Partial password
A partial password is a mode of password authentication intended to make keystroke logging and shoulder surfing less effective.[1]
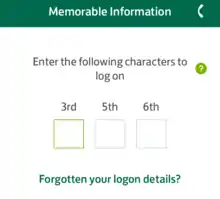
By asking the user to enter only a few specific characters from their password,[2] rather than the whole password, partial passwords help to protect the user from password theft. As only part of the password is revealed at once it becomes more difficult to obtain the password using techniques such as keystroke logging or shoulder surfing.
A paper by David Aspinall and Mike Just describes partial password implementations and attacks in a detailed study.[1]
Tested with 110,000 simulations using passwords longer than 8 characters long, Junade Ali has noted:[3]
- 58% of passwords are revealed in entirety after 7 logins, 90% after 12 and 99% after 19 logins.
- Using a dataset of 488,129 breached passwords, 58% of tested 3-character password segments were only valid for that password in the database. Additionally, 28% could be associated with only one other password and 8% with two other passwords.
Verifying partial passwords
It is considered good practice to not store passwords in plaintext.[4] Instead, when checking a whole password, it is common to store the result of passing the password to a cryptographic hash function. As the user does not supply the whole password, it cannot be verified against a stored digest of the whole password. Some have suggested storing the digest of each combination of letters that could be requested, but they note that this results in generating and storing a large amount of digests.[5][6] A better solution in terms of storage space and security is using a secret sharing scheme.[6][7]
References
- ""Give Me Letters 2, 3 and 6!": Partial Password Implementations & Attacks" (PDF). Retrieved 2015-10-14.
- "What is partial password verification?". The Co-operative Bank. Archived from the original on 2011-06-28. Retrieved 2011-03-03.
- "Banking-Grade Credential Stuffing: The Futility of Partial Password Validation". The Cloudflare Blog. 20 December 2018.
- Password storage
- "Partial Passwords and Keystroke Loggers". Retrieved 2011-03-03.
- "Partial Passwords Done Right". Retrieved 2022-12-30.
- Update to Partial Passwords