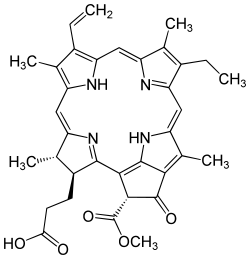
Pheophorbide
Pheophorbide or phaeophorbide is a product of chlorophyll breakdown and a derivative of pheophytin where both the central magnesium has been removed and the phytol tail has been hydrolyzed. It is used as a photosensitizer in photodynamic therapy.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S,4S)-9-Ethenyl-14-ethyl-21-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,8,13,18-tetramethyl-20-oxo-3-phorbinepropanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.110 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C35H36N4O5 | |
| Molar mass | 592.68 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Pheophorbide may be generated by digestion of ingested plant matter. Both worm (Caenorhabditis elegans) and mouse mitochondria are able to use the molecule in a form of ad hoc photoheterotrophy.[2]
References
- Chen, K.; et al. (2009). "Novel photosensitizer-protein nanoparticles for Photodynamic therapy: Photophysical characterization and in vitro investigations". Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 96 (1): 66–74. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2009.04.006. PMID 19442534.
- Xu, Chen; Zhang, Junhua; Mihai, Doina M.; Washington, Ilyas (2014-01-15). "Light-harvesting chlorophyll pigments enable mammalian mitochondria to capture photonic energy and produce ATP". Journal of Cell Science. 127 (2): 388–399. doi:10.1242/jcs.134262. ISSN 0021-9533. PMC 6518289. PMID 24198392.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.