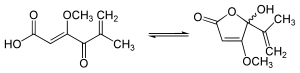
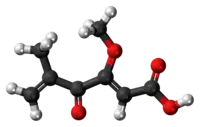
Penicillic acid
Penicillic acid is a mycotoxin that is produced by Aspergillus flavus and Penicillium roqueforti mold. It is also the major product of acid degradation of penicillin. Its first practical synthesis was reported in 1947 by Ralph Raphael, who had worked on penicillin during World War II.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Hydroxy-5-isopropenyl-4-methoxy-furan-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.826 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 170.164 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Raphael, Ralph (1947). "Synthesis of the Antibiotic, Penicillic Acid". Nature. 160 (4060): 261–262. Bibcode:1947Natur.160..261R. doi:10.1038/160261c0. PMID 20344393. S2CID 4066740.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.