Public involvement (UK health initiative)
Public involvement (PI, formerly PPI, for Public and Patients' Involvement), in the context of health and care research, is the term for involving lay people (members of the general public, including patients and those close to them) as volunteers in influencing and shaping research.[1] It is a worldwide initiative to give the public an effective, active role in health and care research. The term "health and care" covers healthcare (medical care), public health, and social care. The purpose is to align research more closely with patients' and the public’s needs, skills and experience and thereby increase its success and cost-effectiveness.
PI is the proper term [2] for the involvement in research of anyone not professionally interested or experienced in health and care. (People with a professional background in these fields have plenty of chance to engage in such research.)
Still sometimes used is PPI, public and patients' involvement. The bodies concerned, NIHR and INVOLVE, have used PI rather than PPI since 2017, most notably in the UK Standards for Public Involvement.[3]
Origins and funding
Public involvement in UK health and care research is the last active remnant of the National Health Service Reform and Health Care Professions Act 2002 (Part 1, Section 5).[4] The Act set up a Commission for Patient and Public Involvement in Health with a remit to move towards lay people's involvement in all aspects of health and care. The Commission had no funding, however, and closed in 2008. The Commission was replaced with a structure of 151 'Local involvement networks'; these had good funding and much the same aims - but were themselves abolished in 2013.
The UK's major funder of health and care research is the state-funded National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) - the research arm of the National Health Service. There are corresponding but subordinate organisations in Northern Ireland,[5] Wales[6] and Scotland.[7]
NIHR claims to “[involve] patients and the public in all our work”.[8] In the context of PI, however, until 2019, as important was an offshoot of NIHR called 'INVOLVE', set up in 1996 and absorbed piecemeal into NIHR in late 2020. One of the aims of this advisory body was “to support active public involvement in NHS, public health and social care research”.[9] NIHR set up the Centre for Engagement and Dissemination in 2020 as a successor of INVOLVE.[10]
A number of key British medical bodies, such as the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)[11] and the Medical Research Council,[12] have adopted formal policies for public involvement.
The mention of the UK's National Health Service has led to uncertainty whether or not there need be public involvement other than in state-funded health and care research. However, by 2020, a number of privately funded studies had started to have PI, some co-funded with NIHR and some with a charity. By 2017 most charities involved in UK health and care research had active public involvement staff and committees, with hundreds, even thousands of PI volunteers. For instance, Parkinson's UK says "Everything we do [in research] is driven by people affected by Parkinson's."[13] Also, the larger health / care charities in particular have increasing interest in public involvement with commercial research. By 2019 too, NIHR had started to research working with the private sector on health and care research, with public involvement. By the end of 2020, they had set up the first five Patient Recruitment Centres (PRCs) which are the first ″NIHR-funded research facilities to be 100% dedicated to delivering late-phase commercial research″.[14]
Even so, as of 2020, there is meaningful (and, therefore, effective) public involvement in only a small proportion of health and care research. That's mainly because, however much good will there may be, PI is still very new and uncoordinated, and any organisation wanting to take it on properly needs a large number of volunteers.
Other relevant public sector health and care research organisations in the UK are:
- The regulatory Health Research Authority (HRA), whose home page says "we involve patients and the public in [our] work to improve health research design, delivery and regulation."[15]
- The Medical Research Council (MRC), which has an Ethics regulation and public involvement committee.[16]
Also, despite NIHR’s example, there are many different models of public involvement in health and care research. Increasingly, public involvement in research is expected and even demanded by those funding it. However, as of 2022, not all funders even ask researchers applying for support to say what PI they've had and how much they plan. Effective PI is anticipated at all stages, from initial twinkles in researchers' eyes to the final dissemination of outcomes.[17]
The 'patient' in PI
The word “patient” appears explicitly in PPI, and remains implicit in PI. This is because it is known that involving people in research about a specific health condition or care situation who have (or have had) direct first-hand experience will demonstrably improve that research.[18] Therefore, “patients” has come to mean: patients and ex-patients, as well as their carers, ex-carers and others close to them; all are members of the public.
The 'public' in PI
As well as "patients", public here is those lay people who do not necessarily have any direct stake in the research itself, but may have a particular interest in the outcomes of that research or who volunteer in the health and/or care research sectors. Professionals such as doctors, nurses, care-home staff and medical researchers have plenty of opportunity to be involved in research, therefore they are explicitly excluded from public involvement in this context.[19] However, such professionals who also have lived experience of a given condition may be able to offer valuable public involvement.
The charity Parkinson’s UK has a national Involvement Steering Group and a number of regional ones. One of the members’ roles is to “look for opportunities to raise the profile of Parkinson’s UK as leaders in involvement”.[20]
Levels of involvement

Members of the public can have a role in health and care research in three broad levels. (This classification[21] follows the eight-rung ladder of citizen participation.[22])
- Participation - the most common level, where research happens one-way on or to people (eg as patients or controls). Participation in research appears as the broad base of the involvement triangle. This is because most people with any role in health and care research are research participants (subjects).
- Engagement - where researchers communicate and describe their work to the public. This can happen in many ways. For instance, if research is not yet complete, a research team may describe their thinking, progress and interim findings. If research is complete, the team may report to a public audience or disseminate findings by press release. Even plays have been put on to explain serious medical issues to lay audiences.[23] For a given research study, engagement is often part of the role of the people involved in that study in the PI sense.
- Involvement - where members of the public have an active role and close contact with the research team. INVOLVE said “public involvement in research [is] research being carried out ‘with’ or ‘by’ members of the public rather than ‘to’, ‘about’ or ‘for’ them.”[24]
There may be hundreds of volunteers in an involvement group or network, with several central full-time staff and/or volunteers working to make them an effective team. For instance, the Alzheimer's Society Research Network has several hundred volunteer members and two staff facilitators; their website lists some fifteen roles for the PI members.[25] The Society spends over £10 million a year on funding research; the Network costs perhaps a quarter of a million pounds a year. There is, however, some commercial sponsorship, for instance from a care home group and a pharma firm for the most recent pre-covid annual conference.
Reporting
Despite the increased demand for public involvement in health and care research, concerns have been expressed at the variable quality of feedback coming from that involvement. In 2017 new guidance was provided in an attempt to address this issue.[26][27] At around the same time, NIHR published the first draft of the UK Standards for Public Involvement.[3]
One of the six standards concerns getting to know the impact of public involvement: "To drive improvement, we capture and share the difference that public involvement makes to research." (That is from the 2018 version; the final, 2019, version is somewhat less clear: "Seek improvement by identifying and sharing the difference that public involvement makes to research.")
Impact relates to PI effectiveness (quality). Indeed, it can lead to cost-effectiveness, important as PI can cost as much as 10% of some research budgets. Knowledge of PI impact has several levels:
- recognising that PI makes a positive difference in specific ways;
- assessing the difference caused by PI (mainly qualitatively, but in some cases semi-quantitatively);
- measuring the difference so we can indeed get a grip on the effectiveness of PI in a given context.
Of course, it's not possible actually to "measure" PI impact, ie the difference it makes. This is because it is not possible to compare a study with PI with exactly the same study without. PI impact "capture" covers just levels 1 and 2 above, therefore; however, it is still important.
An overview of the subject of PI impact was published by the UK's Alzheimer's Society in 2018.[28]
Involvement in the research cycle
Apart from cost, there are few reasons why all stages of health and care research should not involve the public. NIHR’s PPI Framework 2015-2018 states: “We ensure that processes are in place to involve the public in all stages of the research we fund and manage … guaranteeing the involvement of patients, carers and members of the public at all points in the research process.”[29] In any event, effective PI can lead to more effective research and that should save money, much by cutting waste. This includes the huge cost of failed research and studies not completed.
Broadly speaking, research – of any kind, not just for health or care – is problem-solving. Once a problem is precisely defined, solving it uses the problem-solving cycle. The research cycle of the scientific method works in the same way.
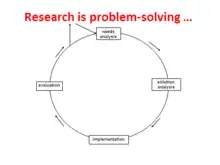
Needs analysis (or problem analysis) is that first stage of defining precisely the problem to be researched: the research question. The next stage – which can take months – is to define precisely the apparently best and most appropriate solution: the research method. Only after this can the research team apply for funding. Public involvement can have much impact throughout this stage, up to helping with the funding bid and even having a presence at interviews at ethics and funding interviews.
Implementation is the main part of the cycle – carrying out the study's research and analysing the results. This may take a couple of years. Again, there's a major role for PI - for at least one or two PI reps or even a PI panel that meets, say, quarterly, with one or two members on the study's management group.
When implementation is over, the research team should evaluate the outcomes. Evaluation means checking with care that they have solved the problem, ie answered the research question asked. There can be many reasons for failing at this stage. In scientific research (science) and inventing (technology), the people concerned go round and round the cycle until they succeed. In other words, they return to needs analysis to tweak the research question, then to solution analysis to tweak the research method, and so on. One of the problems with much of health and care research is that the study runs out of funded time so evaluation can be hasty, and re-cycling is left out. The team leaves the cycle top left and goes on to the stages of reporting and disseminating. Or not, if the study failed to meet its objectives (or even came up with the "wrong" answers). There are many causes of research failure; PI helps reduce them. Note that the rigidity of funding's so often being for three or four years not only increases the chance of failure. It makes it less likely that high-risk, high-reward research is funded and that a failing study can switch to a higher risk aim.

One of the benefits of public involvement is to help the research team understand lay people's needs and perspectives and ensure that research is relevant and acceptable to them.[30] This can reduce the chance of failure and make the research more effective and more cost-effective.
A recent study of Parkinson's UK public involvement made those points clearly.[31]
References
- "About Public Involvement". People in Research. Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- "UK-Standards-for-Public-Involvement_Nov19.PDF - Google Drive". Archived from the original on 29 August 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- "UK Standards for Public Involvement". UK Standards for Public Involvement. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "National Health Service Reform and Health Care Professions Act 2002". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- "Northern Ireland Clinical Research Network (NICRN)". nicrn.hscni.net. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Homepage". Health Care Research Wales. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "NHS Research Scotland". www.nhsresearchscotland.org.uk. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "NIHR - National Institute for Health and Care Research". www.nihr.ac.uk.
- "INVOLVE Supporting public involvement in NHS, public health and social care research". UK National Institute for Health Research.
- McKee, Selina (2 April 2020). "NIHR launches new Centre for Engagement and Dissemination". PharmaTimes. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Patient and public involvement policy". NICE. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- "Patient and public involvement". Medical Research Council. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- "Research". Parkinson's UK. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- "National Patient Recruitment Centres". NIHR. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Homepage". Health Research Authority. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Ethics, regulation and public involvement committee". UK Research and Innovation (UKRI). Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Patient and Public Involvement". www.ucl.ac.uk. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- Brett J, Staniszewska S, Mockford C, Herron-Marx S, Hughes J, Tysall C, Suleman R (October 2014). "Mapping the impact of patient and public involvement on health and social care research: a systematic review". Health Expectations. 17 (5): 637–50. doi:10.1111/j.1369-7625.2012.00795.x. PMC 5060910. PMID 22809132.
- "Lay (lay person) – INVOLVE". www.invo.org.uk.
- "Parkinson's UK - Your Network". www.parkinsons.org.uk.
- "Briefing note two: What is public involvement in research? – INVOLVE". www.invo.org.uk.
- Arnstein SR (July 1969). "A ladder of citizen participation" (PDF). Journal of the American Institute of Planners. 35 (4): 216–24. doi:10.1080/01944366908977225. hdl:11250/2444598. S2CID 4668939.
- Rawling, Jennie (8 December 2017). "Surgical mistakes explored on stage". Imperial College London. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Briefing note two: What is public involvement in research? – INVOLVE". www.invo.org.uk. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- "The Research Network". Alzheimer's Society. Retrieved 28 December 2017.
- Staniszewska S, Brett J, Simera I, Seers K, Mockford C, Goodlad S, et al. (2017). "GRIPP2 reporting checklists: tools to improve reporting of patient and public involvement in research". Research Involvement and Engagement. 3 (1): 13. doi:10.1186/s40900-017-0062-2. PMC 5611595. PMID 29062538. S2CID 1795443.
- "New guidance for reporting patient and public involvement in research". On Medicine. 2 August 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2017.
- Morgan N, Grinbergs-Saull A, Murray M (2018). "The impact of the Alzheimer's Society Research Network" (PDF). U.K. Alzheimer’s Society.
- "NETScc'S PPI Framework and Activity Plan 2015-18" (PDF). Evaluation, Trials and Studies coordinating centre. U.K. National Institute for Health Research. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 October 2017.
- Brett J, Staniszewska S, Mockford C, Herron-Marx S, Hughes J, Tysall C, Suleman R (October 2014). "Mapping the impact of patient and public involvement on health and social care research: a systematic review". Health Expectations. 17 (5): 637–50. doi:10.1111/j.1369-7625.2012.00795.x. PMC 5060910. PMID 22809132.
- Staley K, Abbey-Vital I, Nolan C (2017). "The impact of involvement on researchers: a learning experience". Research Involvement and Engagement. 3: 20. doi:10.1186/s40900-017-0071-1. PMC 5611580. PMID 29062545. S2CID 26453405.
Further reading
- University College London Hospitals: How patients have helped us with our research
- National Standards for Public Involvement in Research website