Phlox maculata
Phlox maculata, common names wild sweetwilliam[1] and meadow phlox, is a species of flowering plant in the family Polemoniaceae, native the eastern United States and introduced to eastern Canada.[1] It is a perennial.[2]
| Phlox maculata | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Polemoniaceae |
| Genus: | Phlox |
| Species: | P. maculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Phlox maculata L. | |
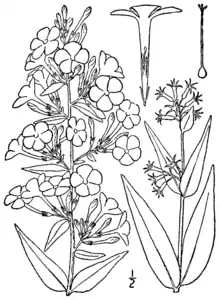
Growing to 2–3 ft (61–91 cm), this erect, clump-forming herbaceous perennial produces clusters of fragrant, deep pink flowers in summer. The stiff stems are spotted red, hence the Latin specific epithet maculata. It prefers damp, well-drained soil in full sun. It is less prone to powdery mildew than the related Phlox paniculata.[3]
The following cultivars have received the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit:
.jpg.webp)

 Botanical illustration
Botanical illustration_(7361660992).jpg.webp) Botanical illustration
Botanical illustration
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Phlox maculata.
References
- USDA, NRCS (n.d.). "Phlox maculata". The PLANTS Database (plants.usda.gov). Greensboro, North Carolina: National Plant Data Team. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- "Phlox maculata". Native Plant Database. Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center, University of Texas at Austin.
- "Phlox maculata". Missouri Botanical Garden. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
- "Phlox maculata 'Alpha'". RHS. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- "Phlox maculata 'Natascha'". RHS. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
- "Phlox maculata 'Omega'". RHS. Retrieved 18 January 2021.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.