- Turillazzi, S. (2012). The Biology of Hover Wasps. Florence: Springer.
- Turillazzi, Stefano (1988). "Social biology of Parischnogaster Jacobsoni (Du Buysson) (Hymenoptera Stenogastrinae)". Insectes Sociaux. 35 (2): 133–43. doi:10.1007/BF02223927. S2CID 31886145.
- Hansell, M. H. (1981). "Nest construction in the subsocial wasp Parischnogaster mellyi (Saussure) Stenogastrinae (Hymnoptera)". Insectes Sociaux. 28 (2): 208–216. doi:10.1007/BF02223706. S2CID 27763458.
- Turillazi, S.; Pardi, L. (1982). "Social behavior of Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Hymenoptera: Vespoidea) in Java". Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 75 (6): 657–664. doi:10.1093/aesa/75.6.657.
- Turillazi, S.; Calloni, C. (1983). "Tegumental glands in the third gastral tergites of male Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Du Buysson) and P. mellyi (Hymenoptera Stenogastrinae)". Insectes Sociaux. 30 (4): 455–460. doi:10.1007/bf02223976. S2CID 44242843.
- Turillazi, S.; Pardi, L. "Ant guards on nests of Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Du Buysson) (Stenogastrinae)". Monitore Zoologico Italiano. 15: 1–7.
- Pardi, L.; Turillazzi, S. "Behaviour and social organization of Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Du Buysson) (Hymenoptera Vespoidea)". Monitore Zoologico Italiano. 15: 322–323.
- Turillazi, S (1985). "Brood reading behaviour and larval development in Parischnogaster nigricans serrei (Du Buysson) (Hymenoptera Stenogastrinae)". Insectes Sociaux. 32 (2): 117–127. doi:10.1007/bf02224227. S2CID 12925949.