Parvocellular cell
Parvocellular cells, also called P-cells, are neurons located within the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. "Parvus" is Latin for "small", and the name "parvocellular" refers to the small size of the cell compared to the larger magnocellular cells. Phylogenetically, parvocellular neurons are more modern than magnocellular ones.
| Parvocellular cell | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Location | Lateral geniculate nucleus |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroLex ID | nifext_43 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Function
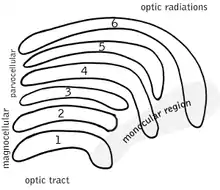
The parvocellular neurons of the visual system receive their input from midget cells, a type of retinal ganglion cell, whose axons comprise the optic tract. These synapses occur in one of the four dorsal parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The information from each eye is kept separate at this point, and continues to be segregated until processing in the visual cortex. The electrically-encoded visual information leaves the parvocellular cells via relay cells in the optic radiations, traveling to the primary visual cortex layer 4C-β. The parvocellular neurons are sensitive to colour,[1] and are more capable of discriminating fine details than their magnocellular counterparts. Parvocellular cells have greater spatial resolution, but lower temporal resolution, than the magnocellular cells.
See also
References
- Xu X, Ichida JM, Allison JD, Boyd JD, Bonds AB, Casagrande VA (February 2001). "A comparison of koniocellular, magnocellular and parvocellular receptive field properties in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus)". J. Physiol. 531 (Pt 1): 203–18. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0203j.x. PMC 2278453. PMID 11179404.