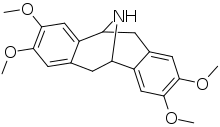
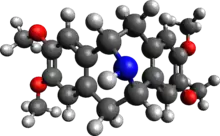
Pavine (molecule)
Pavine is an alkaloid found in a variety of plants in four families, Papaveraceae, Berberidaceae, Lauraceae, and Ranunculaceae.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
(+/-)-Pavine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H23NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 341.407 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
The elucidation of its chemical structure was reported in 1955.[2]
The N-methyl derivative of pavine is argemonine.
See also
- Isopavine, a related alkaloid
References
- Gözler, Belkis; Lantz, Melinda S; Shamma, Maurice (1983). "The Pavine and Isopavine Alkaloids". Journal of Natural Products. 46 (3): 293. doi:10.1021/np50027a001.
- Battersby, Alan R; Binks, R (1955). "Pavine. Part I. The structure and chemistry of pavine". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 2888. doi:10.1039/JR9550002888.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.